What is Diabetes?
One of these hormones is insulin. It is a chronic and progressive disease that occurs as a result of deficiency or ineffectiveness of insulin hormone and progresses with high blood sugar levels.
Insulin is secreted by the pancreas in our body and acts as a key to the use of sugar in food taken from food by entering the cell as energy.
As a result of the absence or ineffectiveness of insulin, sugar cannot enter the cell. And it begins to rise in the blood. Although it varies according to regions, our country has diabetes with an average rate of 7%. Classification of diabetes according to the most recently accepted form;
- Type 1 diabetes,
- Type 2 diabetes,
- Pregnancy (Gestational) diabetes,
- Other causes (drug use, hormonal disorders, etc.).
How Does Your Body Regulate Glucose Normally?
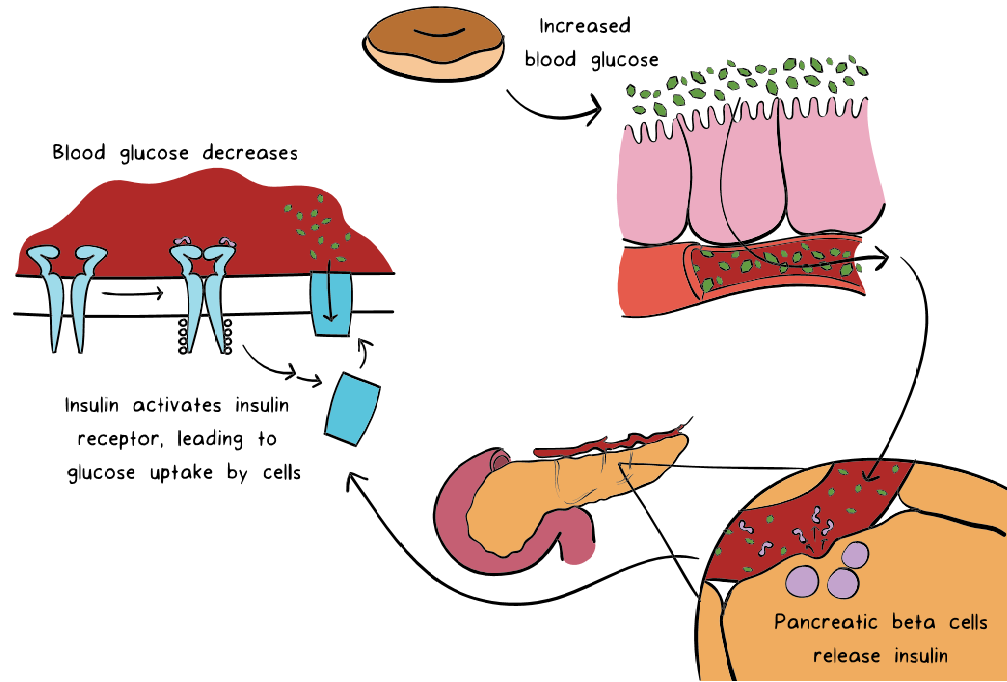
When you consume food, the amount of glucose in your blood rises suddenly. This is because the nutrients you consume are converted to glucose (the energy available to your cells) and entered into the blood to be distributed to the cells in your body.
The special cells in your pancreas can understand the increase in glucose and secrete insulin into your blood. Insulin has many tasks, but one of the most important tasks is to help lower blood sugar levels. It does this by activating a system that carries glucose from your blood to your cells.
Insulin also helps to lower your blood sugar levels by stimulating an enzyme called glycogen synthase in the liver. This molecule is responsible for producing glycogen (a long strip of glucose), the glycogen produced is stored in the liver and is used when the blood sugar level is low.
When insulin acts on your body, the amount of glucose in your blood slowly returns to the state before eating. Glucose levels (fasting blood glucose) measured when you are not eating recently are between 3.5-6 mmol / L (70-110 mg / dL). The values measured immediately after a meal may increase to 7.8mmol / L (140 mg / dL) depending on what you eat and how much.
