What is Pulmonary Embolism?
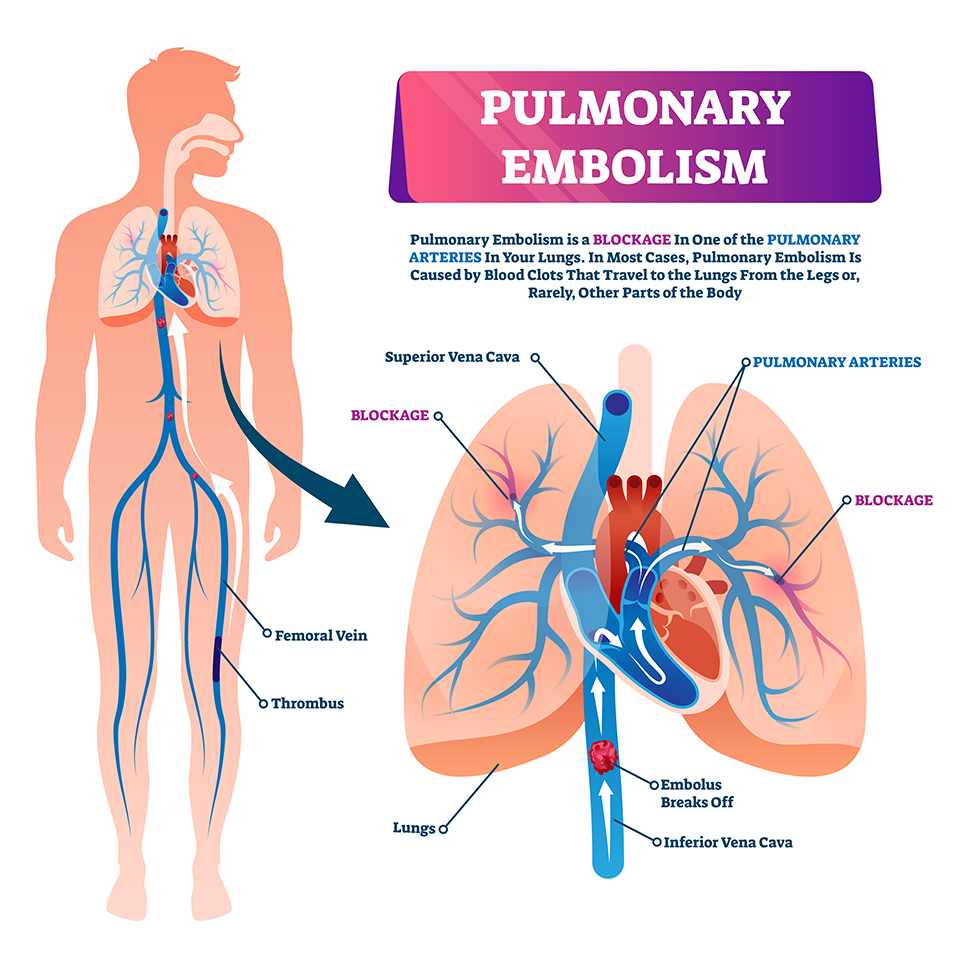
Pulmonary embolism is a disease that occurs when a blood clot creates a blockage in the arteries in the lungs. Pulmonary embolism, medically known as pulmonary embolism, is among the cardiovascular diseases. The clot usually occurs in a vein in the leg area. However, clot formation may also occur in a vein in another part of the body. In this way, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs as a result of a blood clot forming in one or more deep veins in the body. Obstruction of blood flow to the lungs as a result of one or more clots can be life-threatening. However, early diagnosis and prompt treatment of pulmonary embolism can help reduce the risks that may occur as a result of the disease.
How Does Pulmonary Embolism Occur?
There are three main reasons why this disease occurs.
-
First Reason:
Damage to the part called endothelium that surrounds the inner surface of the vessels,
-
Second Reason:
stagnation in blood flow, called stasis, in the vessels,
-
Third Reason:
is an increased tendency to clot. This is called hypercoagulability.
As a result of these three reasons, the clot formed in the veins in the leg and foot parts of the body, called the lower extremities, and more often in the abdominal area, reaches the part of the heart called the right ventricle, from there it reaches the lungs through the pulmonary arteries and causes embolism.
The clot that reaches the lungs blocks multiple large or small vessels on the right or left, depending on its size, disrupting the circulation in that part of the lung. The larger the vessels blocked in the lung, the more severe the consequences.
What are The Causes of Pulmonary Embolism?
The origins of this disease are diverse, and the main causes of this serious health problem are:
-
Damage to the Inner Surface of the Vessel:
One of the main causes of pulmonary embolism is damage to the layer called endothelium, which covers the inner surface of the vessels. This damage paves the way for the development of embolism.
-
Stasis in Blood Flow:
Stasis, where blood flow in the vessels slows or stops, is another cause of pulmonary embolism. This may trigger clot formation.
