Goitre
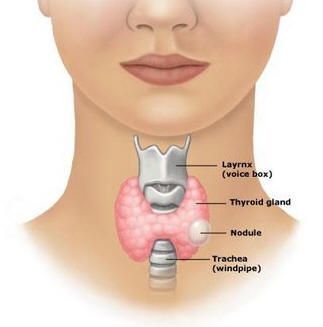
Thyroid glands are the butterfly-shaped formations located just below Adam’s diamond in the root of the neck. As a result of the swelling of these thyroid glands, a disease called goitre occurs. Goitre, which causes coughing and difficulty swallowing, is often a painless disease. If this swelling of the thyroid glands is small and the goitre does not cause any other adverse condition, treatment is generally not needed. Of course, that doesn’t mean we shouldn’t pay attention.
How Does Goiter Occur?
The thyroid glands are responsible for producing two important hormones called thyroxine (T-4) and triiodothyronine (T-3). These hormones strengthen metabolism by controlling blood flow in the body. It controls the body temperature, heart rhythm and the amount of protein needed while maintaining the carbohydrate and fat content the body needs. If these hormones are not produced in sufficient amounts, it may cause goitre formation and goitre caused by another reason may prevent the production of these hormones.
-
Lodine Deficiency
Iodine, which is extremely important in the production of thyroid hormones, is mostly found in seawater and soils in coastal areas. In today’s world, people who have to live offshore, inland or higher than sea level often have an iodine deficiency. This causes the thyroid glands, which try to produce more iodine, to grow and form a goitre. Iodine deficiency is further increased if diets containing hormone-inhibiting foods such as pumpkin, broccoli or cauliflower are used.
-
Toxic goitre disease (Graves’ disease)
Goitre sometimes occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone (hyperthyroid). In Graves’ disease, antibodies produced by the immune system inadvertently attack the thyroid gland, producing excessive amounts of thyroxine. This stimulation causes the thyroid gland to swell.
-
Hashimoto’s disease
In contrast to Graves’ disease, goitre in Hashimoto’s disease occurs when the thyroid gland is under-worked (hypothyroid). In both diseases, the source of goitre is caused by disorders in the immune system. However, in Hashimoto’s disease, instead of causing the thyroid gland to work hard, it causes tissue damage and produces fewer hormones. The pituitary gland, which senses low hormone levels, stimulates the thyroid gland more, causing swelling of the gland.
-
Multinodular goitre
The presence of more than one nodule in the thyroid gland is called multinodular goitre in medical language. In multinodular goitre, nodule pellets formed in solid or liquid-filled states form on both sides of the thyroid gland and cause swelling of the gland.
In this case, the nodule occurs in a single wing of the thyroid gland and causes the swelling of the gland in the same way. Nodules often contain no harmful cancer cells and do not cause cancer, but they need to be kept under control or taken if needed.
-
Thyroid cancer
In some cases of nodule-related goitre, nodules can cause cancer. However, this is very unlikely. In case of doubt, the doctors take a piece of thyroid gland biopsy and send it for examination and a roadmap is determined according to the result.
-
Pregnancy
The hormone known as human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) is produced during pregnancy in women. The chorionic gonadotropin hormone produced by the cells that feed the egg and then attach to the uterine wall may cause the thyroid gland to swell.
-
Goitrogenic foods
Goitre disease is the most common in the Black Sea Region in Turkey. The reason for this is the local consumption of black pepper which is a goitrogenic vegetable. In addition to black cabbage, consumption of goitrogenic foods such as peanuts, soybeans, radishes, turnips, spinach causes swelling of the thyroid glands.
What are the Symptoms of Goiter?
In mild cases, swelling of the thyroid gland is not a problem. However, in some progressive goitre cases:
- Swelling at the root of the neck, which becomes evident when applying makeup or shaving
- Feeling bored in the larynx
- Excessive sweating
- Snore
- Irritability
- Irregular period
- Sudden weight gain and weight loss due to increased appetite or loss of appetite
- Cough
- Hoarseness
- It is manifested by symptoms such as difficulty in swallowing and breathing.
How to Tell Goitre?
An endocrinologist should be consulted for the diagnosis of goitre disease. Here, after the doctor’s examination of the throat with his hands, the patient’s complaints are heard. To find the source of the goitre, the doctor asks for some tests.
