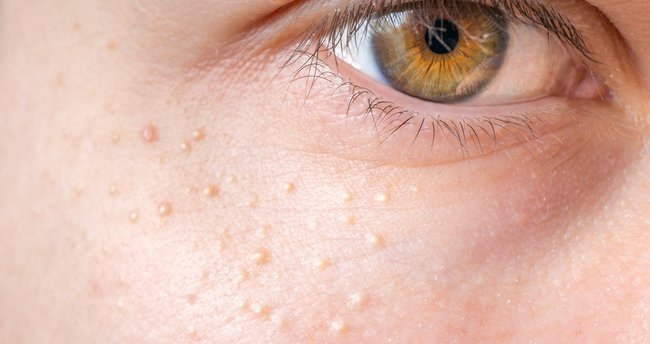
What is Milia?
Milia are small, round, yellow-white, pearly projections around the eyes. When there is one or when naming one it is called milium, when there are many and when describing this condition it is called milia. Around the eyes and above the cheekbones are the most common areas, but it can be seen in every sweat of the body.
What Causes ?
Searching the internet, you’ll see that there are many reasons, but almost none of them are shown as “definitive reasons”. In fact, the main reason is the person’s body, that is, his genetic structure.
Cortisone Usage:
The incidence in those who use cortisone cream or in other ways is about the same as in those who do not use cortisone at all, it can even be seen at the time of birth of the baby.
Sunlight:
The fact that it is also seen in the parts of the body that does not go out to the sun or does not see the sun refutes this idea.
Malnutrition:
It is not possible to say that the substances in its content are related to food, this is due to the fact that it is confused with the similar disease xanthelasma, it is difficult to associate it with nutritional habits.
Having Skin Sensitivity:
It is not seen more often in people with sensitive skin. High blood cholesterol is more common in xanthelasma than in the normal population, but the same is not true in milia.
What Are the Symptoms ?
The characteristics of milium allow us to recognize milia and distinguish it from infancy acne and Epstein pearls, the condition most often confused with milia.
We can list its main features as follows;
- Milia are not usually found as a single lump. The lumps are found in groups.
- The areas where milium are observed are mostly around our eyes, eyelids, cheeks, chin and nose.
- Sometimes, although very rarely, it can be seen on our body and genital area.
The point that should be noted here is that milia are not seen on the inside of our lips and on our gums, which distinguishes them from Epstein pearls.
Epstein pearls are keratin cysts that appear on the inside of our lips and on our gums.
- The cysts are white – yellow in color.
- These cysts do not itch.
- These cysts are painless.
What are The Types?
There are two types, primary and secondary. Those that develop spontaneously are called ‘Primary Milia’, those that develop for another reason are called ‘Secondary Milia’.
The primary ones are small masses formed by the metabolic deposits originating from the hair-oil glands and the secondary ones from the sweat glands.
What is Primary Milia?
Primary milia are types of milia that develop spontaneously for no reason. There are different types seen at different ages.
Neonatal Primary :
It is the primary milia that is common in newborns and regresses within a few weeks after birth. Typically, it is on the facial scalp and upper body.
Primary Milia in Children and Adults:
It is similar to newborn milia. It is most common on the cheeks and around the eyes. Apart from this, it can also be seen on the forehead and genital area. It has no tendency to disappear on its own. It usually stays in the same place for a long time. Less frequently, it can be seen around the nose and chest due to itching in atopic children who are prone to allergies.
Multiple Milia:
Multiple milia develop over months. The place of residence is usually the head and trunk. There is also a form that can be genetically transmitted. It may accompany genetically transmitted skin diseases.
What is Secondary Milia?
It is a type of milia that occurs after a drug use, trauma, or illness. They either disappear on their own or they can stay for a long time.
Examples of these include:
Milia Developing After Epidermoliosis Bullosa:
Epidermoliosis bullosa, which is a skin disease with blisters filled with water, may accompany milia.
Milia That Creates Plaques:
Many milium come together to form plaque. It occurs on the head, neck and around the ears. It is more common in women and middle age.
Some skin diseases, such as Lichen Planus, can occur as a result of trauma or kidney transplants. In addition, some drugs used after organ transplantation can also cause milia.
Nodular :
The reasons for its formation and its location are as in milia, which forms plaques. However, the appearance is nodular (similar to chickpea).
Apart from these, it may also occur in the following situations;
- 2nd degree burns and post-radiotherapy
- From skin peeling treatments,
- From a skin graft (skin patch)
- Taking heel blood in newborns,
- Using some drugs,
- After using oil-based cosmetics
Diagnosis
Most of the time, no special tests are needed to diagnose milia. While the doctor examines your skin, he or she can examine your cysts and easily diagnose milia. The clusters of white lumps under the eyes, nose, cheeks and chin are in favor of milia.
In cases where the doctor finds it difficult to grind the lumps with his naked eye, he can use a device called a dermatoscope, which acts as a magnifying glass and facilitates the examination of the skin.
Very rarely, the doctor may need to take a biopsy of the skin lesion to confirm the diagnosis of milia.
What Precautions Should Be Taken?
- Avoid sun exposure and use oil-free sunscreen, as excessive sun causes illness.
- Good skin care shrinks the cysts. Therefore, pay attention to skin care.
- Do not use oily cosmetic products.
- Do not try to tighten.
- Use cosmetic products containing low concentrations of salicylic acid, glycolic acid or retinol at home.
Treatment
Milia, which occurs between 0-1 years of age, usually occurs within a few weeks in older children and adults. It resolves spontaneously within a few months.
If it is an underlying genetic disease causing the skin, it is not expected to resolve spontaneously.
If it did not heal on its own and its appearance began to bother the person, there are various treatment methods to purify our skin from it. All kinds of treatment, albeit in different ways, is the removal of milia from our skin.
-
Cryotherapy:
It is the most commonly used method for the removal of milium. Nitrogen given as a liquid freezes the cyst and allows it to fall out of our skin.
-
Laser Ablation Treatment:
It aims to remove the milia cyst using laser.
-
Diathermy
Applying a very high temperature to the milia cyst causes it to break down and disappear.
-
Deroofing
In the treatment option, the cyst is emptied by entering the cyst with a sterile needle.
-
Chemical Peeling:
The application of facial tonics or peeling creams containing salicylic acid and glycolic acid, in particular, causes our skin to shed and peel over time, and to reveal a renewed skin texture from below. Along with our peeling skin, milia cysts are also poured from our skin.
-
Creams Containing Retinoids:
Applying it to your skin once a day ensures that our skin is cleaned from milia. Retinoid is vitamin A. Vitamin A makes our dead skin shed.
While our dead skin is shedding, keratin cysts, which are part of our dead skin, will also be poured with our skin, and a new, fresh and smoother skin will emerge from the bottom.