-
Increased Tendency to Coagulate:
If blood tends to clot more than normal, it can increase the risk of pulmonary embolism. This condition is called hypercoagulability.
-
Cardiovascular Diseases:
Cardiovascular diseases can increase the risk of clot formation and lead to pulmonary embolism.
-
Varicose Veins:
In occupational groups that constantly work standing, varicose vein formation may increase the risk of clots.
-
Medicines:
Some medications can increase the rate of blood clotting. Birth control medications, in particular, can have this effect.
-
Inactivity:
For people who are bedridden or traveling for long periods of time, such as those lasting longer than 4 hours, immobility can lead to clot formation and embolism.
-
Surgeries:
Some surgical procedures, especially operations such as abdominal or leg surgeries, may increase the risk of embolism.
-
Fat Removal Surgeries:
Fat embolisms may occur as a result of liposuction surgeries.
-
Deep Diving:
Divers who dive deep run the risk of oil or air embolisms when they ascend to the surface quickly. This situation is called “profiteering”.
-
Cancer:
Especially in cancer types such as lung cancer, the tendency for blood to clot is high and the risk of pulmonary embolism increases. Cancer patients receiving chemotherapy treatment have a high risk of clot formation.
-
Genetic Factors:
Genetic predispositions can increase the blood’s tendency to clot.
For example, genetic factors such as Protein C deficiency, Factor (V) Leiden disease or antithrombin III deficiency may be among the causes of pulmonary embolism.
-
Smoking and Being Overweight:
Smoking habits and being overweight can also increase the risk of pulmonary embolism.
What are The Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism?
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism may vary from person to person, and the severity of symptoms may vary depending on the size and location of the clot and the damage it causes to the lungs.
However, common symptoms associated with pulmonary embolism may include:
-
Shortness of Breath:
Sudden onset or feeling of difficulty breathing.
-
Chest Pain:
Sharp, sudden or pressing chest pain. It may increase especially with deep breathing, coughing or movement.
-
Fast or Irregular Heartbeat:
A feeling of rapid or irregular pulse.
-
Cough:
Cough with dry or bloody sputum. Bloody sputum may result from blood vessels damaged by a clot.
-
Severe Chest or Back Pain That Occurs Suddenly During Breathing:
This symptom may be a sign of an emergency due to pulmonary embolism.
-
Fainting or Dizziness:
It may occur due to impaired blood flow.
-
Sudden Sweating:
Cold sweats or sweating spells.
-
Weakness and Fatigue:
It may occur due to rapid breathing and lack of oxygen in the body.
Other symptoms that may occur with a pulmonary embolism may include;
- Leg pain or swelling, usually occurring in the calf
- Moist and pale skin (cyanosis)
- Increase in body temperature
- Excessive sweating
- Fast or irregular heartbeat
Additionally, in addition to the above-mentioned symptoms, you may experience pain, redness and swelling in one of your legs (usually the calf). These are symptoms of blood clot formation in the leg called deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which is the most common cause of pulmonary embolism.
Pulmonary embolism is a life-threatening health problem. For this reason, in case of complaints such as unexplained shortness of breath, chest pain or cough causing bloody sputum, 112 should be called immediately or the emergency room should be applied.
What are The Risk Factors for Pulmonary Embolism?
Although anyone can get a blood clot resulting in a pulmonary embolism, some factors increase the risk. Risk factors for pulmonary embolism are detailed below.
-
Patient’s Medical History
If the patient or any family member has had a venous blood clot or pulmonary embolism in the past, this poses a high risk for a new embolism. This condition may be due to inherited disorders that predispose the patient to clotting disorders. Additionally, some medical conditions and treatments that occur in the patient increase the risk of embolism.
Some of these factors are:
-
Cardiovascular Diseases:
Cardiovascular diseases, especially heart failure, lead to an increased risk of clot formation.
-
Cancer:
Pancreatic, ovarian and lung cancers, and many types of cancer that have spread to distant parts of the body, increase the risk of pulmonary embolism by increasing the levels of some substances involved in blood clotting.
-
Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy treatment is another risk factor that increases the risk of clot formation.
-
Surgeries:
Surgical procedures are one of the leading causes of blood clots. For this reason, the patient can be given anticoagulant medications before and after major surgical procedures.
-
Long Term Inactivity:
Blood clots are more likely to form during periods of prolonged inactivity, such as:
-
Bed Rest:
Prolonged bed rest after surgery, heart attack, leg fracture, trauma or any serious illness makes the person more vulnerable to blood clot formation.
When the legs remain horizontal for a long time, venous blood flow slows down and blood pools in the legs and becomes prone to clotting.
-
Long Journeys:
Sitting in a cramped position during long plane or car journeys slows blood flow in the legs and increases the risk of clot formation.
-
Other Risk Factors
Smoking. Smoking predisposes some people to blood clots, especially when combined with other risk factors.