-
Hormone test
The blood test checks the amount of hormone produced by your thyroid gland and checks whether the thyroid gland produces a balanced amount of hormone.
-
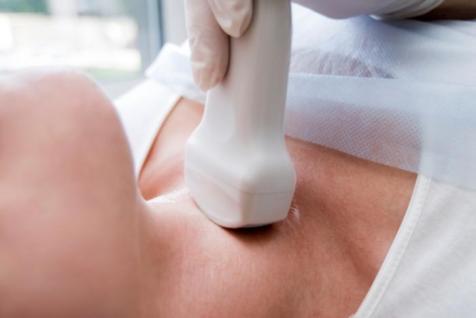
Ultrasonography
Ultrasonography, which is commonly used in pregnancy, examines your throat and larynx region to determine the size of your thyroid gland and whether or not a nodule is formed.
-
Antibody test
In the antibody test, a count of antibodies in the blood is performed and it is determined whether the cause of goitre is due to an excess of antibodies.
How is Goiter Treated?
Treatment of goitre varies according to the size of the goitre, whether it causes other problems in the person and the symptoms. Therefore, it is possible to give more than one answer to the question of how goitre goes. If the size of the goitre is small, treatment is not needed but requires regular control in case it grows. Your doctor may refer you to one of the following treatment methods if you see fit.
-
Lodine supplementation
If the goitre is caused by iodine deficiency, iodine supplementation is given to the patient. These basic foods can be taken from the patient as well as radioactive iodine supplementation. Although radioactive iodine supplementation allows the thyroid glands to reach normal dimensions, it may cause laziness in the thyroid gland.
-
Drug treatment
Hormonal balance is tried to be achieved by drug treatment in goitre disease caused by hypothyroid or hyperthyroidism. In the case of hypothyroidism, drugs containing levothyroxine are prescribed to reduce the production of thyroid-stimulating hormones. In hyperthyroid-induced goitre, hormone-lowering drugs are used.
-
Surgical intervention
If it is the nodules that cause the thyroid gland enlargement, your doctor will perform an ultrasound biopsy to find out if the nodules are benign. If the result is negative, the patient is taken to the operation and the nodules are removed from the thyroid gland by surgery.
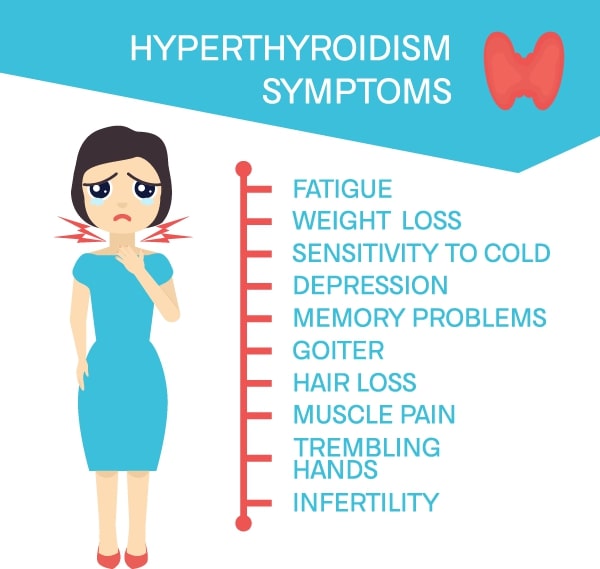
Hyperthyroidism
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism (Poisonous Goiter);
- Palpitation,
- Shaking hands and body,
- Sudden weight loss,
- Hair loss,
- Itching,
- Feeling fullness in the throat,
- Eating too much food and drinking water due to excessive appetite,
- Excessive sweating,
- Quick fatigue,
- Irritability is a common complaint.
Hypothyroidism Treatment
Following the confirmation of the diagnosis as a result of blood tests, it is possible to recover very quickly by giving the missing thyroid hormone. These patients have to use medication for life. There is no standard dose of thyroid hormone used in treatment. Therefore, each patient should have a true and accurate maintenance dose with measurements and follow-up.
