What is Albino (Albinism)?
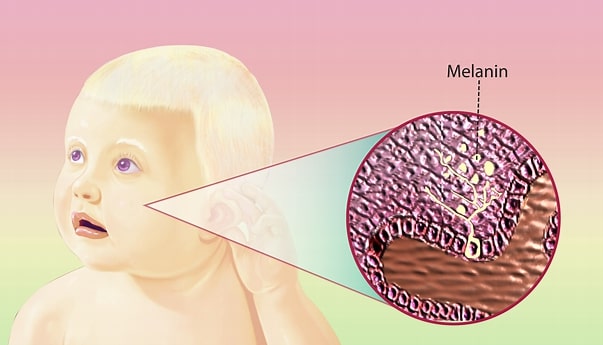
Albinism; It is a genetic disease in which there is little or no color pigment in the eyes, skin and hair. The disease occurs as a result of insufficient or no production of melanin, the coloring pigment in the body, for some reasons. People with albinism are called albinos.
Significant color changes in the hair, eyes and skin of these individuals are among the most prominent findings. But in some cases the color change is not very obvious. These color changes in their skin cause albino patients to be very sensitive to the sun.
Because of this sensitivity, the risk of developing skin cancer is high. The pigment melanin, which gives color to the skin, also plays a role in the development of the optic nerve, which is involved in the visual function. Therefore, these people also have visual defects.
What Causes Albino (Albinism)?
Albinism is the result of the body’s inability to produce and distribute melanin due to a genetic defect.
Melanin is a natural substance in the body that gives color to the hair, skin and iris of the eyes. It is completely inherited from the parents. And it is innate.
External and environmental factors have no effect. Although it seems to be a condition that only affects the external appearance, it actually develops with visual impairment or low vision.
The disease gene is carried recessively on body chromosomes. The probability of the disease being seen in children also varies according to the gene characteristics of the mother and father.
The two most common forms of inheritance are seen:
-
X Linked Inheritance Form:
The most common form of albinism is due to damage to the X chromosome.
Boys with ocular albinism (OA) have an X chromosome inherited from their mothers.
This disease is seen in 50% of the sons of mothers who carry the wrong X chromosome.
Daughters are carriers if their fathers do not have OA. Or they are not affected at all.
-
Autosomal Recessive (Recessive-Non-Dominant) Inheritance Form:
The less common form of albinism is albinism, which is caused by a defect in autosomal recessive genes.
Both parents carry the faulty recessive gene. In this case, their babies will also have the effective gene.
No child has albinism in 25% of cases. The incidence is equal in boys and girls.
What are The Symptoms of Albino (Albinism) Disease?
Albinism usually manifests itself with skin, hair, eye color and vision problems.
Symptoms of albinism usually include:
-
Skin:
It is the most well-known feature of albinism, and it usually manifests itself with white hair and light-colored skin compared to the patient’s siblings. Skin color (Pigmentation) and hair color can range from white to brown or almost the same as the color of parents or siblings without albinism. Skin manifestations may not be evident in ocular albinism. Tanning can be seen with increasing pigment and sun exposure with age.
-
Freckles:
Pigmented or generally pink colored unpigmented moles may be seen. There may also be freckle-like spots the size of a lentil in patients.
-
Hair:
The patient’s hair color can vary from white to brown. People of African or Asian descent with albinism may have blond, brown or a tone in between. Some minerals caused by environmental factors that the patient is exposed to in his later years may cause the hair to become stained or become darker with age.
-
Eye Color:
The eyelashes and eyebrows of albino patients are usually pale. Eye color can vary from very light blue to brown. A translucent appearance may occur due to a lack of pigment in the colored part of the eyes, namely the iris.
This situation in the iris means that the patient cannot completely prevent light from entering their eyes and that the light enters, causing a decrease in visual acuity. For this reason, very light colored eyes can also be seen as red in some lights.
-
Defect of Vision:
It is one of the most important symptoms for albino patients.
