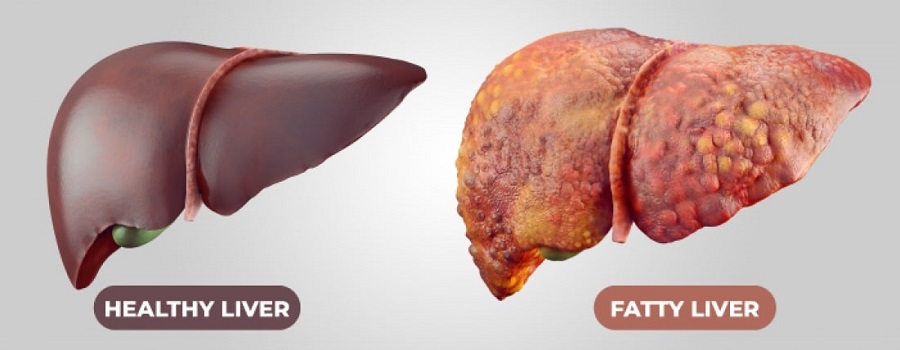
What is Fatty Liver (Hepatic Steatosis)?
Fatty liver, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition in which too much fat is stored and accumulated in liver cells.
Under normal conditions, a small amount of fat is found in the liver. However, too much causes various health problems.
The liver is the second largest organ in the human body. It helps to process nutrients from food and drink. And it cleans the blood by filtering harmful substances in the blood.
But having too much fat in the liver can damage the liver. And it can cause liver inflammation, which can form scar tissue. In more severe cases, these scar tissues can lead to liver failure.
What Causes Fatty Liver (Hepatic Steatosis)?
On the basis of fatty liver, liver cells can be damaged as a result of increased fat production in the body.
Fatty liver is basically classified as alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver. In alcoholic fatty liver disease, alcohol entering the body after long-term alcohol consumption causes damage to both the liver.
It also triggers oil production. Recycling is possible with the cessation of alcohol. In non-alcoholic (non-alcoholic) fatty liver disease, different diseases and conditions can be found.
-
Obesity:
As a result of an unbalanced and wrong diet and a sedentary lifestyle, the foods taken into the body are stored as fat. As a result, there is an increase in the fat tissue in the liver.
- Alcohol Use
-
High Blood Sugar and Diabetes:
Fat production increases when blood sugar is high due to insulin resistance, which is also known as hidden sugar among the people. And in this case, uncontrolled blood sugar rises.
-
High Blood Cholesterol:
The increase in cholesterol in the blood, which is harmful to the body, triggers an increase in the amount of fat.
-
Viral Liver Infections (Hepatitis):
In various infections such as hepatitis C, liver cells are damaged and replaced by adipose tissue.
-
Pregnancy Associated Fatty Liver:
Severe fatty liver and liver disease may occur as a result of certain mechanisms during pregnancy.
-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NASH):
Fatty liver can be seen in people who do not drink alcohol, similar to alcohol use, due to various mechanisms.
-
Autoimmune Hepatitis:
As with viral infections, the immune system perceives the liver as a threat and causes inflammation, resulting in fatty liver and liver damage.
-
Some Rheumatological Diseases:
Fatty liver is encountered in various rheumatological diseases involving the liver and biliary tract.
-
Fast Weight Loss:
Sudden and massive weight loss disrupts the cholesterol and fat balance in the body, resulting in fatty liver.
-
Poisoning with Some Chemicals:
Toxic substances such as carbon tetrachloride can directly damage and lubricate the liver.
-
Side Effects of Some Medications:
Various drugs such as amiodoron, tamoxifen, methotrexate can cause liver damage and fatty tissue.
What are The Symptoms of Fatty Liver (Hepatic Steatosis)?
The symptoms of fatty liver may not be very obvious and may not show any symptoms in the initial stages.
However, the following symptoms can be seen in the later stages:
-
Abdominal Bloating:
As the liver enlarges, there may be a bulge in the abdominal cavity.
-
Weakness and Fatigue:
Fatty liver can affect the normal functioning of liver cells, causing symptoms such as weakness and fatigue.
-
Irregular Menstrual Cycle:
Fatty liver can cause irregular menstrual cycles.
-
Dark Colored Urine:
Fatty liver can cause symptoms such as dark urine.
-
Light Colored Stool:
Fatty liver can cause symptoms such as light-colored stools.
If you notice any of these symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. Fatty liver can cause liver damage and even liver failure over time, so it’s important to take preventive measures.
What are The Types of Fatty Liver (Hepatic Steatosis)?
Fatty liver occurs mainly due to 3 different conditions. These are acute fatty liver due to pregnancy, fatty liver due to alcohol use, and simple fatty liver not related to alcohol or pregnancy. In hepatosteatosis, which is basically examined under these 3 groups, there are stages determined according to the progression level and type of the disease.
The stages of fatty liver are:
-
Stage 1:
It is the mildest stage of the disease called simple fatty liver disease. Fatty in this stage does not cause damage to the liver.
-
Stage 2:
In this stage, which is also called Non-Alcoholic (Non-Alcoholic) Steatohepatitis, inflammations occur due to fatty liver in the liver.
-
Stage 3:
In the third stage, which is the fibrosis stage, the liver tissues begin to harden and turn into connective tissue. This indicates liver damage.
-
Stage 4:
In this stage, which is the most advanced stage of fatty liver disease, the development of liver cirrhosis is in question.
