Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
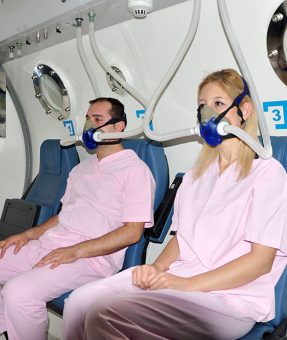
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) is a medical treatment that is applied to the patient who is completely pressurized in a pressure chamber by breathing 100% oxygen intermittently. It is a modern and scientific treatment supported by more than 6000 studies. The patient may take oxygen from the mask, head, medium, or endotracheal tube, depending on the type of pressure chamber and the patient’s condition.
What is Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)?
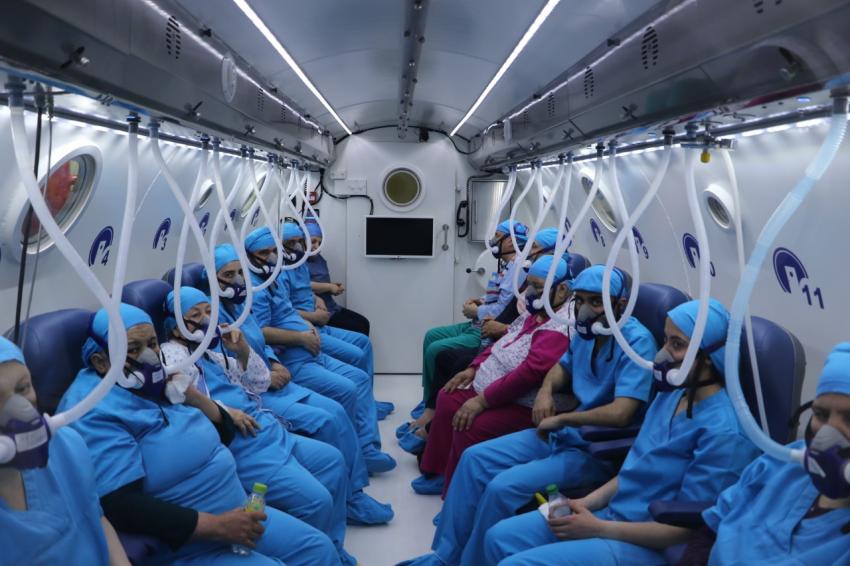
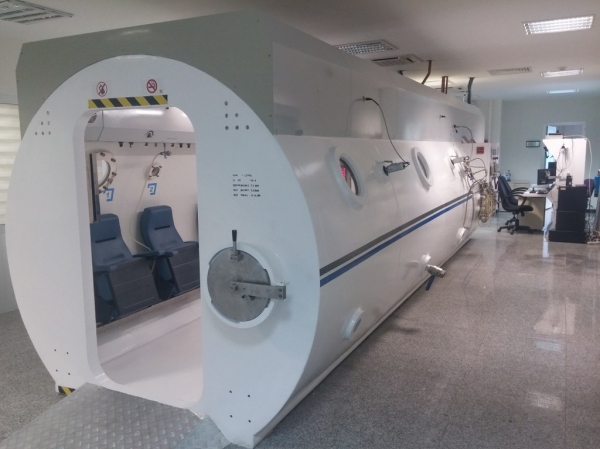
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is an evidence-based treatment based on 100% oxygen inhalation intermittently at pressures higher than 1 Ata, i.e. above sea level, to the patient who is completely pressurized in a closed pressure chamber. It is applied with mask, hood or endotracheal tube (tube attached to the windpipe) according to the clinical condition and needs of the patient in single or multi-person pressure chambers.
What Diseases is HBOT Treated?
- Diabetic foot infections
- non-healing wounds
- bone inflammation (chronic osteomyelitis)
- bone death (avascular necrosis)
- soft tissue trauma (crush injuries)
- burns
- brain abscess
- risky skin and tissue patches (risky grafts and flaps)
- sudden hearing loss
- sudden vision loss
- vascular obstruction due to wounds
- after radiotherapy wounds (Radionecrosis, osteoradionecrosis)
- stove and tube gas poisoning (carbon monoxide poisoning),
- include air gas embolism, soft tissue infections (necrotizing fasciitis).
- Multiple sclerosis, autism, Crohn’s disease, scleroderma in many diseases, such as the trial and research stage.
How is Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Applied?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is applied to the patient who is completely pressurized in 2-3 ATA in pressure rooms, which is a closed environment equipped with new technology in clinics, by inhaling 100% oxygen from mask or hood. Thus, the solubility and diffusion of oxygen in the blood, plasma and tissues increases and its healing effects occur. These rooms are designed to be single or multi-person.
Pressure chambers are also therapeutic devices that provide important services for divers. Pressure decompression applications, diver training, diving simulations and surface decompression during underwater studies can also be performed for decompression sickness and gas embolism treatments in the pressure chamber.
HBOT compliance and treatment protocols of the patients are determined by the Underwater Physician and Hyperbaric Medicine Specialists. The frequency of treatment, which lasts for 2 hours per day, can start from 5 sessions and can be up to 60 sessions depending on the case. While the treatment session is administered once a day, in some emergency cases it can be up to 2-3 sessions a day.
How Many Sessions Are Applied?
The duration of treatment and the number of sessions vary according to the characteristics of the patient and the disease present. During the treatment, in the pressure chambers, the air pressure is increased to approximately 2.5 times the normal air pressure and pure oxygen is inhaled under high pressure. Under these conditions, the amount of dissolved oxygen in the blood increases. Since dissolved oxygen is independent, it can travel long distances under high pressure and is transported all over the body.
This makes it easier for us to fight bacteria, accelerates the healing of wounds, reduces oedema, and reduces air and gas bubbles and removes them from our body. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy also supports the development of new vessels and cells involved in body defence.
What Do Patients Feel During Treatment?
During the hyperbaric oxygen treatment, the air pressure in the pressure chamber increases, while fullness in the ears is felt similar to the descent on a plane journey. Patients can equalize the pressure in the ear with some movements, such as swallowing. Patients are informed in detail about how they can easily equalize middle ear pressure to outdoor pressure.
What Are The Effects Of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy On Diseases?
Breathing 100% oxygen under high pressure increases the oxygen that is transported to tissues through haemoglobin in red blood cells and improves tissue damage and pathologies caused by insufficient oxygenation by delivering dissolved free oxygen to very high values in the blood. Also;
- Production of wound healing substances increases,
- Cells involved in body defence are supported,
- Has oedema reduction effect,
- New vascular development is supported,
- Reproduction of bacteria that grow in an oxygen-free environment is prevented,
- The effectiveness of some toxins released by bacteria decreases,
- Effect of some antibiotics is increasing,
- Tissue damage due to air and gas bubbles is eliminated.