The following eye problems are encountered in albinism:
- Decreased visual acuity
- Partial or complete vision loss
- Sensitivity to light caused by light scattering in the eye (Photophobia)
- Misdirection of the image on the retina that does not follow the normal nerve pathways (abnormal crossing of optic nerve fibers)
- Rapid, involuntary movement of the eyes (Nystagmus)
- Head movements such as nodding or tilting the head to reduce involuntary eye movements and see better
- Both eyes cannot look at the same point or move at the same time (Strabismus / Strabismus)
- Inability to see far/near clearly (Myopia/Hypermetropia)
- Abnormal curvature of the front surface of the eye or the lens inside the eye that causes blurred vision (Astigmatism)
- Poor depth perception
What are The Types of Albino (Albinism) Disease?
Different gene defects characterize multiple types of albinism.
Types of albinism include:
- Oculocutaneous Albinism (OCA1 – OCA2- OCA3- OCA4)
- Ocular Albinism
- Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome
- Chediak-Higashi Syndrome
- Griscelli Syndrome
-
Oculocutaneous Albinism
OCA affects the skin, hair, and eyes. About 1 in 70 people have a mutation in the OCA gene.
There are several subtypes of Oca.
Oculocutaneous Albinism (OCA1)
- Albinism OCA1 or oculocutaneous type 1 is a type of genetic disease caused by a genetic mutation.
- OCA1 affects the production of melanin in the skin, hair and eyes.
- These individuals will have white skin, white hair and light colored eyes due to the complete absence of pigment.
- OCA1 is caused by a defect in the tyrosinase enzyme. OCA1 has two subtypes:
- People with OCA1a.Oca1a have a complete absence of melanin.
- People of the subtype have white hair, very pale skin, and light-colored eyes. And people with Jan1b produce some melanin.
- They have fair skin, hair and eyes. As they age, their color may increase.
Oculocutaneous Albinism (OCA2)
- Albinism OCA2, or oculocutaneous type 2, is a more common type of albinism caused by a genetic mutation.
- OCA2 comes with some differences from oca1. Individuals may have some pigment in skin color and hair color.
- OCA2 comes from a mutation in the P gene, which is also associated with other rare genetic disorders such as Prader-Willi syndrome.
- OCA2 is less severe than oca1. It is caused by a defect in the OCA2 gene that causes decreased production of melanin.
- People with Jan2 are born with light colored skin. Their hair can be blond, blond or light brown.
- OCA1 and OCA2 are the most common subtypes globally.
Oculocutaneous Albinism (OCA3)
- OCA3 is the result of a defect in the TYRP1 gene. It usually affects people with dark skin, especially Black people in southern Africa.
- People with OCA3 have reddish-brown skin, reddish hair, and hazel or brown eyes.
Oculocutaneous Albinism (OCA4)
- OCA4 is caused by a defect in the SLC45A2 protein. It results in minimal melanin production and is usually seen in people of East Asian descent.
- People with OCA4 have symptoms just like people with OCA2.
Other Subspecies
OCA5, OCA6 and OCA7 are very rare subtypes of oca.
-
Ocular Albinism
Ocular albinism is the result of a gene mutation on the X chromosome and occurs almost exclusively in males.
People with ocular albinism have reduced coloration in the retina and iris. This condition does not affect the skin or hair.
-
Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome is a rare form of albinism caused by a defect in one of 10 genes. It produces symptoms similar to Oca. The syndrome occurs with lung, intestinal and bleeding disorders.
-
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome
Chediak-Higashi syndrome is another rare form of albinism that is the result of a defect in the LIST gene.
It produces symptoms similar to Oca.
However, it may not affect all areas of the skin.
Less than 500 cases have been reported worldwide. The skin is usually creamy white or grayish in color.
The hair is usually brown or blond with a silvery sheen. People with this syndrome have a defect in their white blood cells, increasing the risk of infection.
-
Griscelli Syndrome
Griscelli syndrome is a very rare genetic disease. It is caused by a defect in one of the three genes.
Between 1978 and 2018, there were approximately 150 known cases of this syndrome worldwide.
It occurs with albinism (but may not affect the whole body), immune problems, and neurological problems. Griscelli syndrome usually results in death in the first decade of life.
How is Albino (Albinism) Diagnosed?
Albinism is usually noticed as soon as the baby is born.
The baby’s hair, skin, and eyes can be examined for signs of missing pigment.
