Fatty Liver
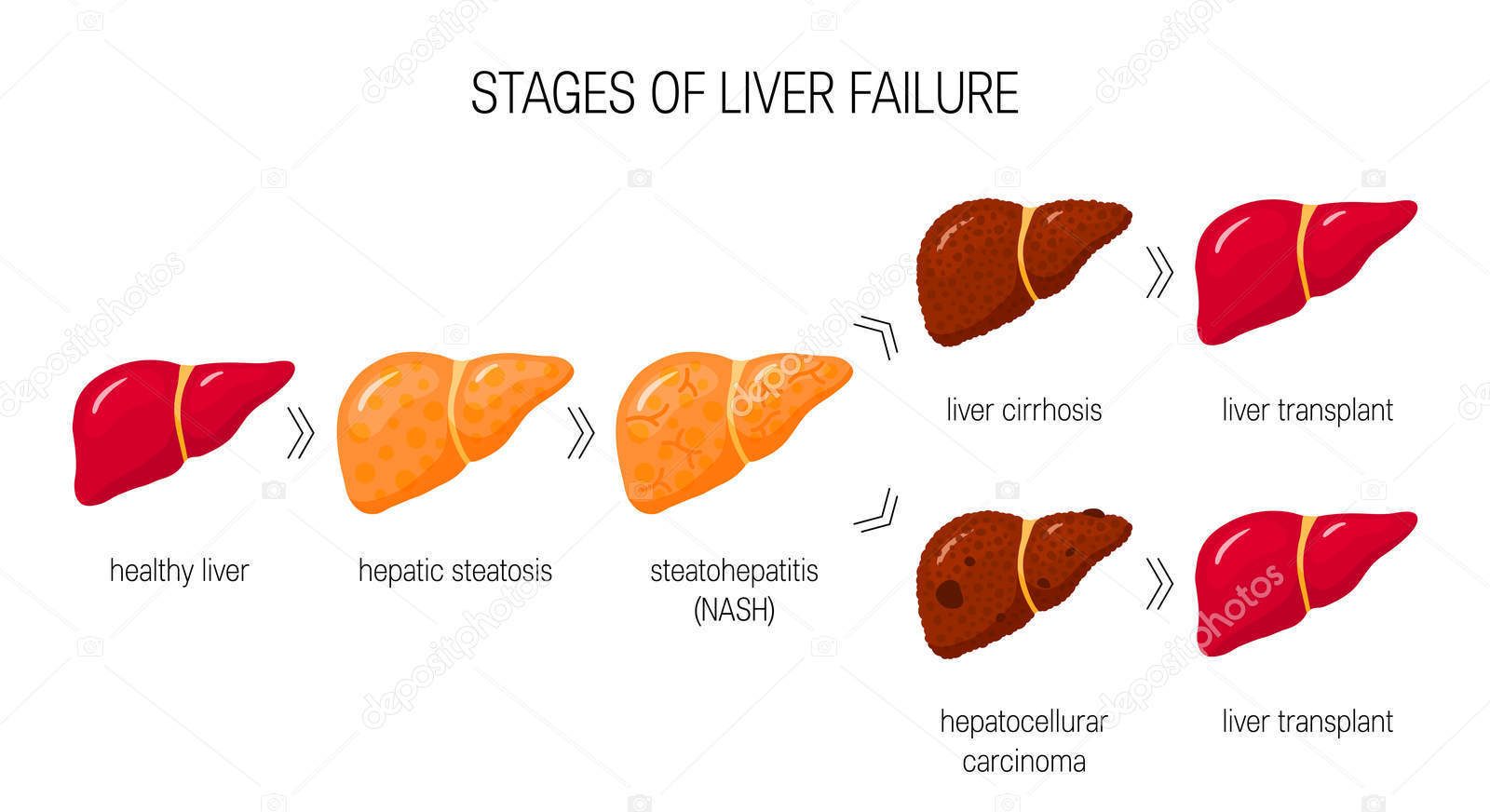
Liver fat is caused by the accumulation of excess fat in the liver cells for various reasons and has serious consequences if left untreated. Early diagnosis is very important in the treatment of liver steatosis. If signs of liver steatosis are observed, a doctor should be consulted and treatment of liver steatosis should be initiated immediately.
