Tonsil Surgery (Tonsillectomy)
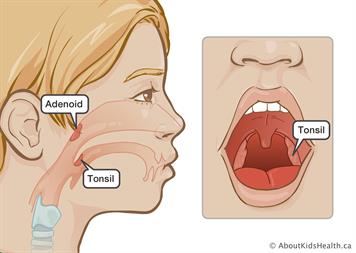
Tonsils are structures located on both sides of the throat in the back of the tongue. Their job is to protect the body against microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses.
However, if the tonsils are larger than normal or are frequently infected / inflamed, various problems may occur. Frequent recurrent tonsillitis; Growth retardation, heart rheumatism, kidney inflammation and diseases affecting joints can cause serious health problems in children.
The tonsils that are bigger than necessary are; sleep apnea and associated snoring can lead to problems such as bad breath, attention disorder, irritability, depression, daytime sleepiness.
Who can have Tonsil Surgery?
Tonsil surgery in cases when the tonsil has become obstructive and has suffered tonsillitis at least once a year; tonsillectomy with its name in medicine is recommended.
Tonsil surgery can be performed in children over 4 years old and adults. Tonsil surgery can also be performed in children under 4 years of age in some of the following situations:
If inflamed tonsils are observed at least 7 times in 1 year
In case of large tonsils that reach obstructive size that cause breathing in sleep, surgery
How is Tonsil Surgery performed?
Tonsil surgery is performed under general anesthesia. The method called “thermal welding” has been used frequently in recent years. With this method, tonsils can be removed without bleeding. In addition, no stitches and very low postoperative pain are among the important advantages.
After Tonsil Surgery
Patients are discharged the same day after tonsil surgery. One day after the operation, patients can return to their normal lives.
Eating can be started 2 hours after the operation. Soft foods; Puree, warm soup, vegetable dishes, fruit puree, pudding and ice cream are among the preferred foods.
Does the body defense system weaken after Tonsil Surgery?
Tonsils are structures that work in the defense system. However, taking them by surgery does not cause the immune system to weaken. Many lymphoid organs in the throat and upper respiratory tract take the role of the removed tonsils.