What Happens in Diabetes?
There are two types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. In both types, your body has difficulty in carrying sugar from your blood to your cells.
As a result, your blood glucose levels rise and your cell glucose levels decrease. The major difference between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes is the different mechanisms that cause your blood sugar to deviate from normal values.
Type 1 Diabetes:
Patients with type 1 diabetes have a complete insulin deficiency in their bodies. Although the main cause of this has not yet been found, it is known that insulin-producing cells are destroyed by the body’s immune system. This condition is known as self-immunity or autoimmunity.
Autoimmunity occurs when the immune system considers some of the body cells as strangers and puts them in the list of destruction. The body eventually destroys all these cells and signs of diabetes appear.
Who Carries a Higher Risk for Type 1 Diabetes?
Risk of developing type 1 diabetes;
- First-degree close relatives such as mother and father siblings who have Type 1 diabetes,
- People with a large number of relatives with Type 2 diabetes,
- It is higher in women who develop diabetes during pregnancy.
Type 2 Diabetes:
Patients with type 2 diabetes may produce insulin, but the cells in their bodies have gained certain resistance to insulin. Type 2 diabetes is a process that begins with insulin resistance and can result in the complete cessation of insulin secretion.
When the cells become insulin-resistant, the body begins to produce more insulin to overcome this effect and to maintain glucose levels within normal values. Insulin levels in early Type 2 diabetes patients are higher than in people without diabetes.
However, the body eventually fails to achieve this balance and blood sugar levels begin to rise. Pancreatic cells constantly work to produce more insulin and eventually become destroyed. As type 2 diabetes continues to progress, patients begin to take insulin supplements to provide enough molecules in their bodies.
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Gestational diabetes mellitus is defined for the first time as glucose tolerance disorder during pregnancy. However, this definition is sometimes insufficient to differentiate between pre-pregnancy and pre-gestational diabetes cases that were diagnosed during pregnancy (although there was no pre-pregnancy diagnosis).
The number of pregnant women with undiagnosed Type 2 diabetes is also increasing, with increased obesity and diabetes. This is why it is recommended that pregnant women who are diagnosed with diabetes according to the standard criteria at the first prenatal visit should be diagnosed with ‘obvious diabetes’ instead of gestational diabetes.
It is estimated that GDM is seen in 10% of pregnancies on average. This ratio varies between 1% and 22% depending on the population studied and the diagnostic methods used.
Gestational diabetes, usually 24 of pregnancy. after the week, it develops due to placenta hormones blocking the effects of insulin (increasing insulin resistance).
Blood glucose regulation disorder in pregnancy can have negative consequences for both mother and baby, especially in patients with diabetes before pregnancy.
Preeclampsia and preterm labour risk are increased in mothers with gestational diabetes. In the newborn, it may cause macrosomia, neonatal hypoglycemia, jaundice, hypocalcemia, polycythemia, respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), congenital malformations and stillbirth.
Although most women with gestational diabetes after delivery have improved glucose metabolism, the risk of recurrence of gestational diabetes is high (approximately 50%) in subsequent pregnancies; also, the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in a future life is up to 70-80%.
For this reason, women diagnosed with gestational diabetes should be considered as prediabetes and taken into diabetes prevention programs and followed up even if their diabetes improves after birth.
What is Prediabetes?
Although a person’s blood sugar level is higher than normal but is not high enough to put on diabetes, the person is defined as prediabetes or sometimes secret sugar among the public, and the risk of developing type 2 diabetes is markedly increased in these people.
Prediabetes patients have normal blood sugar levels throughout the day and do not have basic symptoms of diabetes. Prediabetes indicates an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Furthermore, the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases is 1.5 times higher. If prediabetes is taken seriously and people change their lifestyle, they can delay or prevent the onset of diabetes.
What are the Symptoms if the Blood Sugar is Constantly Elevated?
