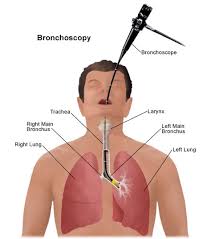
What is Bronchoscopy?
Bronchoscopy is a procedure that can help diagnose and treat problems in the lungs and airways. It is usually performed using local anesthesia. In rare cases, general anesthesia may be required. In the bronchoscopy procedure, the lungs and airways are examined with a thin, plastic camera tube.
Why is it Done?
- Any infection in the lung (especially pneumonia in smokers)
- Cough that does not go away despite treatment,
- Biopsy from lung tissue,
- Suspicion of a tumor in the lung and removal of a piece from the tumor
- Clearing mucus or removing a blockage such as a tumor,
- Placement of a stent (a small tube) in the airway to keep the blocked airway open,
- In case of bleeding in the lung, locating and stopping the bleeding,
- Biopsy from lymph nodes near the lungs,
- Bronchoscopy can be performed to remove foreign bodies blocking the respiratory tract.
How is Bronchoscopy Done?
- Local anesthetic spray is applied to the nose and throat during bronchoscopy. Also, the doctor may prescribe a sedative to help the patient relax. Oxygen is usually given during this administration. General anesthesia is very rarely required
- After the patient is relieved, the doctor places the device in the nose area. The device reaches the bronchi by passing through the nose and throat.
- Brushes or needles may be attached to the bronchoscope to take tissue samples from the lung. These samples can help the doctor diagnose any lung disease that may be present.
- The doctor may also use a process called bronchial washing to collect cells. This is done by spraying the saline solution onto the surface of the airways. Cells washed from the surface are then collected and examined under a microscope. If the airways are blocked, a stent may be needed to keep it open.
- A stent is a small tube that can be inserted into the bronchi with the device. When the doctor finishes examining the lungs, he removes the device again and finishes the procedure. After this procedure, it is necessary to avoid eating or drinking anything for 1.5-3 hours.
- This test can take an average of 25-30 minutes. After the test, breathing and blood pressure are monitored for a while. There may be temporary pain, hoarseness and wheezing in the throat area for a few days. No medication is needed for these symptoms.