What is Fatty Liver?
Your liver produces and stores fat like any other cell. This product is very limited and in total 3-5% of the liver tissue consists of fats.
If your liver increases this fat production and storage for various reasons, small fat vesicles begin to form in your liver cells. Although this situation gives only simple findings at the beginning, these pouches which accumulate excessively in the cell in later periods damage the structure and cause irreversible liver damage.
Liver fat is caused by the accumulation of excess fat in the liver cells for various reasons and has serious consequences if left untreated. Early diagnosis is very important in the treatment of liver steatosis. If signs of liver steatosis are observed, a doctor should be consulted and treatment of liver steatosis should be initiated immediately.
Causes of Fatty Liver
Obesity is one of the main causes of liver fat.
Also, inflammation (inflammation) cells that increase with obesity increase fat storage by an unclear mechanism at the liver level.
Some of the most important causes of obesity also cause fatty liver. Excessive calorie intake mainly increases fat production in all body cells.
Also, carbohydrate intake closely affects the liver, which is the capital of carbohydrate metabolism.
Also, simple carbohydrates cause an increase in inflammation in the body.
Insulin resistance is another risk factor for fatty liver. Insulin resistance causes elevated blood insulin levels.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver
Liver fat is a condition that can range from simple damage to cirrhosis. Therefore, the severity of symptoms varies according to the location.
- Fatigue and fatigue
- Right upper quadrant pain
- Increase in liver enzymes
Diagnosis of Fatty Liver
Fatty liver is also known as hepatic steatosis and is a problem associated with obesity, hypertension, high cholesterol and diabetes. Almost 80% of those who have these diseases have a fatty liver.
Hepatic steatosis may also be caused by excessive alcohol consumption.
Fatty Liver Can be Recognized in the following ways:
Ultrasonography
Decides the severity of the disease and the amount of fat in the liver.
Liver biopsy
This method allows you to obtain a definitive diagnosis and is used in the group at high risk of having a fatty liver.
Laboratory Tests
In general, the results of tests of patients with this liver problem are 2-3 times higher than those of normal people. People suffering from this problem have high levels of glucose, cholesterol and triglycerides.
How is Liver Fat Treated?
The type of liver fatty tissue we look at is related to lifestyle and nutrition. Likewise, if the correct approach is provided, many liver fats can be reversed.
Especially when the problem is simple fat (no inflammation and increase in connective tissue), diet, exercise and, if necessary, obesity, hyperlipidemia and diabetes if any, is fought as necessary and fatigue decreases or even disappears. The scope of the problem is broad and necessitates a multidisciplinary approach, involving specialists in internal medicine, cardiology, endocrinology and gastroenterology, as well as diet and healthy nutrition experts.
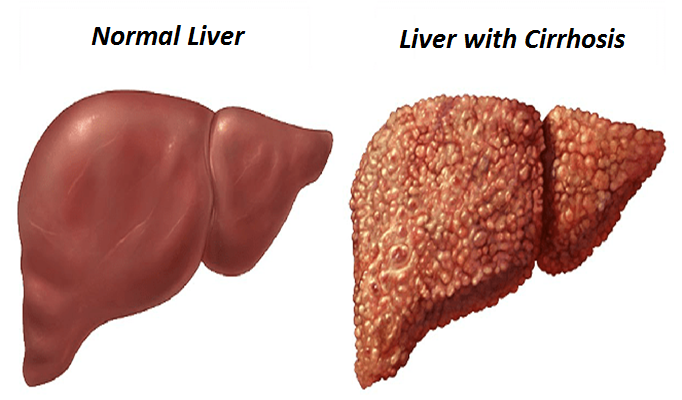
Cirrhosis
What is Cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis is a permanent disorder caused by long-term damage to the liver. The resulting damage results in the formation of a non-functional tissue called scar in the liver. Scar tissue prevents blood flow through the liver; slows the liver’s ability to process nutrients, medicines, and toxins. Cirrhosis can eventually lead to liver failure, which can be fatal.
