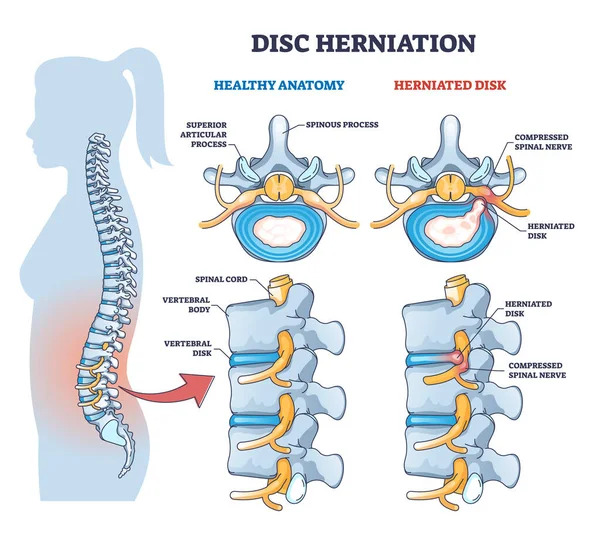
What is Herniated Disc (Lumbar Disc Herniation)?
A herniated disc is a condition characterized by nerve compression resulting from the rupture of discs in the spinal cord region. This condition usually causes severe lower back pain and pain radiating down the leg. Hernia can occur at any level of the spine.
The main reason for herniated disc is the rupture of the ring-shaped ligamentous structure at the back and its contents being transported through this tear into the canal. This is a condition associated with the aging process. Additionally, sudden movements and strain can also cause a herniated disc. Lifting particularly heavy objects can put a lot of pressure on the lumbar vertebrae, increasing the risk of a hernia. So you have to be careful.
What are The Causes of Herniated Disc (Lumbar Disc Herniation)?
- Obesity: Excessive weight is one of the most important causes of herniated disc. Our spine carries the weight of our body. Exposure to excessive pressure on the discs, which provide the flexibility of the spine and serve as a kind of support cushion, causes them to become deformed and deformed. The herniated disc, which loses its normal shape and bulges outward, affects the functions of the nerve it presses on, causing various signs and symptoms. During pregnancy, the body’s center of gravity shifts forward, causing additional load on the spine.
- Not acting in accordance with spinal physiology in daily life
- Overweight and sedentary life
- Smoking as it causes dehydration
- Injuries
- Making movements suddenly
- Those who are drivers by profession
- Those who work at a desk job
- Pregnancy
- Factors related to the profession:
- Professions that require heavy physical activity and heavy lifting. (Ex: Construction workers),
- Professions that require constant bending forward and bending over; Occupations that expose the body to constant vibration, such as driving a car, bus, truck, etc.
- Professions that require standing or sitting for long periods of time,
- The frequency of lower back pain and herniated discs increases in people who engage in football, weightlifting, rowing and wrestling sports.
What are The Symptoms of Herniated Disc (Lumbar Disc Herniation)?
A herniated disc is a disorder that causes severe pain in the lower back region and symptoms such as numbness and weakness in the legs due to damage to the intervertebral discs.
The symptoms of a herniated disc are explained below:
Severe Lower Back Pain:
The most common hernia symptom is severe lower back pain. The pain is concentrated in the lower part of the spine in the lumbar region. And it is often felt unilaterally.
Numbness and Tingling in Legs:
The herniated disc puts pressure on the surrounding nerves, causing numbness and tingling in the legs. This condition occurs together with lower back pain. It usually occurs in the direction of spread of the pain.
Weakness in Legs and Feet:
The disease can interfere with the normal function of the muscles in the legs and feet, causing weakness. For this reason, the patient may have difficulty lifting weights, walking or standing.
Urinary and Bowel Problems:
In severe cases of a herniated disc, problems with urination and controlling bowel movements may occur due to pressure on the spinal cord or nerves. This situation may require urgent medical attention.
Difficulty Standing and Sitting:
People with a herniated disc may have difficulty standing or sitting for long periods of time. Symptoms usually increase with movement and relieve with rest.
Increased Pain During Coughing and Sneezing:
A herniated disc can cause increased pain when coughing, sneezing, or strenuous movement. This is a sign that the pressure on the spine and nerves has increased further.
The severity of symptoms can vary depending on the size of the herniated disc, where the pressure is applied, and the person’s overall health.
Symptoms provide important clues to diagnosing a herniated disc, so it is important for people aware of the symptoms to see a specialist. Early diagnosis and proper treatment can help alleviate problems caused by a herniated disc and speed up the healing process.
How is Herniated Disc (Lumbar Disc Herniation) Diagnosed?
During the physical examination, the doctor evaluates your pain, muscle reflexes and muscle strength.
Following physical examination, the following methods are used to diagnose a herniated disc:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
The most common and accurate imaging test for suspected herniated disc is MRI.
X-Ray:
The aim of X-ray is to quickly evaluate and monitor conditions such as back pain, bone fractures and spinal misalignment.
