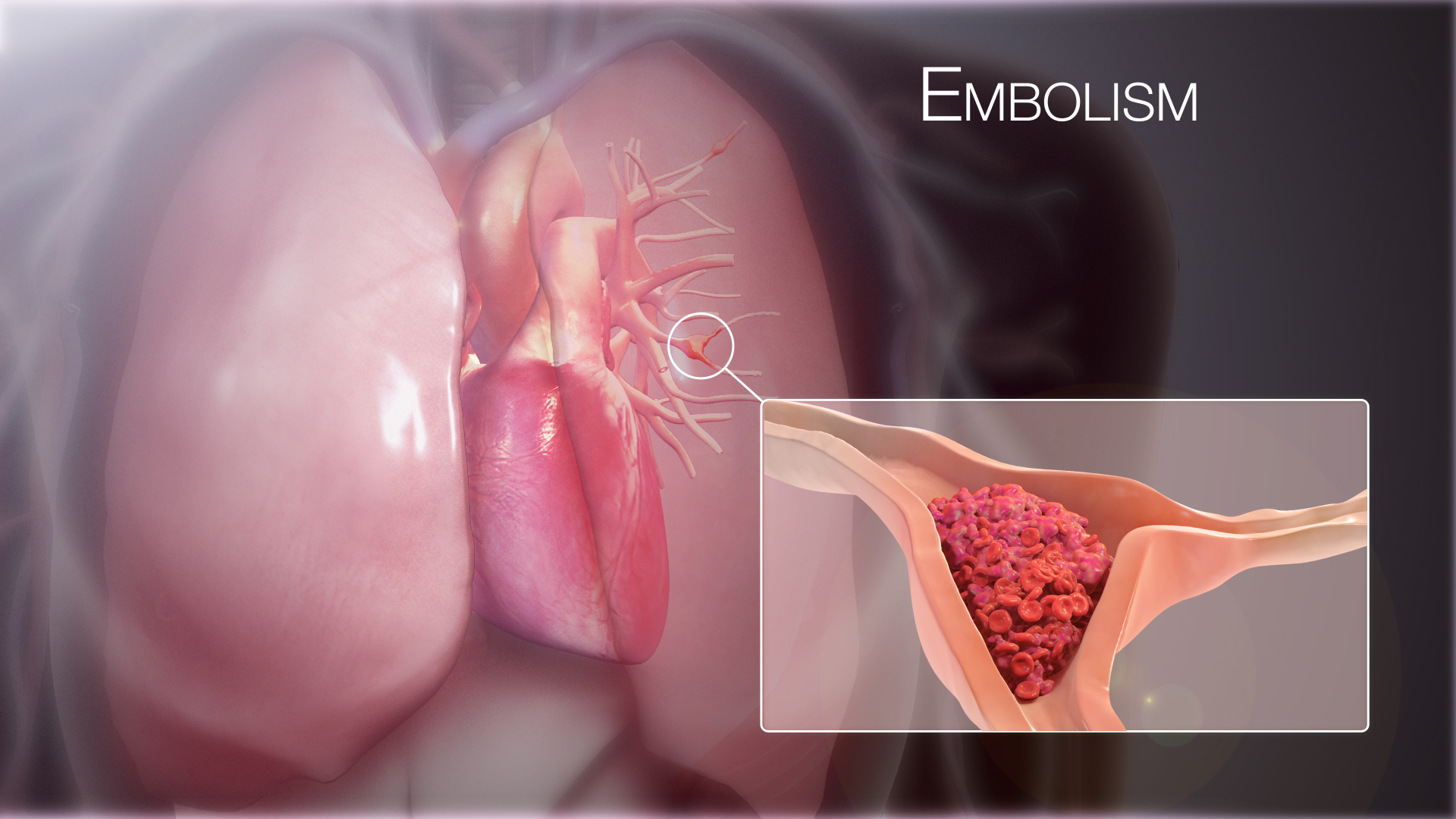
What is Embolism?
Embolism is a term that describes blockages that usually occur as a result of a blood clot (thrombus) or other material in the blood circulation system being carried through blood vessels and traveling to another area. This blockage often impedes blood flow, preventing adequate oxygen and nutrients from being supplied to the tissues.
What Are The Types Of Embolism?
Embolism can often be of different types, such as thromboembolism or fat embolism.
Thromboembolism:
It usually occurs as a result of clots that form in large vessels in the blood circulation system or heart chambers and are carried by the bloodstream. These clots can result from conditions such as deep venous thrombosis (DVT), usually in the legs. If these clots mix with the blood and reach another area in the circulatory system, thromboembolism may develop.
Thromboembolism can cause blockages in various organs in the body and lead to serious complications. For example, a thromboembolism that blocks the lung vessels is called a pulmonary embolism and can be life-threatening. Similarly, a thromboembolism that blocks a vessel in the brain can cause a stroke.
Fat Embolism:
Fat embolism is a condition in which fat in the body passes into the bloodstream and blocks the vessels, usually as a result of a broken bone or traumatic injury. This type of embolism often occurs following bone fractures, especially breaks of long bones (for example, the femur), bone surgery, traumatic injuries, or sometimes plastic surgery.
Signs And Symptoms Of Fat Embolism
Symptoms of embolism most commonly manifest as shortness of breath, rapid breathing, cough and bloody sputum, and severe chest pain.
Respiratory Distress:
Respiratory distress may occur when a fat embolism reaches the lungs.
Shortness of Breath:
When it reaches the lungs, it can cause shortness of breath.
Rapid Heartbeat:
The heartbeat may become rapid as the heart tries to filter out circulating fat from the body.
Skin Changes:
May cause bluish discoloration of the skin.
Changes in Consciousness:
Serious fat emboli can cause changes in consciousness, confusion, or loss of consciousness.
Embolism Treatment
Embolism can cause serious complications that may require immediate medical attention. Treatment is usually determined by the type of embolism, its cause, and the area it affects. Physicians may try to prevent blood clots by using anticoagulant medications or other treatment methods.
Fat embolism is a serious condition that often requires immediate medical attention. Treatment is aimed at relieving symptoms and stabilizing the patient’s condition. Administration of oxygen, use of respiratory support devices, and other appropriate treatment methods can support the patient’s recovery process.
To reduce the risk of fat embolism, especially after a fracture, it is important to limit movement and take appropriate precautions. Following a traumatic event or surgical interventions, such complications may require careful observation and treatment.
What Can Be Done To Prevent Embolism?
It is important to have routine examinations and eat regularly. It is necessary to eat fat-free foods and keep sugar and salt intake to a minimum. Exercising, walking and doing sports reduce cholesterol and fat levels.
Does Blood Thinning Medication Eliminate Clots?
These medications prevent a new clot from forming in the body. But this is not 100% blocking. Rarely, a clot may form in someone taking blood thinners. These medications prevent clots from forming and preventing the clot from growing. However, it does not eliminate clots that have already formed.