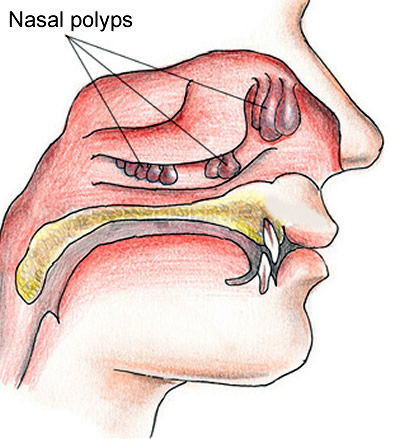
Nasal Polyps
Adenoid is the name given to spongy tissues that help protect babies and children from becoming sick. The nasal flesh is on the back of the nasal cavity and the roof of the mouth and, like tonsils, helps to keep the body healthy by catching harmful bacteria and viruses and stimulating the immune system. Nasal flesh also contains antibodies that help the body fight infections.
What are the Factors that Cause the Growth of Nasal Flesh?
In some cases, swelling of the nasal flesh may occur while fighting the microbe trying to enter the body. This swelling usually resolves on its own, but sometimes treatment may need to intervene in bloating. The growth of nasal flesh is a common condition. In this case, tonsils may also grow.
What are the Symptoms of Nasal Flesh Growth?
- Nasal congestion occurs; therefore, the child has difficulty breathing through the nose.
- Because breathing becomes difficult, difficulty falling asleep and snoring occur. Therefore, the child becomes sleepless and tired.
- Sore throat and difficulty swallowing.
- Glands occur on the neck.
- Ear problems occur.
How is Nasal Flesh Growth Diagnosed?
To diagnose nasal flesh growth, your doctor will first perform an ear, nose and throat examination. In some cases, the nasal flesh can be examined by the endoscopic method or an x-ray may be requested.
How is Nasal Flesh Treated?
In the treatment of nasal flesh, drug treatment is applied primarily. Before starting antibiotic treatment, the type of microbe causing the disease should be determined.
If the inflammation is repeated frequently, the nasal flesh is no longer protective and becomes a damaging structure. In this case, they should be removed by surgery.
Nasal surgery is an easy operation and painful operation. Under general anaesthesia, the enlarged nasal flesh is removed. The patient may return home on the same day after surgery. In rare cases, it may be necessary to place a tampon behind the nose and stay in the hospital overnight. In some patients, the nasal flesh may grow again. In this case, the operation is repeated.
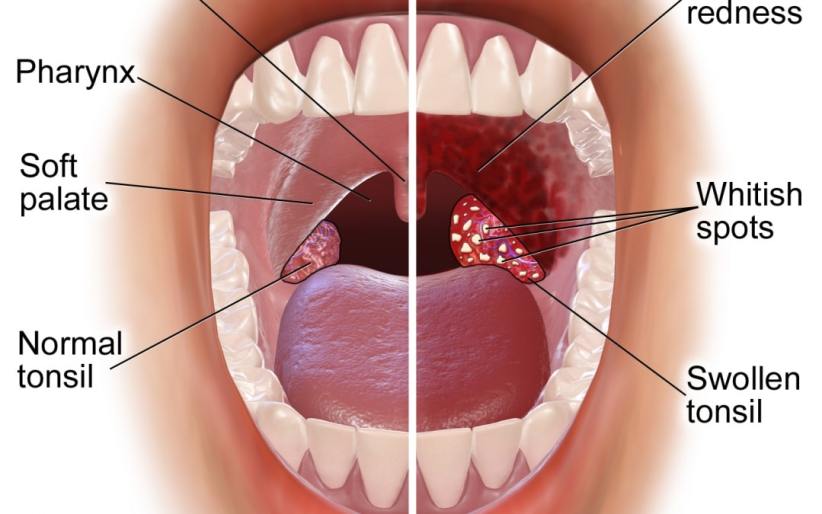
Tonsil
Tonsils are structures located on both sides of our throat and check whether intruders such as bacteria, viruses and allergens entering the throat enter the body. Tonsils are composed of lymphoid cells and produce lymphocytes that are part of the body’s immune system.
Tonsillitis (tonsilitis), tonsils and germs to develop as a result of swelling. Tonsillitis is more common in children aged four to five years and grows due to infections.
What are the Symptoms of Tonsillitis?
The most obvious symptoms of tonsillitis are:
- The tonsils are fried, swollen and covered with a white-yellow substance
- Throat ache
- Pain or discomfort during swallowing
- Bad breath
- Fire
- Bifurcation of sound
- Swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck
How Is Tonsillitis Diagnosed?
