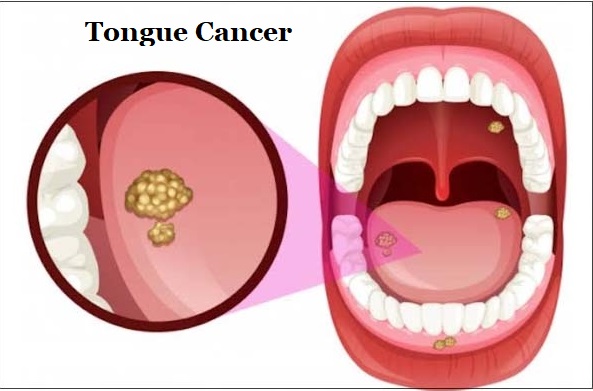
What is Tongue Cancer?
Tongue cancer is a type of oral cancer that develops mostly in the epithelial cells on the surface of the tongue or in a different tissue in the body.
Like other types of cancer, it occurs as a result of uncontrolled proliferation of cells. Compared to other head and neck cancers, tongue cancer can be diagnosed more easily because it occurs in the front and open area of the head.
In the early stages, patients consult a doctor and a visual examination called standard inspection is performed. If there is a suspicion of cancer, the spread of the disease is checked, as in other cancers.
Tongue cancer usually occurs in squamous cells, which are thin and flat cells covering the surface of the tongue. Tongue cancer, which manifests itself with sores, canker sores or white spots on the tongue, may seem like a simple wound at first, but if it does not heal for a long time, it can turn into cancer.
What Causes Tongue Cancer?
The answer to the question “What Causes Tongue Cancer?” can be said as tobacco product use, alcohol consumption, HPV infections and genetic predisposition factors. Factors affecting the formation of tongue cancer are listed below:
-
Gender:
Tongue cancer is twice as common in men than in women. This difference may be associated with smoking and alcohol use. The use of alcohol and cigarettes, which are the most important risk factors, are more common in men.
-
Age:
The average age at diagnosis is around 50-60 years. However, tongue cancer can also be seen in young patients.
-
Genetic Predisposition and Family History:
Genetic predisposition in people with a family history of tongue cancer may increase the likelihood of this type of cancer.
-
Cigarette:
Nearly 80% of people with tongue cancer are smokers or users of other tobacco products. The risk increases with the number of years smoked and the amount of cigarettes smoked per day.
-
Alcohol:
In tongue cancer, alcohol is another important risk factor. The risk of cancer increases many times with the combined use of alcohol and cigarettes.
-
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection:
The human papillomavirus family is a family of viruses that includes nearly 100 similar viruses. While most HPV types cause benign bumps such as warts, some HPV types are associated with cancer. The most common of these cancers is cervical cancer, but it can also cause tongue and oropharynx cancer.
In particular, the association of HPV type 16 with oropharynx (middle region of the pharynx) cancer is evident. HPV-related cancer types tend to respond better to treatment.
-
Poor Oral Hygiene:
Dental prostheses made due to the absence of teeth, if they are not made correctly, can cause wounds that do not heal in the same place and subsequently cancer.
Although not fully proven;
- Fractures in Teeth,
- Bad Fillings,
- Rotten Teeth
- And Mouthwash with High Alcohol Content
The incidence of tongue cancer is higher in people who use it frequently.
-
Immune System Impairment:
The use of drugs that suppress the immune system (for example, drugs that are used for a long time after kidney or other organ transplants and prevent the rejection response, etc.) are among the risk factors of tongue cancer.
What are The Symptoms of Tongue Cancer?
Symptoms of tongue cancer are symptoms that occur due to the growth and spread of abnormal cells in the mouth and tongue area.
Below are some of the most common symptoms of tongue cancer:
-
Wounds or Wounds on the Tongue or Mouth That Do Not Heal Permanently:
These sores can often be painful and do not heal despite long-term treatment.
-
Changes in Tongue Color or Structure:
Abnormalities in the color or texture of the tongue may be a sign of tongue cancer.
-
Pain or Tenderness in the Mouth:
Constant pain or tenderness in the tongue or mouth area is a condition that requires attention.
-
Difficulty in Swallowing:
As tongue cancer progresses, difficulty swallowing may occur. And the person may have difficulty eating.
-
Swelling or Lumps in the Neck Area:
When tongue cancer spreads, swelling or lumps may form in the lymph nodes in the neck area.
-
Numbness or Tingling Sensation in Tongue and Mouth:
Tongue cancer can affect nerves and cause numbness, tingling, or loss of sensation in the tongue or mouth.
-
Bleeding Gums and Bad Breath:
Tongue cancer can cause bleeding gums and bad breath.
These symptoms may also occur in the early stages of tongue cancer. However, it can be difficult to detect. Because they are usually painless.
Therefore, it is important to visit the dentist and doctor regularly for early diagnosis of tongue cancer.
Particularly people with risk factors such as smoking, use of tobacco products, excessive alcohol consumption or HPV infection should benefit from regular screenings. Early diagnosis can increase the success of tongue cancer treatment.
What are The Types of Tongue and Oral Tumors?
-
Benign Tumors:
Some tumors seen in the tongue;
- Papilloma (Warty Tumor),
- Fibroma and Granuloma
They are called benign tumors.
