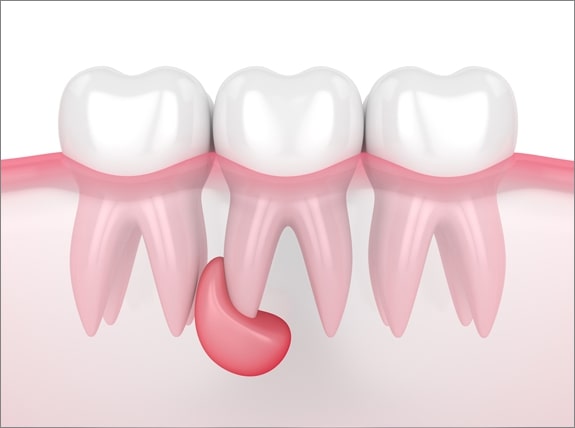
What is a Dental Cyst?
Dental Cyst is among the dental diseases and is noticed by the dental problems and eating disorders that occur in the person. Although cystic structures occurring in the teeth are a negative situation for patients, treatment should be started as soon as they are noticed.
Rather than containing inflammation, a dental cyst consists of fractures and small decays remaining inside the tooth. In addition, there are also substances such as air, water and semi-liquid. These form dental cysts over time. Cyst formation on teeth is a condition that can occur after a long time.
These dental cysts, which form over time, cause severe damage to the teeth later on. There are many methods used for this procedure, which prevents negative situations with early treatment. This service, which is offered at a very affordable price, gives 100% positive results and dental cyst procedures are performed at very advantageous prices.
What Causes Dental Cyst?
There may be various reasons for dental cyst formation.
Here are some common causes of dental cysts:
-
Infections:
Oral infections, such as tooth decay or gum infections, can cause dental cysts to form. Infections occur when bacteria reach the inside of the tooth or under the gum and can lead to the formation of a fluid-filled sac.
-
Tooth Root Inflammation:
A tooth root inflammation or abscess can cause damage to the surrounding tissues and the formation of a dental cyst. This situation usually occurs as the infection inside the tooth progresses.
-
Complications of Dental Root Canal Treatment:
During dental root canal treatment, it is important to remove all infected tissue and bacteria. However, in some cases, complete cleansing may not be achieved and the infection may recur. This may lead to dental cyst formation.
-
Dental Injuries:
Traumas or injuries to the teeth may cause a cyst to form inside the tooth. As a result of the injury, the tissue inside the tooth is damaged and the formation of a fluid-filled sac may begin.
-
Missing Teeth:
If a tooth is extracted or lost and is not replaced by a new tooth, a cyst may form under the gum. This occurs because there is no tooth that needs to fill the gap.
Dental cysts are usually painless, and symptoms can be difficult to notice. Therefore, it is important to diagnose dental cysts early with regular dental examinations and x-rays.
What are The Symptoms of Dental Cyst Disease?
Cavities in the teeth, which are the main causes of cysts, are often not noticed by the patient.
If the person does not go for dental check-ups regularly, this disease is not detected until the cavities reach the pulp and cause discomfort, and cysts are not noticed until they reach advanced stages.
Cyst symptoms begin suddenly, it is recommended that the patient not delay treatment, otherwise it may greatly affect daily life.
If there is a constant and throbbing pain in the tooth, if pain is felt when chewing something, or if sensitivity to hot and cold foods begins to occur, the presence of a cyst may be considered.
-
Pain:
Dental pulp contains all the nerve and blood cells that keep the tooth alive. When the bruise reaches here, pain will begin to appear. The pain of cyst inflammation hits suddenly. This sudden pain can be seen in more than one area. Pain can also be seen on the cheek, chin, and face. This pain, which soon becomes severe, forces the patient to go to the dentist urgently. Many patients may not understand which tooth is the diseased one. The diseased tooth can be found by biting the teeth in the painful area separately with the help of a stick.
-
Swelling in The Area Where it Occurs:
One of the symptoms of cysts is swelling. Swelling occurs in the gums around the diseased tooth. These swellings also cause pain. While we can see the swelling in the gums, we can also see it occurring in the chin area, cheeks and certain parts of the face.
-
Bitter Discharge into the Mouth:
Having bitter discharge in the mouth may also be a symptom of a dental cyst. It is recommended that people who complain about this condition undergo a dental examination.
-
Nerve Entrapment:
As cysts grow, they put pressure on the nerves, and as a result of this pressure, nerve compression may occur. Nerve compression causes numbness around the mouth and face. The person experiencing this complaint should go to the oral and dental center as soon as possible.
-
Loosing Tooth:
As the dental cyst progresses, swellings occur in the soft tissue around the roots. These swellings expose the tooth and bone structure to displacements. This both exacerbates the pain and creates the appearance of a loose tooth.
-
Decay in the Tooth Area:
Decay on the tooth is the most basic element of cyst formation. If a person has many decaying teeth, precautions should be taken. He/she should have the cavities treated and then pay attention to oral hygiene. It is necessary to remember that each cavity can be the starting point of infection and to make appointments with the dentist at regular intervals in order to minimize the possibilities. In addition, daily dental cleaning should not be interrupted to reduce the risk of cyst formation.