The presence of an infectious agent is important in the treatment of tonsil infections. Throat culture or rapid antigen screening test is recommended. Tonsil infections are usually self-limiting, but sometimes the infection can spread to surrounding tissues and the infection can expand. Some patients who are not treated adequately may have poor results affecting the joints and kidneys. Therefore, if a bacterial infection is detected in the throat culture in tonsil infection, antibiotic treatment should be administered within the first 7-10 days.
How Is Tonsillitis Treated?
When tonsils are inflamed, firstly, medication treatment is applied. Before starting antibiotic treatment, the type of microbe causing the disease should be determined.
Angina
Pharyngitis (inflammation of the throat) is an inflammation of the back wall of the nose and oral cavity. There are two types of pharyngitis, acute and chronic, and the two are different. Sudden, severe inflammations are acute pharyngitis. Pharyngitis, which is milder but lasts longer, is chronic pharyngitis.
What are the Symptoms of Pharyngitis?
During ingestion, solid and liquid foods pass from the pharynx to the oesophagus and from there to the stomach.
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of pharyngeal tissues;
- Fire,
- Throat ache,
- Redness
- It is characterized by difficulty in swallowing.
Tonsillitis may also be included in pharyngitis. In addition to the described acute pharyngitis, there is also a disease defined as chronic pharyngitis,
In chronic pharyngitis;
- No fever or resentment,
- Difficult to swallow,
- Coughing,
- Combustion, stress,
- It feels like a foreign body has been worn, and there is often a desire to clean the throat.
- Infection is another factor.
For example;
- Air pollution,
- Smoking,
- Alcohol,
- Spicy foods,
- An agent that irritates the throat, such as very hot-cold drinks and foods,
- Continuous oral breathing due to nasal congestion plays a greater role in chronic pharyngitis.
If acute pharyngitis is repeated frequently, it may turn into chronic pharyngitis.
What are the Risk Factors in Pharyngitis?
Many microorganisms can cause pharyngitis.
90% of adult pharyngitis and 60-75% of pediatric pharyngitis are caused by viral agents. Since the viruses that cause colds affect the upper respiratory tract, they can also cause pharyngitis. Bacteria account for 25% of all tonsillopharyngitis.
Risk factors for viral upper respiratory tract infections can also be mentioned here.
These:
- Crowded environments (nursery, classroom)
- Cigaret,
- Nutritional deficiency,
- Chronic diseases,
- Insufficient sleep,
- Stress is such factors.
How is Pharyngitis Treated?
Antibiotics are not used in acute pharyngitis caused by viruses. However, antibiotics may be recommended in severe infections or in cases where the immune system is very weak.
In addition to antibiotics, painkillers and antipyretics, antihistamines, nasal sprayers, cough suppressants and saline carbonated water and mouthwashes can be used in patients with allergy.
Chronic pharyngitis is difficult to treat. Both the doctor and the patient should pay attention to certain conditions. However, chronic pharyngitis is often not eliminated. To determine the treatment, it should be investigated whether there is any other factor that causes chronic pharyngitis. If it is found, it must be treated first.
Antibiotics are often useless. Diseases such as allergies, the curvature of the nasal bone or hypertrophy of the turbinates in the nose, sinusitis, reflux should be corrected by surgery if necessary.
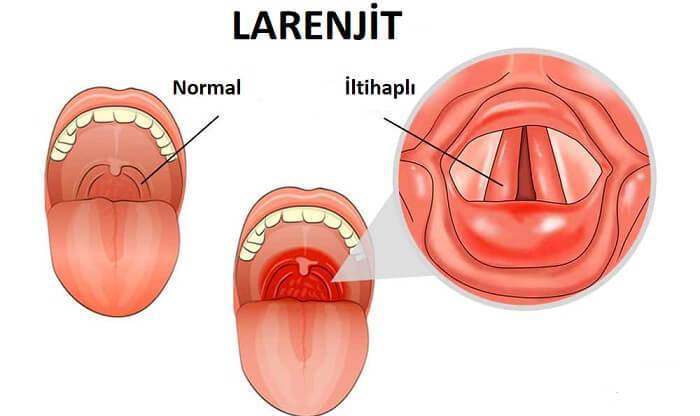
Laryngitis
Laryngitis is inflammation of the vocal cords. The problem is usually of viral origin and is resolved by routine measures such as rest, abundant fluid intake.