Computed Tomography (CT):
It is an imaging scan that uses X-rays and computer technology to produce images of the body.
CT Scan shows detailed images of any part of the body, including bones, muscles, fat and organs.
Myelogram:
Myelogram involves injecting dye into your spine using X-ray guidance for a CT scan. Dye can reveal narrowing of the spinal canal (spinal stenosis) and the location of your herniated disc.
Electromyogram (EMG):
EMG is a test that measures muscle response, or electrical activity, in response to a nerve stimulating a muscle.
What Should Be Taken İnto Consideration to Prevent a Herniated Disc?
The first step to preventing a herniated disc is weight control. Excess weight can put extra pressure on the lumbar vertebrae, increasing the risk of a herniated disc. Additionally, it is important to adopt an active lifestyle. Disc herniation is less common in individuals who exercise regularly, especially in those with strong waist and abdominal muscles. Because not only the spine but also the abdominal muscles carry the load of our body. Therefore, regular exercise, strengthening the muscles and ensuring proper support of the spine can reduce the risk of herniated disc.
It is important to pay attention to spine health in daily life to prevent herniated disc. For example, when lifting something from the floor, it is important to bend the knees and lift in a squatting position. This helps avoid putting extra pressure on the spine. Additionally, it is important to receive training in correct lifting techniques and spine health from childhood. Additionally, children should be taught to make waist exercises a habit.
It may not always be possible to prevent a herniated disc, but the following steps can be taken to reduce the risk:
- Using correct techniques when lifting weights.
- Maintaining a healthy body weight.
- Developing correct body posture, especially when walking, sitting, standing and sleeping.
- Doing stretching exercises after sitting for a long time.
- Not using high-heeled shoes.
- Doing regular physical activity to strengthen back and waist muscles.
- Quitting tobacco use.
- Adopting a balanced eating habit.
What are The Risk Groups for Herniated Disc?
- Those with a family history of a herniated disc,
- Those who are overweight,
- Smokers,
- Those who lift heavy or do sports by lifting heavy,
- Those who have experienced major trauma such as a traffic accident or a fall,
- Wrong exercises,
- Those who work sitting for long periods of time.
In Which Age Group is Herniated Disc (Lumbar Disc Herniation) More Common?
- It is more common in the 30-35 age group.
Can People with a Herniated Disc (Lumbar Disc Herniation) Do Sports?
The ability of people with a herniated disc to do sports may vary depending on the severity of the hernia, its location, and the person’s general health condition. But in general, people with a herniated disc are recommended to do some sports and physical activities, while avoiding others.
Sports and Activities You Can Do:
-
Swimming:
Swimming is an excellent exercise that works the spine and muscles without creating extra load due to the water supporting the body.
-
Walking:
Walking, a low-impact and simple cardio activity, is generally a safe and recommended exercise for people with a herniated disc.
-
Pilates:
When done correctly, Pilates can strengthen core muscles and support the lower back.
-
Cycling:
Types of bicycles that support the waist, such as recumbent bicycles, may be more suitable for people with a herniated disc.
-
Stretching and Mobilization Exercises:
Stretching exercises recommended by a physiotherapist can increase flexibility and reduce pain.
Sports and Activities to Avoid:
-
Weight Lifting:
Lifting especially heavy weights can put extra pressure on the disc.
-
Running:
Running hard on the ground can create shock waves in the waist and spine, causing further damage to the herniated disc.
-
Team Sports:
Sports that involve sudden movements and contact, such as football and basketball, may be risky for people with a herniated disc.
-
Golf:
Spinning movements made during golf can create extra stress on the waist.
As a result, if a person with a herniated disc plans to play sports, they should first consult a doctor or physical therapist.
A personalized exercise program can help both maintain physical health and relieve symptoms caused by a herniated disc.
What are The Treatment Methods for Herniated Disc?
There are many methods for the treatment of people diagnosed with a herniated disc. These can be explained as follows.
Non-Surgical Treatment Methods for Disc Herniation
When low back pain occurs in society, the first aim is to relieve the patient’s pain, usually through physical exercises.
In the treatment of herniated disc without surgery;
- Manual Therapy,
- Hot-Cold Application,
- Dry Needling,
- Some Electrical Warnings,
- Ultrasonic Applications
- Some movement and regular exercises
These treatments help reduce pain.
Drug Treatment for Disc Herniation
The main drug treatment preferred to reduce low back pain is analgesic painkillers.
In cases where these painkillers do not relieve pain, both painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications may be recommended by a doctor.
These medications can be used to reduce both pain and the inflammation that causes pain. Despite these, in cases of persistent and increasing back pain, cortisone medications can be prescribed by the doctor.
Side effects of these drugs should be taken into account. If there is a situation that needs to be changed to minimize side effects depending on the side effects of the drugs, for example, nutrition-drug interactions should be taken into consideration.
