What is Sciatica (Nerve Compression)?
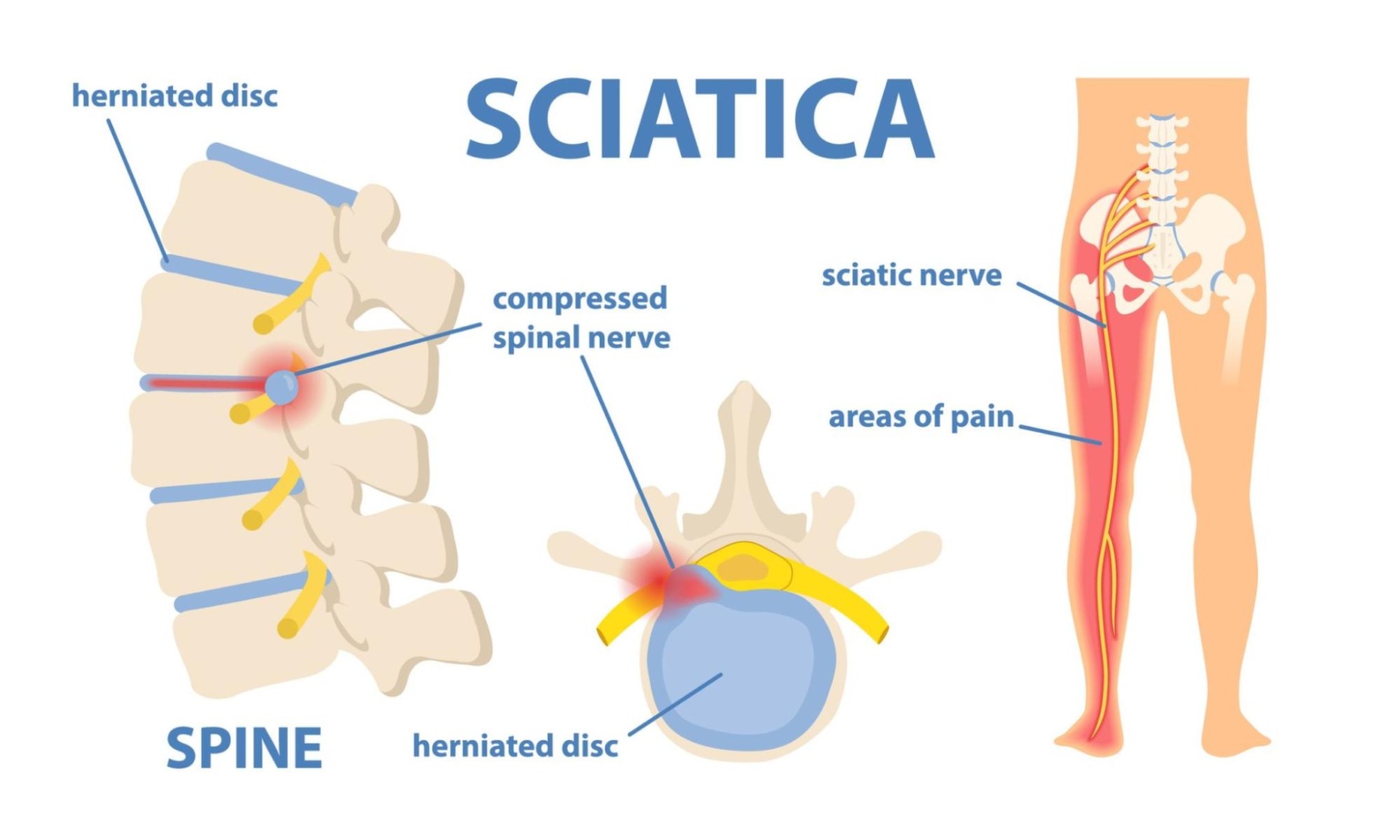
Sciatica (Nerve Compression) is the longest and thickest nerve in the body. Its name in medical terminology is nervus ischiadicus. It originates from the last vertebra of the waist and ends just below the knee.
In other words, the sciatic nerve, which is formed by the union of L4, L5, S1, S2 and S3 nerve roots located in the lower part of the waist, passes through the perforated area in the pelvis, located in the hip and defined as the coxa, and extends to the back of the leg.
It divides into branches at the knee joint and reaches the foot, creating motor and sensory functions in this region. Sciatica is actually the name given to the pain caused by nerve compression.
Compression or stretching of the roots of the sciatic nerve in the waist area causes pain in the leg.
In some cases, reasons such as vertebral slippage, inflammation, tumor and cyst presence may also cause sciatic nerve pain.