The factors that cause laryngitis are:
- Bacteria, viruses, fungi,
- antihistamines
- Throat reflux
- Misuse of sound
- Allergy
- Cigarette smoke
- Tuberculosis
What are the Symptoms of Laryngitis?
- Throat ache,
- Hoarseness that lasts for several days,
- Sore throat, cough and fever,
- Even if the symptoms of other colds or influenza have disappeared, hoarseness continues and is a symptom of laryngitis.
How is Laryngitis Diagnosed?
For diagnosis, it is first detected by laboratory tests caused by viruses or bacteria and the appropriate treatment is provided.
How is Laryngitis Treated?
Drug treatment is necessary for bacterial laryngitis. However, laryngitis caused by viruses can be resolved with warm drinks. Your doctor may give you antibiotics in the future. It may be dangerous to perceive hoarseness as laryngitis, which lasts more than 2 or 3 weeks if there is another reason behind the sound problem. Since vocal cords are more delicate during this period, intensive use of vocal sounds should be avoided and avoiding respiratory irritation. Forcing the vocal cords can lead to polyp and cyst formation.
Swallowing Disorders
Swallowing; It is a complex function of the passage of liquid and solid foods into the oesophagus through the coordination of the nerves and muscles in the mouth, throat and stomach.
Swallowing disorders may be caused by the accumulation of solid or liquid foods in the throat, then poured into the area of the vocal cords, resulting in hoarseness, throat clearing or coughing.
What Causes Swallowing Disorders?
The most common causes of dysphagia are:
- With advancing age, swallowing muscles; it loses both strength and coordination. Therefore, sometimes even normal secretion may not pass into the stomach.
- Swallowing during sleep is less and secretion accumulates in the mouth. Coughing or sore throat may be felt when waking up.
- Irritation and stress can cause contractions in the throat muscles and as a result, there is something in the throat, making it difficult to swallow.
- The deviation of the septum prevents the normal discharge of the sinuses and causes chronic sinusitis. A protrusion in the septum will cause irritation and abnormal secretion.
- Growth or swelling along the path through which food travels slows or prevents the passage of solid and/or liquid foods.
- Enlarged or deformed turbinates (structures that emerge on the sidewalls of the nose and regulate, moisturize the airflow) or polyps (benign growths due to infection, allergies or irritation) may also cause the same complaints.
- Reflux can also cause swallowing disorders.
What are the Symptoms of Swallowing Disorders?
Major Symptoms in Swallowing Disorders;
- Burning and pain in the throat
- Indigestion.
These symptoms include; especially after eating, it increases, even more, when you go to bed. Bag-shaped hernias that occur at the junction of the oesophagus and stomach can also cause swallowing problems.
How is Swallowing Problems Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of swallowing problems includes a detailed ENT examination, some laboratory tests, endoscopic examination and x-ray.
How are Swallowing Disorders Treated?
Swallowing problems are treated according to the source of the problem:
- Bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics, but they provide temporary recovery. For example, in chronic sinusitis, surgical intervention is needed to open the mouth of the closed sinuses.
- If the allergy is caused by difficulty swallowing, the allergy should be treated to pass the problem. Antihistamines and decongestants, cromolyn and steroid nasal sprays, steroids in other shapes and hyposensitization (vaccine therapy) can be used for allergy treatment. However, some antihistamines cause drying and further thicken the secretion.
- Decongestants cause increased blood pressure and aggravation of heart and thyroid disorders. Steroid sprays can usually be used safely for years under medical control.
- Reflux treatment; 12-15 cm to remove the head of the bed, eat less and frequent, the prohibition of alcohol and caffeine, not to be strenuous, such as sports to begin with life-regulating recommendations.
- If the swallowing problem is not caused by a particular disease, treatment; thinning outbreak for easy flow. Those receiving this treatment should drink at least eight glasses of water a day, stop caffeine and not use diuretics if necessary.
- Washing the nose with a liquid prepared by adding food soda or salt into hot water two or six times a day with special devices made for the nose helps correct the thick and reduced epidemic.
- Prescription-free, simple salt solutions can be used to moisten the nose.
