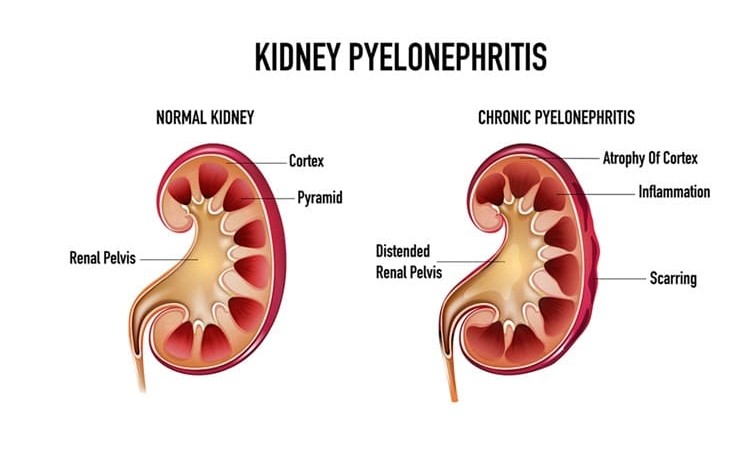
What is Kidney Inflammation (Pyelonephritis)?
Kidney inflammation, also known as “pyelonephritis,” is an infection of the kidneys. This condition occurs when bacteria reach the kidneys through the urinary system and cause infection there. Infection usually originates from the urinary tract and may occur due to reflux of urine into the kidneys.
Kidney inflammation usually results from primary urinary tract infections (bladder infections). Bacteria reach the kidneys from the bladder using the urinary channels called ureters and cause infection there. Rarely, infection from another part of the body can spread to the kidneys through the blood.
This condition can usually affect one or both kidneys. Pyelonephritis can lead to serious complications and impair kidney function if left untreated or if recurrent infections occur.
What are The Types of Kidney Inflammation (Nephritis)?
What is Glomerulonephritis?
Filter-like structures that filter blood in the kidneys are called glomerulus. Inflammation of these structures is called glomerulonephritis.
Acute Glomerulonephritis: It is the sudden onset of inflammation and lasting less than 3 weeks.
Chronic Glomerulonephritis: It occurs slowly and lasts longer than 3 weeks.
Membranous Glomerulonephritis: It is one of the types of Glomerulonephritis. Membranous glomerulonephritis develops due to inflammation in the kidney or deterioration of kidney functions. It is more common between the ages of 30-50. Diagnosis is made by kidney biopsy.
Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis: It is another type of glomerulonephritis and is a disease mostly seen in children. It occurs as a result of the accumulation of immune proteins in the kidneys in systemic diseases in the body. Diagnosis is made by kidney biopsy.
What is Interstitial (Tubulointerstitial) Nephritis?
The structures that reabsorb important substances such as protein and water from the blood filtered in the kidneys are called tubules.
The disease that causes swelling and inflammation in the tubules of the kidneys is called interstitial nephritis or tubulointerstitial nephritis. If the disease develops suddenly and lasts less than 3 weeks, it is called acute interstitial nephritis, and if it lasts longer than 3 weeks, it is called chronic interstitial nephritis.
What are The Causes of Kidney Inflammation (Nephritis)?
Causes of Pyelonephritis
Most cases of pyelonephritis occur after the E.coli bacteria causes disease in the body. This type of bacteria is normally found in the large intestines and is excreted in the feces. This bacteria causes disease in the urinary tract and causes damage to the kidneys, resulting in pyelonephritis.
Although bacterial infection is the most common cause of pyelonephritis, there are other causes:
- Examination of your urinary tract with an instrument called cystoscope
- Bladder (urinary bladder), ureter (urinary tract) and kidney surgery
- Reasons such as stone formation in the kidneys and urinary tract may also cause pyelonephritis.
Causes of Glomerulonephritis
The main cause of glomerulonephritis is often not clearly known.
Some of the following reasons may cause glomerulonephritis:
- Long-term inflammatory diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus can cause glomerulonephritis.
- Diseases that lower the immune system or drugs that lower the immune system.
- Vascular diseases such as vasculitis can cause glomerulonephritis.
- An infection that progresses to the kidneys through the blood or an abscess in the kidneys may cause glomerulonephritis.
Causes of Interstitial (Tubulointerstitial) Nephritis
- Interstitial nephritis is usually caused by an allergic reaction to a drug or antibiotic. An allergic reaction is the response of the body’s immune system to a foreign substance, such as drugs.
- Lower than normal potassium electrolyte in the blood is another cause of interstitial nephritis. Potassium is necessary for many events in the body, such as regulating heartbeat and metabolism.
- Long-term use of certain medications, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics, may cause interstitial nephritis.
What are The Symptoms of Kidney İnflammation?
Kidney inflammation, namely pyelonephritis, usually occurs as a result of a urinary tract infection spreading to the kidneys.
The symptoms that occur in this case may be:
-
Back Pain:
Since the kidneys are located behind the waist area, localized pain in the back may occur as a result of inflammation. These pains are often felt in one or both kidney areas.
-
High Fever:
High fever (38°C or above) may occur as the infection spreads throughout the body. Body temperature rises as a systemic response caused by inflamed kidneys.
-
Shivering and Chills:
There may be chills and chills along with high fever. The body may try to warm up with shivering while fighting off the infection.
-
Nausea and Vomiting:
Some people may experience nausea and vomiting during kidney inflammation.
-
Urine Changes:
Changes in the color and odor of the urine may be observed. Urine can often be cloudy, dark and foul-smelling. Additionally, blood may be seen in the urine.