Sciatic pain, which begins with lower back pain radiating towards the hip, spreads along the nerve from the groin to the back of the leg and from there to the foot.
In severe cases of sciatica, the leg becomes weak. Knee and ankle reflexes are reduced. The higher the person lifts his leg, the more severe the pain becomes.
What is Causes Sciatica (Nerve Compression)?
Although the main cause of sciatica is a herniated disc, it is also possible to develop sciatica due to different reasons. Compression in the waist area, compression of the sciatic nerve passing through the hip muscles, injury or strain in the feet or knee joints due to trauma can be shown as the most common causes of sciatic pain.
We can list the following as other causes of sciatica pain encountered in society:
- The weakening of muscles, bones or tissues around bones is generally due to changes in the spinal cord due to advancing age. This may cause the discs to herniate and result in bone spurs. All of these may pave the way for sciatica pain.
- Obesity or being above the body’s ideal weight increases the pressure accumulated on the spine. Spinal changes that occur with this pressure cause sciatica.
- Traumatic situations such as accidents can cause sciatic nerve compression.
Driving for a long time means being exposed to vibration for a long time. This is one of the causes of sciatica. - Carrying heavy loads or sudden changes in direction of the back trigger sciatica.
- Individuals who work sitting for long periods of time or have a sedentary lifestyle are likely to develop sciatica.
Damage to the nervous system may occur due to diabetes. The nerve damage in question can also occur in the sciatic nerve. - Weight gained during pregnancy can put pressure on the sciatic nerve. Especially the growth of the breasts and abdominal area causes the body’s center of gravity to change. This can increase the pressure on the sciatic nerve, causing nerve compression.
What Medical Problems Cause Sciatica Pain?
-
Lumbar Disc Herniation:
The most common cause of sciatica (90%) is a herniated disc. A herniated disc can directly compress the spinal nerve root that forms the sciatic nerve, causing pain. Additionally, sometimes an acidic chemical can leak from inside the disc, causing inflammation and irritation around the sciatic nerve.
-
Spinal Canal Narrowing (Lumbar Spinal Stenosis):
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spinal canal (spinal cord in the lower back). It is more common over the age of 60.
-
Waist Slippage (Spondylolisthesis):
Sometimes one vertebra slides forward over another due to a minor stress fracture or severe trauma. This compresses the sciatic nerve, causing pain. Spondylolisthesis may also be congenital.
-
Degenerative Disc Disease:
Discs, which act as cushions between the vertebrae, wear out over time and lose their protective properties due to age. As a result, they can compress or irritate the sciatic nerve.
-
Cauda Equina Syndrome:
It is a rare condition that usually requires surgical emergency intervention.
It affects the nerves in the lower part of the spinal cord. And it can lead to urinary or fecal incontinence or permanent paralysis of the legs.
-
Piriformis Syndrome:
It occurs as a result of involuntary contraction of the piriformis muscle, which connects the lower part of the spine to the thigh bones. Piriformis syndrome can put pressure on the sciatic nerve, causing pain. It is a rare condition.
Sciatica occurs as a result of damage or injury to the sciatic nerve. Pain extending from the waist area to the hip area and legs is typically sciatica.
What are The Symptoms of Sciatica (Nerve Compression)?
Different symptoms may also occur along with pain:
- Pain radiating from the hip and back of the thigh to the leg (the most common and obvious complaint).
- Tingling, numbness or weakness in the lower leg and foot,
- Feeling like needles are sticking in the heels and toes,
- Loss of sensation and difficulty in movement,
- Symptoms increase when sitting (the sciatic nerve is stretched), and symptoms decrease when standing up.
- Pain that worsens when moving, coughing or sneezing,
- Urinary and gas incontinence,
- Difficulty in standing upright, bending and turning movements,
- In later cases, thinning of painful leg muscles.
What are The Types of Sciatica (Nerve Compression) Pain?
There are different types of sciatica pain. These types are also effective in determining the treatment.
-
Acute Sciatica
It is a term used for sciatica pain that is in its initial stages. It is used for sciatica pain that lasts between 4 and 8 weeks. The pain is mild and does not require treatment.
-
Chronic Sciatica
It is used to indicate cases where sciatic pain lasts longer than 8 weeks and the intensity of pain does not decrease. Patients need to be treated because they have persistent sciatica pain.
-
Alternative Sciatica
In alternative sciatica, both legs are affected. Although it is one of the rare types of sciatica, it is generally seen due to degenerative problems in the joints.
-
Bilateral Sciatica
It is the name given to sciatica pain that occurs in both legs at the same time. Although it is one of the rare sciatica pains, it usually occurs due to serious health problems such as degenerative changes in the vertebrae or disc or caudo equina syndrome.