Frequent urination
When insulin cannot be made in the body, functions that the insulin hormone is normally responsible for cannot be performed, that is, glucose cannot be used as energy by the cells and accumulates in the blood.
After a certain level of sugar from the kidneys, urine begins to be thrown. Since the sugar excreted in the urine will also drag the water, the person starts to urinate a lot and urinate frequently.
Drink lots of water –
When excessive water is lost in the urine, excessive water is needed.
Weight loss –
On the other hand, the body cells, which cannot benefit from the food taken, start to use the fats in the stores as fuel and weaken the person.
Blurred Vision –
High blood glucose levels cause blurred vision. The main reason for this is the loss of fluid caused by increased urination with increased blood glucose levels. Since water is drawn from all tissues of the body, the eye and the lens lose fluid and have difficulty focusing.
Nausea and Vomiting-
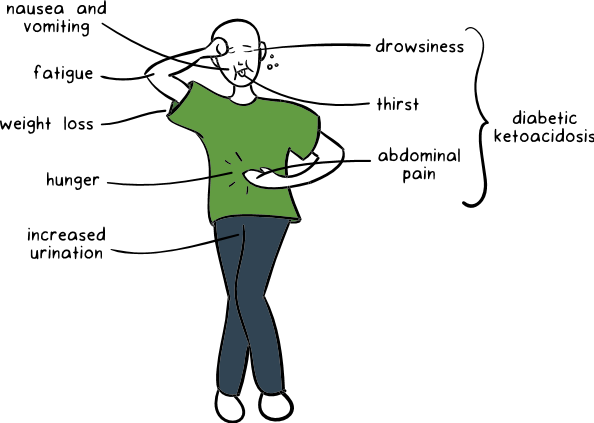
As diabetes progresses, insulin-producing pancreatic cells are damaged. Insulin deficiency also causes cells to be unable to use blood glucose. To produce energy, fat cells begin to break down and ketone bodies are formed.
Ketones provide energy to cells; however, they also increase the acidity of the blood. This is called ketoacidosis. Causes nausea. In children with diabetes, these nausea and vomiting complaints are very common.
Tendency to Infections
People with diabetes are more likely to have infections. This can have consequences such as being more easily influenza. Urinary tract infection may also occur more frequently.
Skin Problems
Skin dryness increases in people with diabetes. This triggers itching. Foot care is also very important.The time it takes for these symptoms to occur depends on the amount and destruction rate of the destruction of the pancreatic gland beta cells.
Destruction can last for weeks, months, or even years. When the damage is completed quickly and in a short time, the body has to use its proteins and fats for energy needs.
The final products called ketone bodies, which are formed especially by the excessive destruction of fats, are harmful wastes for the body and they accumulate in the body to form an emergency table called ketoacidosis.
The symptoms of ketoacidosis are abdominal pain, rapid breathing, fatigue and fatigue. In such a case, it is necessary to consult the hospital immediately.
How Is Diabetes Treatment Done?
When you learn that you are suffering from a chronic illness, such as diabetes, you will rightfully be upset. However, the positive side is that diabetes is a disease that responds very well to treatment.
Moreover, when you tell people around you that you have diabetes, you will be surprised to see how much you know is in the same situation as you and that they lead a very normal, productive life.
Also, enormous research on diabetes means that you will continue to be introduced to new treatments in the years to come.
Purpose of Diabetes Treatment:
- The aim of diabetes treatment is to keep your blood sugar and other risk factors (such as cholesterol and blood pressure) under control and not to cause long-term complications.
- The extent to which you can achieve this will vary depending on your age, weight, diet and exercise habits, your work program, your previous health problems, and whether your diabetes is Type 1 or Type 2.
- You will need to implement a personal treatment plan that takes into account all factors, and you will need patience and determination to carry out this plan regularly.
- For many people with diabetes, this means continually monitoring blood sugar levels, restricting certain foods, losing weight and taking medication orally or by injection.
