What is Glass Bone Disease (Osteogenesis Imperfecta)?
Glass bone disease, also known as osteogenesis imperfecta, is a genetic disease characterized by easy fracture of bones, which develops due to collagen deficiency that forms the structure of the musculoskeletal system.
Especially when babies are born with glass bone disease, they have a sensitive and fragile bone structure. In glass bone disease, which generally develops due to collagen deficiency, which forms the building block of the muscular and skeletal system in the body, bones break easily without any injury.
Common symptoms of brittle bone disease, which vary in severity from person to person, are easy-to-develop bone fractures, blueing of the whites of the eyes, and hearing loss. With early diagnosis and treatment methods, the symptoms of brittle bone disease can be reduced as well as the risk of complications.
What are The Causes of Glass Bone Disease (Osteogenesis Imperfecta)?
The most abundant protein in bones is type 1 collagen. If there is a dysfunction in the synthesis of this protein, osteogenesis imperfecta, or brittle bone disease, occurs. This disorder is transmitted genetically. In other words, this defective gene in parents can be passed on to children.
This gene can be dominant or transmitted recessively. If it is the dominant gene, it is definitely visible in the child. If the gene is recessive, the disease may not be seen in children.
The disease can occur even if there is no history of this disease in the person’s family. New mutations are held responsible. Mutations in the gene can occur as a result of situations such as exposure to radiation and chemicals. This can occur individually, even if there is no brittle bone disease in the person’s family.
What are The Symptoms of Glass Bone Disease (Osteogenesis Imperfecta)?
Brittle bone disease or osteogenesis imperfecta is a genetic disorder that causes bones to break easily due to the lack of collagen protein in the structure of bones and connective tissues.
The symptoms and severity of this condition can vary from person to person.
-
Bone Fractures:
Bones that break easily are the most obvious symptom of the disease. Bone fractures can occur even with minor trauma or light activities.
-
Nosebleeds:
Frequent nosebleeds may occur.
-
Bleeding Problems:
It is difficult to stop bleeding even after minor injuries.
-
Bruises:
Bruises and bruises can occur easily.
-
Crooked Legs:
Curves or distortions may appear in the legs.
-
Breathing Problems:
Breathing problems may occur.
-
Dental Problems:
Weak and yellowed teeth.
-
Scoliosis (Spine Curvature):
Spinal curvature is a common symptom.
-
Short Stature:
The neck is shorter than normal.
-
Tiredness:
Feeling of chronic fatigue.
-
Inability to Stand the Heat:
Hypersensitivity due to hot weather or activity.
-
Eye Problems:
Blueness or color change in the whites of the eyes.
-
Loose Joints:
Looseness and flexibility in joints.
-
Weak Muscles:
Muscle weakness.
What are The Types of Glass Bone Disease (Osteogenesis Imperfecta)?
Glass Bone Disease is clinically classified into five different types, and each type has distinct characteristics.
These types are:
-
Type I Glass Bone Disease (Mild Type):
- Fewer symptoms are observed.
- Bone deformity is rarely or never observed.
- The size remains normal.
- The number of bone fractures is relatively less and may decrease during adolescence.
- There are usually no dental problems, but blueing of the whites of the eyes may be observed.
- There is a risk of hearing loss in adulthood.
- The joints are loose and a slight curvature of the spine may be observed.
-
Type II Glass Bone Disease (Fatal Type):
- During the postnatal period, serious bone fractures and breathing problems occur.
- Babies’ bones are long and wide.
- Babies are often born with broken bones.
- The white of the eye is dark.
- This type is a disease that can lead to death.
-
Type III Glass Bone Disease:
- Tends to be short and may have a triangular face shape.
- Scoliosis (curvature of the spine), almost gray whites of the eyes and dental problems are common.
- This can cause serious deformities of the spine and rib cage.
- Muscle development is weak, muscle mass is low.
- Babies can be born with broken bones.
- There is a risk of hearing loss.
-
Type IV Glass Bone Disease:
- Short stature is seen, but it is not as pronounced as in Type III.
- Bone fractures may be more common.
- Complications such as scoliosis, hearing loss, spinal curvature and bone deformations are common.
-
Type V Glass Bone Disease:
- There is short stature, but it is not as pronounced as in Type III and Type IV.
- Bone fractures may occur more frequently than other types.
- Problems such as scoliosis, spinal curvature and bone deformations may also occur.
How is Glass Bone Disease (Osteogenesis Imperfecta) Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of brittle bone disease is based on the symptoms observed in the patient, family history and clinical examinations.
The methods used for this purpose are:
-
Clinical Evaluation:
The first step in diagnosing the disease is to examine the patient’s symptoms and review their medical history. The patient’s bone fractures, short stature, bone deformities, and dental problems are examined.
-
Genetic Testing:
Since the disease is genetic in origin, DNA analysis is an important part of the diagnostic process. During these tests, mutations that can cause diseases can be detected.
-
Views:
The structure of bones and fractures can be observed through direct bone graphics, CT scan, or MRI.
-
Collagen Analysis:
The level of collagen in the body can be determined using blood samples. In this way, a disorder in collagen production can be determined.
-
Bone Biopsy:
In rare cases, a bone biopsy may be necessary.