How is Sciatica (Nerve Compression) Diagnosed?
The doctor first reviews the person’s medical history. Then he will ask about your symptoms.
During the physical examination, the doctor asks the person to walk to see how his spine is supporting his weight. The patient may be asked to walk on his toes and heels to check the strength of the calf muscles.
The doctor may also perform a straight leg raise test. For this test, you lie on your back with your legs straight. The doctor slowly lifts each leg. And notes the point where the pain begins.
This test helps pinpoint the affected nerves. And it reveals if there is a problem with one of the disks. Your patient will also be asked to do other stretches and movements to pinpoint pain and check muscle flexibility and strength.
The doctor may order imaging and other tests depending on what they discover during the physical exam.
These are as follows:
Spinal X-Ray:
It looks for spinal fractures, disc problems, infections, tumors and bone spurs.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) or Computed Tomography (CT):
Scans are taken to see detailed images of the bones and soft tissues of the back.
An MRI can show pressure on a nerve, disc herniation, and any arthritic condition that puts pressure on a nerve. MRIs are often ordered to confirm the diagnosis of sciatica.
Nerve Conduction Velocity Studies/Electromyography (EMG):
It examines how well electrical impulses travel along the sciatic nerve and the response of the muscles.
Myelogram:
It determines whether the vertebra or disc is causing the pain.
What are The Sciatica (Nerve Compression)Treatment Methods?
Sciatica treatment is planned according to the cause of nerve compression and the general health condition of the patient. For the treatment to be successful, it is important to start the treatment early. Both surgical and non-surgical methods are used to treat sciatica.
Non-Surgical Methods
Medication:
Medications such as painkillers and muscle relaxants can help relieve sciatica symptoms.
Physiotheraphy:
The aim of physical therapy is to reduce the pressure on the nerve with personalized sciatica exercises.
In this treatment;
Stretching exercises or low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming and water aerobics can be performed.
In addition, manual therapy, posture training and ergonomic adjustments can be made to reduce pain and increase mobility.
Cold and Hot Application:
Applying cold is effective in relieving sciatica pain and reducing swelling.
You can use an ice bag for this.
However, you should wrap the ice pack with a towel to avoid ice burns on your skin.
Applying it several times a day for 20 minutes will be enough.
After applying cold for a few days, you can switch to hot application.
You can apply it in the same way several times a day for 20 minutes.
Spinal Injections:
In cases of severe pain and inflammation, corticosteroid injections may be given to reduce inflammation around the nerve.
Local (regional) anesthesia is used in these injections. Its effect usually lasts up to 3 months. And it can be applied maximum 3 times in a year.
Surgical Methods
Sciatica Surgery:
Surgery to treat sciatic pain is usually considered for patients who do not respond to other treatment methods (medication, physical therapy, injections) or show signs of severe nerve damage (loss of bladder or bowel control, severe motor loss).
Problems that cause sciatica are usually related to the spine. Therefore, surgery often targets specific spine problems.
The two main sciatica surgery methods are: Discectomy and Laminectomy.
Discectomy:
In this procedure, the surgeon removes the part of the disc pressing on the sciatic nerve that touches the nerve. However, sometimes it may be necessary to remove the entire disk. The operation is performed with general anesthesia. And the patient can go home the same day.
Laminectomy:
The lamina is the back part of the spine that covers the spinal cord. During the operation, the surgeon removes the lamina and tissues that put pressure on the sciatic nerve. It is done with general anesthesia. And it may take about 2 hours.
What Should Sciatica Patients Pay Attention to?
Sciatica patients must take certain precautions to manage symptoms and reduce the severity of pain.
Some important points that sciatica patients should pay attention to are listed below.
Correct Posture
When sitting or standing for long periods of time, it is important to maintain correct posture. Ergonomic chairs and appropriate sitting positions should be used to support the spine and reduce pressure.
Regular Exercise
Regular light exercises help strengthen the spine and abdominal muscles. Low-impact activities such as swimming, walking and pilates may be preferred.
Flexibility Exercises
Regular flexibility and stretching exercises can help reduce muscle tension and relieve nerve pressure.
Weight Control
Maintaining a healthy body weight reduces the load on the spine. And it can relieve sciatica pain.
Avoiding Heavy Lifting
Lifting heavy objects puts extra stress on the spine. If you have to lift, it is important to use correct techniques and engage your leg muscles.
Sleeping Position
It is important to keep the spine in a natural position while sleeping. Lying on your side and placing a pillow between your knees can provide support for the spine.