Causes Cirrhosis?
A wide variety of diseases and conditions can damage the liver and cause cirrhosis. The most common causes of cirrhosis:
- Consuming excessive alcohol for many years
- Chronic viral inflammation of the liver
- Diabetes-related fatty liver
- NASH (Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis): It is a type of non-alcoholic hepatitis where the liver is inflamed as a result of excessive fat accumulation.
- Hemochromatosis: An inherited disease that causes iron build-up in the body
- Wilson’s disease: A familial disease characterized by copper deposition in the liver
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency: Absence of a specific enzyme in the liver
- Disorders of hereditary sugar metabolism
- Genetic digestive disorder (Alagille syndrome)
- Cystic fibrosis
- Infections such as syphilis or brucellosis
- Liver autoimmune diseases (chronic conditions in which the body’s immune system attacks the liver or bile duct cells)
- Some drugs such as methotrexate or isoniazid
- Obstruction of the bile duct: The bile duct carries bile formed in the liver to the intestines to help digest fat.
- As a result of repeated heart attacks and heart failure, fluid accumulates in the liver and causes a blockage.
- Excessive intake of liver-damaging drugs such as paracetamol and vitamin A
Symptoms of Cirrhosis
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Weakness
- Nausea
- Unexplained weight loss and anorexia
As Cirrhosis Progresses, The Following Symptoms May be Observed;
- Jaundice (Yellowing of skin and eyes)
- Blood Vomiting
- Itching of the skin
- Dark, tea colour urine
- Light coloured stool
- Blood in stool
- Easy bleeding in the body
- Nose bleeding
- Bleeding and bruising of the gums
- Easy bruising on the skin
- Redness of palms
- Painful oedema in the legs
- Formation of spider-like blood vessels in the skin
- Abdominal fluid collection (Acid)
- Discontinuation of menstrual bleeding in women (not associated with menopause)
- Loss of libido in men, breast enlargement (gynecomastia) and testicular shrinkage
- Recently confusion, sleep and speech impairment (hepatic encephalopathy)
Cirrhosis Treatment
There is no treatment for cirrhosis except liver transplantation. If cirrhosis is diagnosed early enough, the damage can be minimized by treating the underlying cause or various complications. Treatment of cirrhosis includes:
- If the person is drinking alcohol, he must immediately quit
- The patient’s vitamins should be checked immediately for low levels. Additional vitamin supplements should be made.
- Since high blood pressure will be seen in cirrhosis, high blood pressure should always be kept low and blood pressure-lowering drugs should be used.
- To relieve abdominal and leg swelling, diuretic oedema suppressants should be given.
- The patient should avoid excessively fatty foods.
- None of the medicines recommended by the doctor should be used.
Hepatitis B (Jaundice)
It is also known as hepatitis B virus jaundice. The hepatitis B virus is transmitted through blood or sexual contact. Delayed treatment may cause death. So, what is hepatitis B, also known as jaundice? What are the symptoms of hepatitis B, how to treat hepatitis B questions about the questions we have compiled for you?
Symptoms of Hepatitis B
Symptoms of hepatitis B usually occur within 90 days of infection. However, this period varies from 6 weeks to 6 months. Common Hepatitis B symptoms include;
- Anorexia,
- Nausea,
- Darkening of urine colour,
- Fire,
- Vomiting,
- Weakness,
- Weight loss,
- Abdominal pain,
- Joint pain,
- Yellowing eyes,
- Yellowing of the skin.
Which Way Does Hepatitis B Transmit?
- Sexual contact,
- Through common materials such as toothbrushes, razors,
- In case of cutting tool injuries by contact with blood.
Important Information about Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis B is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic disease.
- The virus is transmitted by contact with the blood of an infected person or other body fluids.
- Approximately 257 million people live with hepatitis B virus infection.
- People are at risk of getting HBV when they visit other parts of the world where the infection is more common.
