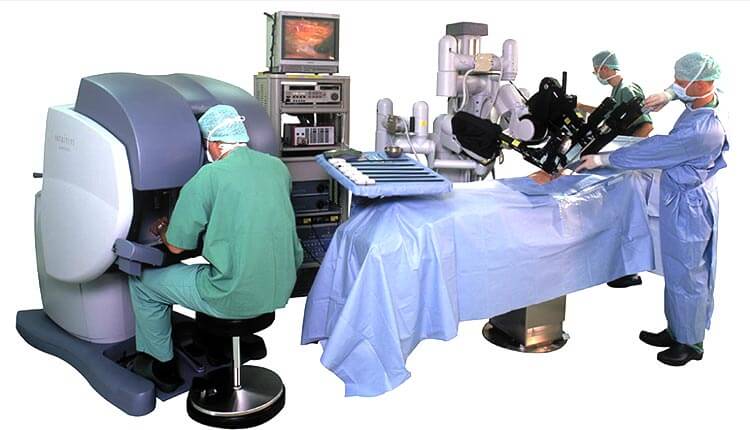
Are All Robotic Systems The Same?
The characteristics and results of different robotic systems used for robotic surgery are not the same. In the systems that were first used and known as active robots, the contribution of the surgeon to the bone incisions is limited to the emergency shutdown button. Once the bone structures are defined to the robot, the robot makes all the incisions on its own. These systems are not preferred today due to unwanted soft tissue complications, and these robots are not available in our country.
In semi-active robotic systems, the robot prevents going out of the planned limits, but the incisions are made by the surgeon. Examples of this group of robots in our country are MAKO (Stryker) and Navio (Smith & Nephew) systems.
In the last group, there are passive robots, these robots bring the incision guides to the desired area, but do not make any restrictions, the surgeon can make the incisions as he wishes. An example of passive robots in our country is the Rosa (Zimmer Biomet) system.
The differences of the 3 robotic systems in our country are as follows.
Stryker MAKO System
Before the surgery, computerized tomography of both legs is taken and planning is made on the 3D real model of the joint. This model is introduced to the robot after surgery and incisions are made. Thanks to the haptic feedback feature, the robot gives audible and mechanical warnings as it approaches the defined limits. It does not allow going out of bounds. There are systems for total hip, total knee and partial knee. Soft tissue balance control is possible at every stage of the surgery.
Smith & Nephew Navio System
Preoperative planning is done on x-rays. During the surgery, certain points are introduced to the robot and a virtual knee model is created. Incisions are made on this virtual model. When the robot goes outside the desired limits, it stops working, but there is no haptic feedback. There is a total and partial knee prosthesis system, there is no hip system. Control of soft tissue balance is possible.
Zimmer Rosa System
Preoperative planning is done on x-rays. During the surgery, certain points are introduced to the robot and a virtual knee model is created. Incisions are made on this virtual model. The robot simply brings the incision guide to the appropriate area. It has no effect on the incision. There is no haptic feedback and no limitations. There is only a system for total knee replacement.