-
Inflammation at The Root Tip:
Over time, inflammation in the tooth root gives way to cyst formation. If an infection is encountered at the root tip, it is essential to get treatment as soon as possible.
What are The Types of Dental Cysts?
-
Periapical Cysts:
Periapical cysts, which form at the tips of tooth roots, are quite dangerous. When it is not treated early or is not done early, it immediately turns into a dental cyst. If these cysts, which occur due to infections in the teeth, are not treated, they cause jaw and tooth problems.
-
Dentigerous Cysts:
Dentigerous cysts, which are frequently encountered after periapical cysts, are generally noticed during routine dental checkups and treated. These types of cysts occur after impacted teeth, do not cause much discomfort in the teeth, and are usually asymptomatic.
-
Lateral Periodontal Cysts:
This type of cyst, which generally appears as a callus, is not widely known.
This type of cyst, which does not have much effect on the person, generally occurs in adults and in some parts of adults.
And this type of cyst, which is clinically symptomless, causes the person to experience swelling.
-
Residual Cyst:
This type of cyst, which can be easily concluded in the dentist’s chair, is a condition that occurs after a person’s teeth are not cleaned properly after the procedure. The treatment method for this procedure, which occurs especially after tooth extraction with chronic infection, is quite simple. This cyst only occurs as a result of the lesioned area not being cleaned properly.
-
Rash Cyst:
Rash dental cyst is a form of dental cyst that occurs throughout the teeth. This situation has become quite common and is becoming more common every day. While some of the treatments are done early, some are late.
What are The Harms of Dental Cysts?
-
Printing on Tissues:
As a dental cyst grows, it can put pressure on surrounding tissues and weaken the bone tissue around the tooth.
-
Tooth Loss:
Progression of the cyst may damage the root of the tooth, causing tooth loss.
-
Inflammation:
The cyst may become inflamed due to fluid accumulation and may cause discomfort in the mouth.
-
Aesthetic Problems:
Swelling or swelling in the facial area can negatively affect the aesthetic appearance.
-
Environmental Tissue Damage:
The growth of the cyst may damage adjacent teeth or jawbone.
-
Cyst Rupture:
In case of cyst rupture, there may be a risk of infection spreading to surrounding tissues.
-
Complications:
Untreated cysts can lead to more serious complications.
When symptoms of dental cysts are noticed, it is important to start the treatment process by consulting a dentist. Early intervention helps prevent harm and is important for the patient’s health.
What are The Treatment Methods?
Dental cyst treatment may vary depending on the cyst size, location, and symptoms. Small and painless cysts usually do not require treatment and are simply kept under regular monitoring. However, large or symptomatic cysts may require surgical intervention.
-
Cyst Removal:
Small cysts can usually be removed surgically. This procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia and allows complete removal of the cyst.
-
Root Canal Treatment:
If the cyst is caused by an infection in the tooth roots, root canal treatment may be applied. This treatment can help eliminate the infection and heal the cyst.
-
Tooth Extraction:
In some cases, the tooth affected by the cyst may need to be extracted. This may be necessary to prevent the cyst from recurring.
-
Medication:
In some cases, medication may be administered to reduce the size of the cyst or control the infection.
Dental cyst treatment is usually successful and the risk of complications is low. However, regular follow-up and control are important during the treatment process. Untreated dental cysts can damage surrounding tissues and lead to infections.
Dental Cyst Surgery
In order to prevent pain or feelings of pain during dental cyst surgery, local anesthesia is among the preferred methods as an alternative to general anesthesia.
The type of surgery varies depending on the type and size of the cyst and the characteristics of the patient.
If the size of the cyst is very large, the size of the cyst can be reduced by installing a drain (a tube that allows fluid and tissue fragments to be transferred from the wound to the outside) before surgery.
Preoperative antibiotic treatment is generally recommended for prophylactic purposes. During the procedure, the gum is surgically cut and the cyst located in the inner layer is cleaned without interfering with the surrounding tissues.
Since it is a sensitive area, it is important to protect the neural network. After the surgery, the gum is stitched and the dental cyst surgery is completed.
What Should Be Taken İnto Consideration After Dental Cyst Surgery?
After dental cyst surgery, there are procedures that the patient must undergo and some points to pay attention to:
-
Hospital Stay:
Patients can usually expect to go home after recovery. In some cases, patients may need to stay in hospital overnight, depending on the situation.
-
Return to Work/School:
Generally, a rest period of 2 days to 2 weeks may be required. This period may be shorter or longer depending on the type of surgery.
-
Physical Activity:
The patient can start light physical exercise as soon as he feels well. However, activities that put the mouth and jaw at risk should be avoided. This includes all contact sports.
-
Nutrition:
A soft diet is recommended for the first 2 weeks after surgery.
-
Pain Control:
The doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory or opioid painkillers. In this way, the patient can control pain and discomfort after surgery.
-
Swelling:
Swelling is a normal side effect of surgery, but the degree varies between individuals. You may experience the most swelling during the 3-5 days after surgery.
-
Wound:
Most such surgeries are performed inside the mouth. Although there may be no obvious scarring, in some cases there may be small cuts. That’s why it’s important to avoid very cold and hot things for a while.