- Hepatitis B is an important occupational hazard for healthcare workers.
- However, it can be prevented by a currently available safe and effective vaccine.
How is hepatitis B treated?
People with hepatitis B should be regularly monitored by specialist doctors. Medication prescribed by the doctor should be used regularly. Adequate nutrition, rest and fluid consumption are extremely important in the treatment process. According to the decision of the doctor, the patient with hepatitis B can be kept under control in the hospital.
Liver Cancer
When liver cancer is diagnosed at an early stage, treatment success is very high; in other states, it can also cause fatal consequences. Metastatic liver cancer starts elsewhere and then spreads to the liver.
What is Liver Cancer?
Liver cancers belong to the group of malignant tumours, but they are less common than other types of cancer. It is more common in men than in women, and the most common type is hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver cancer is usually classified as primary or secondary. Primary liver cancer starts with liver cells. Secondary liver cancer develops when cancer cells of another organ spread to the liver.
Liver Cancer Symptoms
- Abdominal discomfort, pain and tenderness
- Yellowing of the skin and skin called jaundice
- White, chalked stool
- Nausea and vomiting
- Easily bruising or bleeding
- Weakness and unreasonable weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
Understanding Liver Cancer Symptoms
Although most of these symptoms are severe, they are not distinctive for liver cancer because they may all result from another condition, such as infection.
Abdominal Swelling: Abdominal swelling due to liver cancer has two reasons. The first is the swelling of the liver to the right side of the abdomen due to a growing tumour. The second is that the fluid accumulated in the abdomen causes swelling in the abdomen as in cirrhosis due to the inability of the liver to function.
Weight Loss: If you do not make any changes in your eating habits and lose weight without any reason, this can be a symptom of liver cancer along with many cancers. Losing 10% of body weight is considered a sudden weight loss and is a harbinger of many dangerous diseases.
Jaundice: Jaundice is not only a cancer-specific symptom but is a symptom of the liver that causes cancer to lose function. It may also be caused by many other diseases such as jaundice, inflammation of the liver, obstruction of the biliary tract and hemolytic anaemia.
Diagnosis of Liver Cancer
For the diagnosis of liver cancer, the doctor first listens to the patient’s medical history and performs a physical examination. Always tell your doctor if you have a history of long-term alcohol dependence or a chronic hepatitis B or C infection. The following methods are used for the diagnosis of liver cancer:
Liver function tests help the doctor determine the health of your liver by measuring blood protein, liver enzymes, and bilirubin levels.
The presence of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in the blood can be a sign of liver cancer.
Abdominal CT or MRI scans produce a detailed image of the liver and other organs in the abdomen.
What are the Treatment Options?
Many treatment options are depending on the stage and type of tumour.
Surgical
Surgical removal of the tumour, called resection, is the most commonly used method for the treatment of tumours that have not spread widely within the organ. The surgeon makes a large incision in the abdominal wall and excludes the tumour-containing part of the liver and a portion of the surrounding healthy tissue. Resection provides a 5-year survival rate of 60-75% for primary liver tumours and 25-39% for metastatic liver tumours. 70-80% of liver cancer patients are not suitable for surgery because their disease is very advanced and/or liver function is very weak.
Radiotherapy
Conventional radiotherapy, also known as external radiotherapy, uses large areas of radiation to calculate the tumour movement that occurs when the patient breathes. Since the large radiation area affects both the tumour and a significant amount of surrounding healthy tissue, the treatment is divided into 30-40 sessions of small doses over several weeks.
This treatment may cause liver diseases that are radiation-induced and may occur during the first few weeks of treatment. In most serious cases, this can lead to liver failure.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is used when cancer cells are located throughout the body or are found in the patient’s blood and body fluids, and these can occur with metastatic tumours and advanced liver cancer.
Stereotaxic Radiosurgery
The ability of stereotaxic radiosurgery to treat tumours with fully targeted radiation is an important advantage for patients with liver cancer. With an accuracy of less than 1 mm, the effect of radiosurgery on surrounding healthy tissue is minimal.