Fatty Liver (Hepatic Steatosis) Mostly Occurs in Who?
This change in the liver is one of the most common diseases worldwide. Most individuals show the first signs of the disease between the ages of 40 and 60. But children and adolescents can also develop fatty liver. Almost all of those affected are overweight, often diabetic, and have high blood lipid levels.
Women are affected slightly more often than men. People with metabolic syndrome also often develop fatty liver disease. Overweight people have an 80 percent risk of developing fatty liver disease, and half of all alcoholics have fatty liver disease.
How is Fatty Liver (Hepatic Steatosis) Diagnosed?
Fatty liver disease can occur without any symptoms. It is usually diagnosed as a result of routine blood tests to check your liver.
Especially if you are obese, your doctor may suspect fatty liver in the presence of abnormal test results.
Imaging of your liver may show fatty deposits in the liver.
Certain imaging tests, including specialized ultrasound and MRI scans, can help diagnose the disease and detect scar tissue in the liver.
But the only way to be sure that fatty liver is the only cause of liver damage is with a liver biopsy.
This is how your doctor diagnoses:
-
Diagnosis of Fatty Liver Disease Independent of Alcohol:
If you have fat but no inflammation or tissue damage, it is a diagnosis of fatty liver disease independent of alcohol.
-
Diagnosis of Alcohol-Independent Steatohepatitis:
If you have fat, inflammation, and liver damage, it’s alcohol-independent steatohepatitis.
-
Diagnosis of Cirrhosis
If your liver has a type of scar tissue called fibrosis, there is a possibility of developing cirrhosis.
Some of the tests that can be done to diagnose fatty liver are:
-
Physical Examination:
The doctor may try to detect fatty liver by examining liver size and swelling.
-
Blood Tests:
Symptoms of fatty liver include high blood levels of liver enzymes. Therefore, a doctor may try to diagnose fatty liver disease by performing blood tests that measure levels of liver enzymes.
-
Ultrasonography:
This test uses ultrasound sound waves to take images of organs within the body. This test can help measure liver size and swelling.
-
Liver Biopsy:
This test is done to take a sample of liver tissue.
When the sample is examined in the laboratory, it can be determined how advanced the liver fat is.
All of these tests can help confirm a diagnosis of fatty liver disease.
However, before diagnosing fatty liver disease, your doctor will choose the most appropriate test, taking into account other health conditions.
What are The Risks of Fatty Liver?
It has been reported that 5% of cases of fatty liver develop cirrhosis in an average of 7 years and 1% result in death.
Fatty Liver Treatment
If you have no other medical problems and only have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, you do not need any special treatment. But making some lifestyle changes can control or reverse the accumulation of fat in your liver.
These changes may include:
- Lose weight
- Reducing cholesterol and triglyceride levels
- Keeping diabetes under control
- Avoiding alcohol
In the presence of alcohol-independent steatohepatitis, there are no drugs that can reverse the accumulation of fat in your liver.
However, in some cases, liver damage stops on its own. And even the liver heals itself.
In some, the disease continues to progress.
If you have any problems that may contribute to fatty liver disease in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, it is important to keep the disease under control.
Treatments and lifestyle changes may include:
- Lose weight
- Drugs that lower cholesterol or triglycerides
- Medicine to lower blood pressure
- Medicine to control diabetes
- Limitation of OTC drugs
- Avoiding alcohol
- Being examined by a liver specialist
What is Good For Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver can be prevented by taking various precautions in daily life.
In this sense, the following health measures are useful in preventing or eliminating fatty liver:
- Ideal weight should be reached.
- Overweight people need to gain adequate and balanced nutrition habits. If necessary, a nutrition program should be prepared with a dietitian.
- At least 30 minutes of exercise should be done on certain days of the week.
- Alcohol intake should be stopped.
- Prolonged and regular use of alcohol can further promote lubrication. And it can cause cirrhosis.
- Low-calorie foods that do not contain saturated fat and trans fat should be consumed.
- Studies show that consuming foods rich in vitamin E is beneficial for fatty liver.
What to Eat with Fatty Liver and What Not to Eat?
Foods recommended to be consumed by those with fatty liver are:
-
Coffee:
It lowers liver enzymes.
-
Green Vegetables:
Limits oil production.
-
Fish:
Since it is rich in omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, it limits the inflammatory reaction in the liver with its antioxidant effect.
-
Oat:
While it facilitates weight loss with its fiber content, it gives energy to the body.
-
Avocado:
It helps the excretion of toxic substances accumulated in the liver.
-
Olive Oil:
Compared to saturated and trans fats, it is beneficial for the body and facilitates weight loss.
-
Green Tea:
It reduces fat absorption, lowers cholesterol and is useful for excretion of toxic substances in the body.
-
Purple – Red Fruits:
Consuming red colored fruits such as raspberries and blueberries is beneficial.
The following foods are recommended not to be consumed by people with fatty liver:
-
Alcohol:
All alcohol-containing foods should be avoided.
-
Simple Sugars:
Sugar-containing foods such as biscuits, fruit juices and cookies should not be consumed.
-
Fries:
Foods fried with oil are inconvenient for those with fatty liver.
-
Salt:
Consuming too much salt triggers food intake and oil production.
-
White Bread, Pasta and Rice:
These foods high in carbohydrates are stored as fat in the body.
-
Red Meat:
Red meats are rich in saturated fat, which is harmful for fatty liver.