- Frequent cleaning of the throat increases the irritation of the throat and causes the condition to worsen…
Bad Breath
When the air coming into the respiratory system is combined with the bacteria and opens out, the individual is disturbed by himself and his environment and this is called halitosis.
We should accept bad breath as a major problem that affects both the individual’s health and his / her relationship with society. Although halitosis is not a disease, the social reasons it causes a decrease in the quality of life of individuals. It is mainly caused by systemic and local causes.
Local Causes of Bad Breath
Bleeding gingival diseases, decayed teeth, faulty fillings and coatings, bacteria accumulated on the tongue, pharyngitis and tonsillitis.
Systemic Causes of Bad Breath
Bad breath; systemic causes include gastrointestinal diseases, liver diseases, diabetes, kidney diseases, cancer drugs used, xerostomia, salivary gland diseases, lung diseases and the like systemic diseases.
Ninety per cent of patients with bad breath wake up in the morning when they feel a bad taste and bad smell in their mouths, but also in these patients during the day to see bad breath. Patients who are aware of this use various mouthwashes and sprays for this reason. However, they do not provide a permanent solution and do not prevent the patient’s complaints.
Possible Causes of Bad Breath
Tobacco: Tobacco products cause bad breath. Also, it increases the likelihood of gum disease, which can lead to bad breath.
Food: The decomposition of food particles adhering to teeth can cause odours. Some foods such as onions and garlic can also cause bad breath.
Dry mouth: Saliva, cleans mouths naturally. The odour may occur due to a specific disease, such as dry mouth (Xerostomia).
Dental hygiene: Brushing and flossing allow the removal of small foodstuffs that can accumulate and slowly break down and produce odours. If the scrub is not regular, a layer of bacteria, called a plaque, is formed.
Crash diets: Fasting and low-carb nutrition programs can create bad breath. This is due to the breakdown of fats from which chemicals called ketones are produced. These ketones have a strong aroma.
Medications: Some medicines can reduce saliva and therefore can increase bad breath.
Mouth, nose and throat conditions: Occasionally, small, bacteria-coated stones can form on the tonsils at the back of the throat and produce odour.
Foreign body: Bad breath can be taken especially if there is a foreign body located in the nasal cavity in children.
Diseases: Some cancers, liver failure and other metabolic diseases may cause bad breath due to specific mixtures of the chemicals they produce. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) may cause bad breath due to persistent reflux of gastric acids.
Determination of Bad Breath
The devices used in the detection of bad breath, electrochemical measurements can determine the severity and effect of this smell. Also, blood gases, saliva ph osmosis, the detection of bacteria on the tongue back can be examined.
If the patient is admitted to the hospital with bad breath, electrochemical measurements are made at the dentistry clinic and if the bad breath is detected after systemic reasons, the bad breath is eliminated in the related branches of the otorhinolaryngology, chest diseases, biochemistry and internal medicine clinics, and if it is caused by local causes, the bad breath is eliminated.
Bad Breath Treatment
If bad breath is caused by any disease, the source must be treated. Generally, bad breath problems can be treated by paying attention to oral and dental health. Providing oral hygiene helps to reduce bacteria. Regular brushing, flossing, tongue cleaning are the necessary steps to treat bad breath.
It is best for those who experience bad breath to consult a specialist to understand the causes of bad breath. It is important to fully understand the reasons for bad breath treatment. Treatments such as mouthwash for bad breath caused by simple hygiene problems may be beneficial. Halitosis treatment aims to reduce bad bacteria in the mouth.
Intraoral Lesions
Intraoral Cancers (Intraoral Cancers)
Intraoral cancers (intraoral cancers) are usually seen in the middle age group. It is 2 times more common in men than in women. In recent years, cigarette and alcohol consumption has increased considerably among women. Therefore, there is a significant increase in the incidence of language cancers in women.
Intraoral cancers occur in the regions of the oral cavity. These areas are tongue, mouth base, hard palate, the front part of soft palate, jaw, cheek and gums. Oral cancers originally originate from the mucosa, which covers the oral cavity but can also develop from 600 to 1000 minor salivary glands in the oral cavity.
Causes of Oral Cancer
The exact cause of oral cancers is not fully known. However, chronic traumas due to tobacco products, alcohol and carcinogenic additives in certain nutrients, poor teeth or prostheses may increase the risk of oral cancers. Genetic predisposition is also among the risk factors for oral cancers.