How is İnsulin İnjected İnto the Body?
Insulin is injected into the subcutaneous fat tissue, just under the skin and just above the muscle.
Although there is fat tissue under the skin in your body, it is not preferred that the vessels and nerves are dense during the injection. Therefore, the recommended areas are the upper part of the abdomen, arms and legs and the buttocks.
If you use an insulin pen; Prepare the pen before.
- Wash your hands.
- Adjust the insulin dose from the scale at the upper end of the pen.
- Open the pen cover.
- Turn the insulin upside down.
- Remove the needle cover from the lower end of the pen.
- Make sure that the tip of the needle comes out with an insulin drop.
If you do not see a droplet on the tip of the needle, remove any possible air by wasting 1-2 units of insulin.
Don’t Be Late for Early Diagnosis in Diabetes!
Blood sugar measurements are performed after 8 hours of fasting for a definitive diagnosis in patients with suspected diabetes. If fasting blood sugar increases to 126 mg/dl, it is diagnosed as diabetes. However, the blood sugar is checked again after a few days to confirm the diagnosis. In the second measurement, if more than 126 mg/dl, a definitive diagnosis of diabetes is made.
If fasting blood sugar is between 100 and 126 mg/dl, sugar loading test is also performed for these people. 75 g of sugary water, 10-16 hours after hunger and in the morning and 2 hours of blood sugar is examined. If the blood sugar is over 200 mg/dl in the 2nd hour, the diagnosis of diabetes is made.
How is Prediabetes Diagnosed?
If fasting blood sugar is between 100-125 mg / dL, prediabetes should be investigated by performing sugar loading test (OGTT: Oral glucose tolerance test).
How is Diagnosed in Children?
Since type 1 diabetes is a sudden onset problem and usually presents with severe symptoms, the diagnosis is not difficult in children. Because drinking too much water, much urination, weight loss are important clues.
Also, the high blood sugar values measured at any time above 200 is sufficient for the diagnosis. If the diagnosis cannot be made by clinical findings and at any time with high blood sugar levels, fasting blood sugar is checked as in adults.
Diabetes is diagnosed as a result of repeated blood glucose readings above 126 milligrams. If the diagnosis is still difficult despite these difficulties, the loading test is applied.
Sugar loading test is rarely used in the diagnosis of diabetes in children. Because most cases are diagnosed without this. It is enough for a child to pass the challenge test for the blood sugar level to be 200 mg higher for the second hour.
OGTT How To?
Step 1:
Measure blood sugar after 10-12 hours of fasting.
Step 2:
Blood sugar is measured again 2 hours after the specially prepared 75 g sugar-containing liquid is drunk.
In people who have undergone a sugar challenge test, the plasma glucose level above 140 mg / dL but below 200 mg / dL at 2 hours is also called impaired glucose tolerance.
Here are prediabetes when fasting blood sugar is between 100-126 mg / dL or if the sugar loading test has a toughness value of 140-200 mg / dL at 2 hours.
Diabetes Patients Should Consider
Diabetes patient should be routinely checked and used regularly. Also, the given diet should be followed and insulin should be sensitive.
Eye and kidney examination should be done at least once a year, and an external examination should be done once every 2 years.
Feet are also important for diabetic patients. For this reason, every day should be washed with warm soapy water and then dried.
Moisturizing cream should be used for skin dryness. Do not walk around with bare feet and wear socks in summer. Cotton should be preferred in the selection of socks that do not tighten the leg and do not leave marks.
When the formation of calluses on the feet begins, the skin should be treated and treated. Toenails should be cut straight.
In the selection of shoes, shoes that fitfully, do not squeeze and hit should be preferred.
Smoking and alcohol should be avoided. Stress and distress should be avoided. A glucose meter should be provided and monitored regularly.
Timely routine check-ups, regular use of medication and insulin, regular nutrition and exercise are now the habits of diabetes patients.