Chemoembolization with Catheter
Patients with liver cancer who cannot undergo surgery or radiotherapy can be treated by catheter chemoembolization. Direct tumour treatment is performed with this minimally invasive method. When using real-time x-ray images for the examination of the tumour, the catheter is inserted through a small incision and advanced in the artery feeding the tumour. A combination of chemotherapy drugs and small solid particles to block the vessel is injected into the tumour. When the particles block the vessel, blood is prevented from entering the tumour and the tumour cells die because they cannot receive oxygen.
What is Liver Failure
Liver failure occurs when a large part of the liver is damaged irreparably and the liver no longer functions.
Liver failure may be acute or chronic.
Acute Liver Failure
Acute liver failure develops rapidly. It may occur suddenly without any symptoms within weeks or even days. Common causes of acute liver failure include poisoning by fungi or overdose.
Chronic Liver Failure
In chronic liver failure, problems occur much more slowly than in the form of acute liver failure. It may take months or even years without any symptoms. Chronic liver failure is usually a result of cirrhosis caused by prolonged alcohol use. Cirrhosis occurs when it damages healthy liver tissue. During chronic liver failure, your liver is inflamed. This inflammation causes the formation of scar tissue over time.
Causes of Liver Failure
-
Hepatitis
A, B, E, hepatitis, which we encounter in different species, targets the liver regardless of the species. In the event of the proliferation of hepatitis viruses in this organ, the control is in the hands of viruses and liver functions can not perform.
-
Weak immune system
The weakening of the immune system can cause different damage in every part of the body. If you have had some diseases that weaken your immunity, you should be more careful about protecting your liver health.
-
Metabolic diseases
Certain diseases, such as Wilson’s disease, and problems in metabolism hurt the liver. As this effect grows, loss of function occurs in the liver.
-
Consume excess alcohol
Excessive use of alcohol causes cirrhosis, severe cirrhosis of the liver in case of progressive loss of function occurs, and this may progress until the liver bankruptcy.
-
Other liver diseases
Other liver diseases can also trigger liver failure. Even the smallest problem needs to be intervened as quickly as possible and prevent the occurrence of larger diseases.
-
Some medications
You take a lot of chemicals into your body by drinking medicine. If you use frequent and unconscious medication, your liver will not be able to perform its duties with the effect of these chemicals.
-
Excessive use of herbal products
Herbal products that provide important benefits to your body when used in the setting, can cause serious damage in case of excessive use. Some plants such as watermelon and skullcap can damage the liver if used too much.
-
Cancer
The presence of cancer that reduces body resistance, liver failure may also occur. It is known that cancer cells formed especially in the liver region spread to other organs with the effect of metastasis and develop a picture that progresses to multiple organ failure.
Symptoms of Liver Failure
The first signs of liver failure can often be due to any condition. Therefore, it can be difficult to diagnose liver failure initially. Early symptoms include:
- Nausea
- Anorexia
- Fatigue
- Diarrhoea
- Skin colour change
- Itching
However, as liver failure progresses, symptoms become more severe and require immediate care. These symptoms include:
- Jaundice
- Bleeding and bruising easier than usual
- High pulse (tachycardia), low blood pressure
- Abdominal swelling
- Mental disorientation or confusion (known as hepatic encephalopathy)
- Blood in stool
- Insomnia
- Coma
Treatment of Liver Failure
The disease or condition causing liver failure should be diagnosed and treated. Treatment of liver failure includes:
1) Drug Treatment
Drugs used in liver failure serve the following purposes:
- Decrease intracranial pressure by eliminating excess fluid accumulated in the brain
- To remove body inflammation
- Preventing blood clots and serious bleeding
- Antidote against poisoning
Some medications used and their characteristics are as follows:
Ursodiol (Ursodeoxycholic Acid):
- Accelerates bile flow
- Prevents hepatic cell death
- Reduces inflammation related to the immune system
- Reduces oxidation damage
Vitamin E:
- Removes toxic toxins
Sucralfate:
- It is a digestive system protector used to treat stomach ulcers.