When continuous white spots (leukoplakia) or red spots (erythroplasia) occur in the mouth, especially on the tongue, they should be considered as cancer-leading wounds and these lesions should be evaluated by an otolaryngologist. Many oral wounds are seen primarily by the dentist. Therefore, dentists play a very important role in the early diagnosis of the disease.
Symptoms of Intraoral Cancers
- A wound that does not heal easily and heals in the mouth
- White or red areas in or around the mouth
- Sensitive, irritated, raised or thickened areas in the mouth
- Loss or numbness in any part of your mouth
- Swelling of the lower or upper jaw and consequent deterioration of existing prosthesis
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing
- Pain in the mouth or hardly defined pain
- Sore throat without a known cause
- Sound change or sensation of an intolerable object in the throat
- Stress in tongue and chin movements
- Swelling of the neck (mass)
Intraoral cancers are painless during the initial period. When cancer progresses and the damage to healthy oral tissues occurs, pain begins. It may be difficult for patients to recognize existing oral cancer. When treatment is delayed, the disease may spread to the lymph nodes of the neck, surrounding neighbouring tissues, and distant organs such as lung and bone.
Diagnosis
Any swelling or tissue changes in the mouth that do not persist within one month should be evaluated by an otorhinolaryngologist. Following a complete otorhinolaryngologic examination, a biopsy from the tumour should be performed to make a definitive diagnosis.
To have an idea about tumour size and its spread to other structures; neck ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET) are used.
Treatment of Oral Cancer
Once the diagnosis is made, the treatment of the disease is planned by the otorhinolaryngologist according to the size and stage of the tumour, the general condition of the patient, and whether the tumour has close or distant metastases. Surgery is the most successful method for the treatment of these tumours. Tumours and surrounding areas with potential for spread are removed from the body. Depending on the stage of the disease, the general condition of the patient and the pathological examination results, radiation and chemotherapy may be added to the treatment. Early diagnosis is crucial for successful treatment outcomes.
Herpes
What are Herpetic Lesions?
Herpetic lesions, also known as herpes; lips and wounds around the mouth caused by the herpes simplex virus. This virus usually enters the body through an opening in the skin or mouth. Open herpes can be transmitted when the wound is touched or contacted with fluid leaking from the wound, sharing food or knife that has come into contact with the germ, kissing it, or touching someone’s saliva.
What are the Symptoms of Herpes?
Symptoms of herpes include; tingling, itching and pain around your mouth, fever, sore throat, swelling of the glands in your neck or body. Once the cold sores are seen, the wound is usually opened and a clear liquid seeps through it, and then the crust is covered. Heals from a few days to two weeks. For some people, herpes can be very painful.
How Is Herpes Treated?
Cold sores usually disappear within a few days by self-healing. It can be treated if it causes pain or makes you feel bad. Treatments include skin creams, ointments and some pills. With these procedures, you can get rid of herpes only a day or two earlier.
One of the most effective ways to get rid of cold sores is laser treatment. If you get the laser treatment on time, you can prevent herpes from escaping. If you feel tingling in this area before exiting herpes, make an appointment immediately for laser treatment. If there is herpes, laser treatment will reduce your discomfort, dry herpes and heal faster.
The herpes virus that causes herpes cannot be destroyed. Once infected, the virus remains in your body for the rest of your life. If you remove herpes too often, treatment can reduce the number and severity of herpes. Usually, herpes always occurs in the same area. After treatment with laser several times, the possibility of cold sores in the same area will be very low.
What are the Benefits of Using Laser in Herpes Treatment?
- High technology, the cost is not too high
- Relaxation is immediate and permanent.
- If the lip starts to tingle, it prevents herpes from escaping.
- After treatment, herpes stops growing.
- Accelerates healing without any discomfort.