-
Frequent and Urgent Urination:
Inflamed kidneys can irritate the urinary tract, causing a frequent and urgent need to urinate.
-
Stomach Ache:
Kidney inflammation can sometimes cause pain in the abdominal area.
-
Fatigue and Weakness:
The body fighting the infection may react with feelings of fatigue and weakness.
Symptoms of kidney inflammation may vary from person to person, and in some people the symptoms may be milder, while in others they may be more pronounced.
Since these symptoms may indicate other health problems besides kidney inflammation, it is important to consult a healthcare professional if in any doubt.
Early diagnosis and treatment will help prevent serious complications.
Who is Seen in it And Who is More Prone To it?
Glomerulonephritis:
- Although certain types are seen especially in male or female patients of certain age groups, they can occur in all age groups.
- Those whose throat or skin is infected with streptococci and is not treated,
- Those who have intravenous (intravenous) medication or drug habit,
- Rheumatic heart valve patients, smokers
- And those with certain rheumatological diseases, especially SLE (Lupus)
- More prone to the development of certain types of glomerulonephritis.
Pyelonephritis,
Although it is seen in all ages and genders;
- Women,
- Patients who prevent easy urination, especially prostate and stone patients,
- Patients with urine leakage from the bladder back to the kidneys (vesicoureteral reflux) due to functional or anatomical disorders in the urinary tract,
- Those with pre-existing kidney failure,
- Kidney transplant patients and patients with a urinary catheter are more prone to the development of pyelonephritis.
Interstitial (Tubulointerstitial) Nephritis
- It can be seen in all ages and genders.
- It is more common, especially in those who use antibiotics and painkillers without the supervision of a physician.
Diagnosis of Kidney Inflammation
When diagnosing Kidney Inflammation, knowing the symptoms of the disease will be very useful for the diagnosis of the disease. To diagnose the disease, the doctor follows certain steps.
-
Story:
It is important when the symptoms of the disease begin and how long they last. If you have a persistent disease or have had a disease, and the medications you have used recently are information that will help diagnose the disease.
-
Physical Examination:
Being able to control the symptoms of the disease is very useful in making a diagnosis. First of all, the patient’s feet and hands are checked for swelling, and the leg is examined to check for edema.
Heart sounds are listened to to understand whether the heartbeat speed and regularity are disrupted.
To measure blood pressure, the patient is seated and his/her blood pressure is measured.
Laboratory Findings:
After the physical examination, some blood and urine tests are requested.
Laboratory tests can help us understand whether the disease is due to an infection. These tests are blood tests, bacterial cultures and urinalysis.
-
In Urine Analysis:
Demonstration of white blood cells (WBC) is a finding supporting infection.
-
In Blood Test:
There are two important indicators in evaluating kidney functions. These are blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine values.
These are waste products circulating in the blood. And the kidneys are responsible for filtering them and removing them from the blood.
If there is an increase in these values, it may indicate that the functions of the kidneys are affected and are not working as well as before.
Imaging Methods
Ultrasound and computed tomography can be used.
-
Ultrasonography:
Ultrasound is used to measure blood flow in the vessels of the kidneys and to visualize the patency of the urinary tract. In order to visualize the urinary tract with ultrasonography, high-frequency sound waves are sent to the place where the vein is located, and as the sound waves are reflected back, the condition of the kidney and urinary tract is reflected on the computer screen.
-
Computed Tomography:
Computed tomography can be used as a further examination if the diagnosis is not certain. Before the computed tomography procedure, contrast material is administered to the patient intravenously. Computed tomography can show whether the kidneys and urinary tract are blocked or whether the kidneys are inflamed.
-
Kidney Biopsy:
A kidney biopsy can be performed for a definitive diagnosis of the disease. Kidney biopsy is not a procedure that should be performed on every patient. It is performed only on patients who require further examination.
Kidney biopsy is performed by examining a piece of the patient’s kidneys with a needle and examining it under a microscope. For this, the patient lies on his back on the stretcher. The area where the needle enters is numbed with local anesthetic. Then, with the help of ultrasound, he inserts a needle into the kidney and removes a piece of it.
What are The Treatments for Kidney Inflammation?
Kidney inflammation (pyelonephritis) is usually treated with antibiotics.
Treatment may vary depending on the severity of the infection, the severity of symptoms, and the person’s health condition.
Treatment of kidney inflammation may consist of the following methods:
-
Antibiotics:
Antibiotics are used to treat inflammation caused by the bacteria caused by the infection. Before starting treatment, a urine culture can be performed to determine which antibiotics are effective against which bacteria to use. Treatment can usually take 10-14 days. It is important to use antibiotics regularly for their full duration, otherwise the infection may return or resistant bacteria may develop.
-
Fluid Intake:
Drinking plenty of fluids helps the kidneys fight infection and increases the excretion of bacteria through urine.
-
Pain and Fever Medicines:
Painkillers and antipyretics may be used to relieve symptoms such as back pain and fever. However, using medication should be avoided without consulting your doctor.
-
Hospital Treatment:
In some cases, hospitalization may be required if the infection is severe, the person’s immune system is weak, or oral antibiotics are not possible.
In the hospital, stronger intravenous antibiotics may be given and the patient’s condition may be monitored closely.
-
Treatment of the Underlying Cause:
If there is an underlying cause of kidney inflammation, for example, an anatomical problem that causes urinary tract infections or urinary reflux, this cause must also be treated.
It is important to cooperate with your doctor during the treatment process and use the prescribed medications regularly. Additionally, following your doctor’s instructions and attending follow-up appointments after treatment will help monitor your recovery. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to preserve kidney function and prevent serious complications.