The following drugs are used in the treatment of herniated disc:
Painkillers and Anti-Inflammatories:
It is used to reduce pain and retard the inflammation process in the area where nerve compression occurs.
Muscle Relaxants:
They relax the muscles in the area where nerve compression occurs and reduce the pressure.
Cortisones:
They are used systemically or locally to relieve very severe pain. Since it has many side effects, it must be administered by a doctor.
Surgical Treatment Methods for Disc Herniation
Open Standard Disc Herniation Surgery (Discectomy):
The aim of surgery is to eliminate the irritation of the herniated disc to the nerve, which causes pain and weakness. The most commonly applied method is discectomy or partial discectomy.
With this method, the herniated disc piece is removed. Sometimes the lamina, the bone behind the disc, is removed to see the disc clearly. This bone removal can be minimal (hemi-laminatomy) or extensive (hemi-laminectomy).
Some surgeons may use an endoscope or microscope. Discectomy can be performed under local, spinal or general anesthesia.
The patient is placed face down on the operating table. A small incision is made over the herniated disc and the muscles between the vertebrae are separated from the bone.
A piece of bone may be removed to see the compressed nerve. The herniated disc and loose parts are removed until the pressure on the nerve is relieved.
If there are any bone protrusions, they are also removed. Generally, there is very little bleeding in this operation.
Laminectomy:
This procedure aims to relieve the pressure on the nerves coming from the arch-shaped back part of the vertebrae (lamina).
This surgery, which can be performed through a small incision, may also require the use of a microscope.
In some cases, the removal of the lamina is called “laminectomy.”
Artificial Disc Surgery:
This surgery is performed under general anesthesia and is generally preferred in cases where a single vertebra in the lumbar region is problematic. This surgical option may not always be preferred, as diseases such as arthritis or osteoporosis may indicate that the patient has more than one disc affected. During the operation, an incision is made in the abdominal area and the problematic disc is removed and a plastic or metal artificial disc is placed in its place. Patients are usually kept under observation in the hospital for a few days after the operation.
Spinal Fusion Applications:
In this surgical procedure performed under general anesthesia, 2 or more vertebrae are permanently fixed together. Bone grafts taken from another part of the patient are used for fixation. Additionally, materials such as plates and screws can be used to support the fusion area. As a result of this method, the operated area is completely fixed. Patients are kept under observation in the hospital for a few days after the operation.
Completely Closed Disc Herniation Surgery (Full Endoscopic Discectomy Surgery):
Microdiscectomy surgery for lumbar disc herniation is traditionally performed through a two-inch incision. To access the disc space, the muscle must be peeled away from the surrounding bone. This causes some local muscle damage. And it can prolong recovery. The general purpose of this technique is quite similar to that of an open microdiscectomy. The endoscopic discectomy procedure is performed through a small tube inserted through a small hole in the skin. A special micro video camera or a microscope and special lighting are used to visualize the nerves and disc. Removal of disc material is accomplished with special microtools.
Closed Herniated Disc Surgery (Microdiscectomy):
The ‘Microdiscectomy’ procedure is a frequently used method in herniated disc surgeries, as it shortens the recovery time of patients and their return to social life.
Thanks to this method, only an incision of 1.5-2 cm is made and no stitches are placed on the skin surface after the surgery. Performing the surgery under advanced microscopes enables the nerves in the surgery area to be seen at a magnification of 25-40 times; Thus, the risk of nerve damage is extremely reduced.
List of Things to Know After Herniated Disc Surgery
- If possible, do not go up and down stairs in the first 3 days after surgery. If you have to, climb the stairs one at a time, bringing the other foot next to you.
- In the first days after surgery, pain, burning and stinging may be felt in the lower back. This situation is normal. It will go away on its own in a short time.
- Check how comfortable your mattress is and how worn it is. Choose an orthopedic mattress that is comfortable and can take the shape of your body. The idea that “sleeping on a hard bed is good for herniated discs” is not true on its own. If you have the habit of sleeping on the couch or armchair, give it up.
- Try not to put pressure on your waist when getting out of bed for the first week after the surgery. When getting up, use your hands and sit down first, then stand up.
- A toilet bowl should be used, not a Turkish toilet.
- Wear your shoes while sitting, do not bend over.
- Do not strain your waist when picking up an object from a height. Ask for help or get a stool.
- When picking up an object from the ground, do not bend over; pick it up by kneeling.
…..
- Try to find your ideal weight and stay at that weight. Excess weight is one of the factors that trigger a herniated disc.
- Use a pillow that supports your waist while sitting.
- The waist should not be sweaty or cold.
- Smoking plays a role in the formation of herniated disc. Therefore, if you smoke, it is recommended that you quit.
- Sexual intercourse should not be attempted for the first week after surgery.
- Car travel should not be done for 1 week after the surgery. It should only be used on the hospital-home-hospital route and should not be driven by oneself. Short trips can be started after 1 week. For long journeys, it is necessary to wait 1 month.
- If there is any discharge, redness or swelling in your wound area, be sure to call your doctor.