- Treatment is completed in a few minutes without anaesthesia
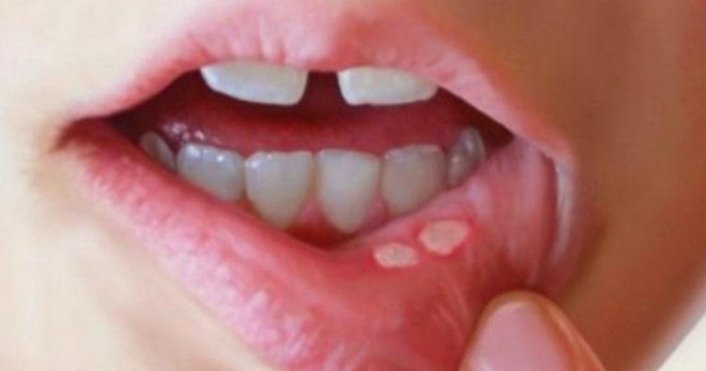
Aft
Aphthous lesions (recurrent aphthous stomatitis – RAS) are the most common intraoral lesions (oral ulcers) or wounds that have negative effects from eating to speech, and even to general health.
Painful, scarred, small (usually less than 1 cm), white wounds. It is more common in women. The incidence decreases with age. Sometimes an aphtha heals and another emerges. Multiple aphthae may occur at the same time. They are not contagious, they are often mistaken for herpes. However, while herpes is caused by viruses, viruses do not affect the formation of aphthae.
In Which Parts of the Body do Canker Sores Occur?
- The mucosa of the cheek and lip,
- Gum,
- Above language,
- pharynx,
- Soft palate.
What are the Causes of Canker Sores?
- Hereditary transition
- Stress and anxiety
- Poor oral hygiene
- Hard Toothbrushes
- Bite of cheek, lips and tongue, oral traumas
- Weak immune system
- Prosthetics
- Salted, spicy, highly acidic foods
- Some drugs such as ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, antirheumatic drugs
- Tobacco products
- Toothpaste containing sodium lauryl sulfate
- Consuming foods too hot or too cold
- Hormonal changes
- Vitamin B, folic acid or iron deficiency
- Some malign diseases
- Behcet’s disease, AIDS
- Allergy to some foods such as tomatoes, strawberries
- Inflammatory bowel diseases
- Overstrain
How is Canker Sores Treated?
In the treatment of aphthae, the underlying cause is eliminated. Also, symptoms are tried to be reduced. They usually pass within 1-2 weeks. If it lasts more than 2 weeks, a doctor should be consulted. Providing oral hygiene, avoiding irritating foods (such as acidic, very hot), and paying attention to certain points such as using soft-tip toothbrushes help to prevent aphthae formation. Use antiseptic mouthwash or mouthwash with saltwater, vitamin B, folic acid, iron supplement, toothpaste containing menthol, sugar and so on. To avoid localization, administering local anaesthetics to the mouth before meals, and corticosteroids help to reduce symptoms. Mild painkillers can be used for pain.
Laryngeal Cancer
What is Larynx Cancer?
Malignant tumours located between the pharynx and trachea are called “laryngeal cancer. Larynx; Speech, swallowing, airway protection and respiration is a very important task.
What are the Symptoms of Larynx Cancer?
Larynx; Anatomically, the region above the vocal cords is divided into three sections: the region of vocal cords and the region below. Laryngeal cancers caused by vocal cords first present with hoarseness and changes in voice.
Laryngeal cancers on the vocal cords cause complaints such as pain during swallowing, difficulty in swallowing, feeling of stuck in the throat, bleeding with cough, and shortness of breath in the later stages. Laryngeal cancers caused by vocal cords also have difficulty in breathing shortness of breath in later periods. On the other hand, cancers in the lower region initially cause shortness of breath.
How is Laryngeal Cancer Diagnosed?
The most important diagnostic method is the evaluation of the larynx by physical examination. If there is a suspicious appearance during this examination, the diagnosis is confirmed by biopsy and histopathologic examination.
What are the Stages of Laryngeal Cancer?
Laryngeal cancers; The disease is graded from 0 to 4 by evaluating the spread in the larynx, as well as the spread to lymph nodes and other organs in the neck. The earliest stage 0 and the most advanced distant metastatic disease is classified as 4C.
Is there Treatment for Larynx Cancer?
Surgical treatment and radiotherapy (radiation therapy) methods can be used in the treatment of laryngeal cancers. The sooner the disease is diagnosed; it is possible to treat the larynx by preserving its functions such as speech and swallowing.
What Should People Pay Attention to?
Particularly, patients who have been diagnosed at an early stage and who have undergone organ-preserving surgery or radiotherapy should quit smoking, comply with follow-up and control examinations at the centres where they are treated.