-
Amniocentesis:
Amniocentesis performed after the 14th week of pregnancy can be used to assess the genetic status of the fetus during the prenatal period and to detect genetic diseases such as brittle bone disease.
What is the Treatment for Glass Bone Disease (Osteogenesis Imperfecta) ?
Brittle bone disease is a genetic disorder and there is no definitive treatment. Treatment aims to relieve the symptoms of the disease, prevent complications and improve the patient’s quality of life.
-
Treatment of Fractures:
When bone fractures occur, they are treated appropriately. Surgical or non-surgical methods such as fixing fractures with plaster or steel rods may be used.
-
Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation:
Physical therapy programs can help patients increase muscle strength and improve mobility. The goal is to reduce bone fractures and increase patient autonomy.
-
Medicine:
Medications such as bisphosphonates can increase bone density and help reduce fractures. Additionally, vitamin and mineral supplements can be used to support bone health.
-
Surgical Intervention:
Surgery may be necessary to correct bone deformities or, in severe cases, to use implants or prosthetics.
-
Dental Care:
Since dental problems are common, it is important to regularly check dental health and carry out the necessary interventions.
-
Precautions to Protect Bones:
To reduce the load on bones, it is important for patients to monitor their weight and create a safe environment to reduce the risk of falls.
-
Regular Medical Checkups:
It is essential that patients see a doctor regularly to monitor the progress of the disease and adjust treatment if necessary.
Treatment is individualized depending on the type of disease, its severity and its symptoms. The treatment plan aims to improve the patient’s quality of life and minimize bone fractures and complications.
It is essential that patients see a doctor regularly to monitor the progress of the disease and adjust treatment if necessary.
Treatment is individualized depending on the type of disease, its severity and its symptoms. The treatment plan aims to improve the patient’s quality of life and minimize bone fractures and complications.
What Diseases Look Like Glass Bone Disease (Osteogenesis Imperfecta) or Have Similar Symptoms?
-
Bruck Syndrome:
Bruck syndrome is a genetic disease that causes bone fragility and joint contractures. Similar to Glass Bone Disease, bones can break easily.
-
Pseudoglioma of Osteoporosis:
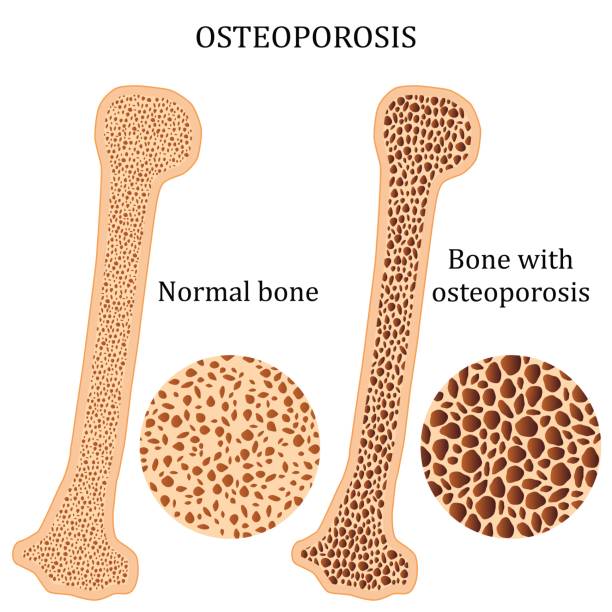
Osteoporosis pseudoglioma is a genetic disease that weakens bones. This disease begins in childhood and can cause vision problems.
-
Panostotic Fibrous Dysplasia:
This rare bone disease affects bone growth and can cause swelling of the bones of the head. This can cause deformity and pain in the bones.
-
Idiopathic Hypophosphatasia:
Idiopathic hypophosphatasia is a disease caused by a deficiency of an enzyme that affects bone mineralization. This can weaken and break bones.
-
Juvenile Paget’s Disease:
This rare genetic disorder causes rapid bone remodeling, leading to bone weakness. Fractures and deformities are common.
-
Juvenile Idiopathic Osteoporosis:
This disease can cause osteoporosis to develop at a young age and lead to weakened bones.
How to Improve The Quality of Life of Osteogenesis Imperfecta Patients?
The support that can be provided to individuals living with glass bone disease and their families can contribute to patients achieving a better quality of life.
-
Physical Activity Recommendations:
It is very important for patients with brittle bone disease to engage in physical activity to increase muscle strength and promote bone health. It is important that these activities are carefully planned and carried out under the supervision of a doctor. Swimming, low-risk sports, and physiotherapy help strengthen bones.
-
Nutrition Consultancy:
A balanced diet is important to support bone health. It is aimed to increase bone density with a diet rich in calcium, vitamin D and protein. Planning is made according to the individual needs of the patient.
-
Psychosocial Support:
Coping with this disease can be difficult for both the patient and their family. Patients’ emotional needs can be met with psychologist support and counseling.
-
Barrier-Free Life Support:
It is important that these patients arrange their home and environment appropriately. The patient’s quality of life can thus be improved.
-
Regular Follow-up and Treatment:
Treatment for people with brittle bone disease is usually lifelong. It is important that these patients visit their doctor regularly for check-ups and comply with the treatment. In this way, complications can be avoided and quality of life can be improved.