- Used on an empty stomach.
- May cause constipation.
Vitamin K:
- It is necessary for healthy blood clotting.
- No serious side effects.
Metronidazole:
- It is a type of antibiotic used to relieve bacterial inflammation in the liver.
- Side effects such as poisoning, drowsiness, vomiting, crisis, depression, dizziness may occur in the nervous system.
Prednisone:
- Used in the treatment of hepatitis.
- If the treatment is stopped suddenly, life-threatening may occur.
- Side effects such as gaining excess weight, thirst, diarrhoea, stomach ulcer, and increased likelihood of blood clots can be seen.
2) Supportive Treatments
General health level should be increased in liver failure and immune system of the body should be strengthened. Food and fluid support are provided for this purpose. Food tubes can be used when the patient cannot eat. In severe cases, serums providing direct intravenous food support may be used.
3) Liver Transplantation
In half of the cases of liver failure, liver transplantation becomes compulsory.
It is decided whether there is priority treatment according to the following conditions:
- Inability to detect the cause of liver failure
- Amount of brain damage
- Possible amount of brain injury after transplant
- Volunteering, texture matching
- The factors affecting the patient transfer order (number of patients, age, general health conditions, alcohol and cigarette use, etc.)
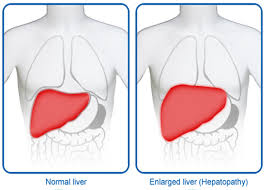
Liver Growth (Hepatomegaly)
What is Liver Growth (Hepatomegaly)?
The liver is one of the largest organs of the body and the body’s most important and critical organs. Liver growth, also known as hepatomegaly, occurs as a result of several health problems.
The liver assumes vital tasks for the body such as the synthesis of cholesterol and fatty compounds and carbohydrate metabolism. It releases edible secretion, which provides regular digestion in the intestines and ensures the destruction of fats. It also helps to remove toxic substances entering the body through the consumption of drugs and alcohol.
Liver growth is not a disease in itself, but it is a symptom of many diseases that cause growth. Most people live without realizing the growth of the liver.
Symptoms of Liver Growth
When the growth in the liver is low, usually no symptoms appear.
But if the liver grows too much:
- A continuous feeling of swelling
- Discomfort occurs in the abdomen.
- Jaundice, chronic fatigue, weakness, nausea and weight loss can also be seen.
Causing Liver Growth?
What Causes Liver Growth?
There are many reasons for liver growth. Several diseases trigger liver growth, such as many diseases that occur later.:
- Circulatory disorders that cause anoxia and hypoxia in particular
- Budd-Chiari Syndrome, leukaemia
- 1-antitrypsin deficiency, traumatic events
- Heart problems, various infections
- Nutrient deficiency
- Multiple sclerosis
- The creator of Crohn’s disease and rheumatoid arthritis diseases
- Alcohol and cigarette use
Diagnosis
Your doctor will perform a physical examination of your liver to check if it is too large. You can also detect liver growth and causes by performing some blood tests:
- Tomography, this method is stronger than an x-ray.
- MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves in this method.
- Ultrasound uses sound waves in this method.
Treatment of Liver Growth
Treatment can only begin with a definitive diagnosis.
- Those with liver growth as a result of alcohol dependence should immediately quit alcohol otherwise it can be fatal.
- In hepatitis, drug treatment is used to stop inflammation in the liver.
- In non-alcohol related obesities, patients are taken to regular weight loss program with regular exercises.
- Blood sugar and cholesterol levels are kept under control in diabetic patients.
- Chemotherapy is used for liver cancer and leukaemia.
- You need to be aware of the risks when using some medical and herbal remedies. Smoking should be avoided as it triggers most of the diseases mentioned above.
- Avoid contact with chemicals. Aerosol cleaners should be used. Pesticides and other toxic chemicals should only be used in well-ventilated areas. Gloves and masks should be used when using such drugs.
- Early detection provides the chance of early treatment before the disease grows. But if diagnosis and treatment are delayed, it can be fatal.