The method used for this is genetic testing. With this method, the defective gene related to albinism is detected.
Also, the baby may be referred to an eye specialist, as albinism can cause a range of vision problems.
Electroretinogram test, which measures the response of light-sensitive cells in the eye, is applied to detect problems in the eye. The diagnosis of albinism is made according to the results of the tests.
Albinos are considered to be between 40 and 90% disabled by the state due to vision loss.
How is The Treatment of Albino (Albinism) Disease?
There is no treatment that completely cures this condition, which is a genetic disease that occurs as a result of defects in DNA. However, some precautions can be taken to minimize the patient’s skin, eye and vision problems.
In the treatment and follow-up process of this disease, dermatology, ophthalmology (eye diseases and surgery) and genetics departments should work together.
Patients should have their eyes checked systematically and regularly. And should use glasses or lenses given by the doctor.
This situation can be eliminated by applying surgical intervention to patients with nystagmus (strabismus) problem. In addition, these patients, for whom dermatology controls should be carried out regularly, are also evaluated for the status of lesions that may cause cancer, while performing skin examination in the controls.
Individuals with this condition should gain some personal care habits from childhood.
Some of these habits are:
-
Suntan Cream:
Patients should use sunscreen that has protective properties against Ultraviolet A (UVA) and Ultraviolet B (UVB) rays. It is important that the protection level of the preferred product is SPF 30 and above.
-
Not Exposure to The Sun:
It should be avoided to go out in sunny weather as sunlight can damage the skin of these people too much.
-
Protective Clothing and Precautions:
When going out, wear a long-sleeved t-shirt that covers your arms and a dress that covers your legs, not short pants.
In addition, wide hats should be preferred to protect from the sun.
-
Eye Protection Precautions:
Sunglasses or special lenses that refract bright light and make it dark help protect the eyes from sunlight.
Some changes to be made in the social lives of children with genetic conditions can increase their self-confidence.
Parents can get information about practical methods that facilitate learning in the classroom and at home by talking to their children’s teachers.
Some practices and methods that can be done in the classroom and home environment for albino children are as follows:
- The child sitting in the front row
- Use of large font books
- Using a black pen on a white background while writing
- Enlarging the computer screen size
- Avoiding the use of bright light while doing homework or studying
- Allowing them to use extra time on reading and writing activities
When the treatment of these patients is delayed, delayed and the necessary support is not provided, these people may encounter very different difficulties in their lives.
Children whose vision problems are not treated may fail academically in the future. They may have difficulty finding a job and obtaining a driver’s license.
On the other hand, these people may experience problems in their social lives and may feel different. In this case, people may experience a lack of self-confidence. In order to prevent these situations, the support of family and friends is very important.
How to Prevent Albino (Albinism) Disease?
As can be seen, albinism;
- It is a genetic disease group that has many different types and is a common carrier in the community.
- For this reason, parents who have a family history of albinism or who are sick themselves should receive genetic counseling before having children.
- It is essential for the risk of disease in future generations. As a result of the tests, albinism carrier can be detected in the family.
- It can be determined if there is a risk for the unborn children. And the probability of passing the disease to the next generations can be minimized.
Frequently asked Questions
Does Albinism Cause Mental Retardation?
Although not all albinos, mental retardation may occur in patients with some special syndromes of albino. Except for these special cases, there is no case in which albino is observed together with mental retardation. The main factor that affects or even slows down people’s social life and development is the loss of vision in the eyes. Since most patients experience losses of up to ninety percent, slowdowns are observed in the learning and perception mechanism.
Is Albino Disease Deadly?
Albinism is not just a skin disease. In some cases, it may be accompanied by mental retardation or physical disability.
People with albinism are very sensitive.
This can even lead to their death if they are exposed to too much sun, as their skin has little or no pigment.
How long do albino patients live? The question is a very curious subject.
As long as they are careful, they can live as long as a normal human life. The average lifespan of albinos on the African continent, where they do not take precautions and are overexposed to the sun, is 35 years.
Can Albino Disease Be Treated With Alternative Medicine Methods?
It is out of question to treat albinism with any alternative or not. Although some drugs are being developed for partial albinism, satisfactory results regarding the success of these drugs have not yet been obtained.