-
Malignant Tumors:
-
Squamous Cell (Epidermoid) Cancer:
It is the most common tumor type in the epithelial layer on the surface of the tongue. This type of cancer is also the most common type of tumor seen in the head and neck region. Examples of areas where tumors can be seen in the head and neck region are the nose, mouth (oral cavity), throat, pharynx (oropharynx), lower pharynx (hypopharynx) and larynx (larynx).
-
Mucoepidermoid Cancer:
It is a type of tumor seen in the salivary gland cells located in microscopic sizes within the epithelial tissue on the surface of the tongue. Apart from the tongue, it may also originate from the epithelial tissues of different organs in the head and neck region.
This tumor also;
- Parotid (Front of Ear),
- Submandibular (Under the Chin),
- Sublingual (In the Salivary Glands Under the Tongue)
It can also occur in areas that open into the oral cavity, called The symptom of this type of cancer is usually swelling.
-
Adenocystic Cancer (Adenoid Cystic Cancer):
Like the mucoepidermoid cancer type, it is seen in the salivary gland cells located in microscopic sizes within the epithelial tissue on the surface of the tongue. It occurs in areas where mucoepidermoid cancer type can be seen, and its symptom is mostly seen as swelling.
What are The Stages of Tongue Cancer?
Tongue cancer can be grouped by staging and grading.
Staging is based on how far the cancer has spread.
The stages of tongue cancer can be listed as follows:
- T is used to express the size of the tumor. T1 is used to indicate a smaller tumor, while T4 indicates a larger tumor.
- N is used to express whether cancerous cells have spread to the lymph area. N0 means that the cancer has not spread, and N3 means that the cancer has spread to more than one lymph node.
- M is used to express whether cancerous cells have metastasized (spread) to other body parts.
The degree of tongue cancer is determined by how malignant the cancer is and the degree of risk of spread.
Tongue cancer grades can be listed as follows:
- Low Grade (slow growing and unlikely to spread)
- Moderate (growing neither too slowly nor too fast)
- High Grade (very fast growing and likely to spread)
How Is Tongue Cancer Diagnosed?
Early diagnosis of tongue cancer is very important for correct and effective treatment of the disease. Diagnosis is usually made using a detailed physical examination and imaging tests. Methods used to diagnose tongue cancer are:
-
Physical Examination:
To evaluate a patient with suspected tongue cancer, the doctor first physically examines the mouth and throat area. Abnormal spots, swellings, ulcers and other symptoms on the surface of the tongue can be observed at this stage.
-
Endoscopy:
Endoscopy is a procedure that uses a flexible lighted tube (endoscope) to look inside the mouth, throat and tongue. With this method, the doctor can directly observe possible tumors and take a biopsy.
- Biopsy:
Tissue samples taken during endoscopy or through a separate procedure are examined for biopsy. This allows the doctor to examine cancer cells under a microscope and make a diagnosis.
-
Imaging Tests:
Imaging tests such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET) are used to determine the size, location, and spread of tumors.
These tests play an important role in assessing the stage of the disease.
-
Lymph Node Biopsy:
Tongue cancer often metastasizes to the lymph nodes. Therefore, lymph nodes are also examined and biopsied when necessary.
What are The Tongue Cancer Treatments?
Tongue cancer treatment involves the use of various methods depending on the stage of the cancer, the extent of spread, and the patient’s general health condition. Generally, tongue cancer treatment can be in the form of surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy or a combination of these methods. The treatment plan is determined by a multidisciplinary healthcare team based on the patient’s condition.
Here are the outlines of tongue cancer treatment methods:
-
Surgical İntervention:
In the early stages of tongue cancer, surgery may be preferred to remove the tumor. Small tumors can often be treated with surgery to remove cancerous tissue from the tongue. It is important to try to protect the healthy tissues around the cancerous tissues as much as possible during surgery.
-
Radiotherapy:
Radiotherapy is a treatment method used to destroy cancer cells using high-energy rays.
For tongue cancer;
Radiotherapy can be used to shrink or completely destroy the tumor. In some cases, radiotherapy may also be applied after surgery.
-
Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy refers to treatment with drugs used to destroy cancer cells or control their growth.
It is often used in combination with other methods in the treatment of tongue cancer.
-
Targeted Therapies:
In some cases, targeted therapies directed at specific proteins or molecules of tongue cancer cells may also be used. These treatments may be effective by directly targeting cancer cells.
-
Immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy is also an option being investigated in the treatment of tongue cancer. This treatment includes medications that support the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
The treatment plan is determined according to the patient’s condition and the stage of the cancer. In many cases, surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy may be used together to treat tongue cancer.
In addition to treatment, supportive treatments can also be applied during the fight against cancer. It is important for patients to pay attention to nutrition, oral care and general health status during treatment.
Regular follow-up and check-ups after treatment are important to watch for cancer recurrence or the development of new tumors. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can increase the chances of survival of tongue cancer patients.
What Can Be Done to Prevent Tongue Cancer?
Although there is no proven method to prevent tongue cancer, the risk of developing tongue cancer can be reduced by considering the following recommendations.
- One should not smoke or use tobacco products. Smokers and/or users of tobacco products should seek professional help if necessary to quit these habits.
- Alcohol consumption should be avoided.
- It is necessary to see a doctor regularly for check-ups and cancer screening examinations.
- Oral hygiene should be taken into consideration.