-
Being Overweight:
Obesity increases the risk of blood clots, especially in women who smoke or have high blood pressure.
-
Taking Estrogen Support:
Estrogen, used in birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy, increases the risk of pulmonary embolism, especially in women who smoke or are obese.
-
Pregnancy:
The baby’s pressure on the veins around the uterus can slow down the return of blood from the legs. If blood flow slows down or blood pools in the leg veins, clots become more likely to form.
How is Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed?
Diagnosing a pulmonary embolism is not always easy. The above symptoms can be seen in many diseases. Physical examination, laboratory and imaging methods are used for the differential diagnosis of these symptoms.
-
Physical Examination:
During the physical examination, your legs are looked at closely to determine if there is any swelling, tenderness, loss of color, or increased temperature. These symptoms are very important because they are signs that you may have a clot in one of your veins.
-
Blood Tests:
If pulmonary embolism is suspected, D-dimer (clot disintegration product) test is requested first.
If the test is normal, pulmonary embolism is not considered. However, if the test result is high, further tests should be performed to confirm the diagnosis of the disease.
Blood tests can also measure the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your blood. A clot in a blood vessel in the lungs will reduce the oxygen level in the blood. Blood tests may also be done to determine if you have an inherited clotting disorder.
Imaging Tests
-
Chest X-Ray:
It is not performed to diagnose pulmonary embolism. It helps us distinguish it from other diseases that may be confused with pulmonary embolism.
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG):
It is also known as heart radiography among the public. This test measures the electrical activity of the heart.
-
Echocardiography (ECHO):
Heart ultrasound. It shows changes in the heart. It provides valuable information both in diagnosis and in regulating treatment.
-
Doppler Ultrasound:
It provides information about whether there is a clot in the deep leg veins. Because it very often accompanies pulmonary embolism.
-
CT Angiography:
It is a computerized tomography method performed by simultaneously injecting opaque material into the arm. It can be decisive in making a diagnosis because it shows whether there is a clot in the pulmonary arteries.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
This scan uses radio waves and a magnetic field to produce detailed images. It allows direct visualization of the clot in the pulmonary arteries.
-
Lung Scintigraphy:
Since it contains less radiation than computer tomography, it can be preferred in young women, pregnant women and patients with kidney disorders. Its biggest disadvantage is that it cannot be withdrawn under emergency conditions.
-
Pulmonary Angiography:
It is considered the gold standard test that provides definitive diagnosis in pulmonary embolism. It is an invasive procedure that is expensive and requires experience. For this reason, it is not preferred in practice.
Pulmonary Embolism Treatment
Treatment of pulmonary embolism aims to prevent the growth of the embolism and prevent the formation of new clots. Early diagnosis and treatment is necessary to prevent possible complications. Treatment for pulmonary embolism may include medications, surgery, and other procedures.
Common treatment methods may include:
-
Medicines:
Blood thinning medications known as anticoagulants are the most common treatment for pulmonary embolism. Additionally, thrombolytic drugs can help dissolve clots. It may be necessary to be careful against sudden and severe bleeding during this treatment. Otherwise, it may cause risky consequences.
-
Clot Removal:
A thin, flexible catheter is passed into the blood vessels and guided into the pulmonary arteries. It can be carried out using special devices to break up the clot or pull it out of the vein.
-
Inferior Vena Cava Filter:
It is the process of placing a filter with a catheter in the main vein of the inferior vena cava, which runs from the legs to the heart. This filter can trap clots and prevent them from moving toward the lungs.
-
Surgery:
In rare cases, surgery may be required to treat pulmonary embolism. Using a catheter, blood vessels can be reached and blood clots can be removed.
What Should Those Who Had Pulmonary Embolism Pay Attention?
Pulmonary embolism is a disease that is life-threatening and has the possibility of recurrence.
- Blood thinners prescribed for treatment should be used regularly.
- Since excess weight increases the risk of clots, the weight should not be excessive.
- Heart and coagulation system diseases should be treated at an early stage.
- Vascular health is important in preventing pulmonary embolism. Exercising regularly and eating healthy protects vascular health.
- People who work or travel while remaining sedentary for long periods of time should drink enough water, stand up from their sitting position, walk and move their legs every hour.
Prevention Methods from Pulmonary Embolism
- If you are in the risk group for pulmonary embolism, you may need to use anticoagulant medication before all surgeries, especially major surgeries.
- Mechanical precautions such as compression stockings and pneumatic compression devices should be taken in hospitalized patients.
- It is necessary to act as early as possible after surgery. Active exercises help the muscles return to activity and activate the veins in the legs.
- Avoid long journeys as much as possible. If you have to, take frequent breaks. Drink plenty of fluids during the journey.
- Exercise as often and regularly as possible. You can choose sports such as running, walking, swimming and cycling.
- Be careful not to increase your weight, because excess weight means a burden on your heart and blood circulation as well as your veins.
- Smoking should be quit.