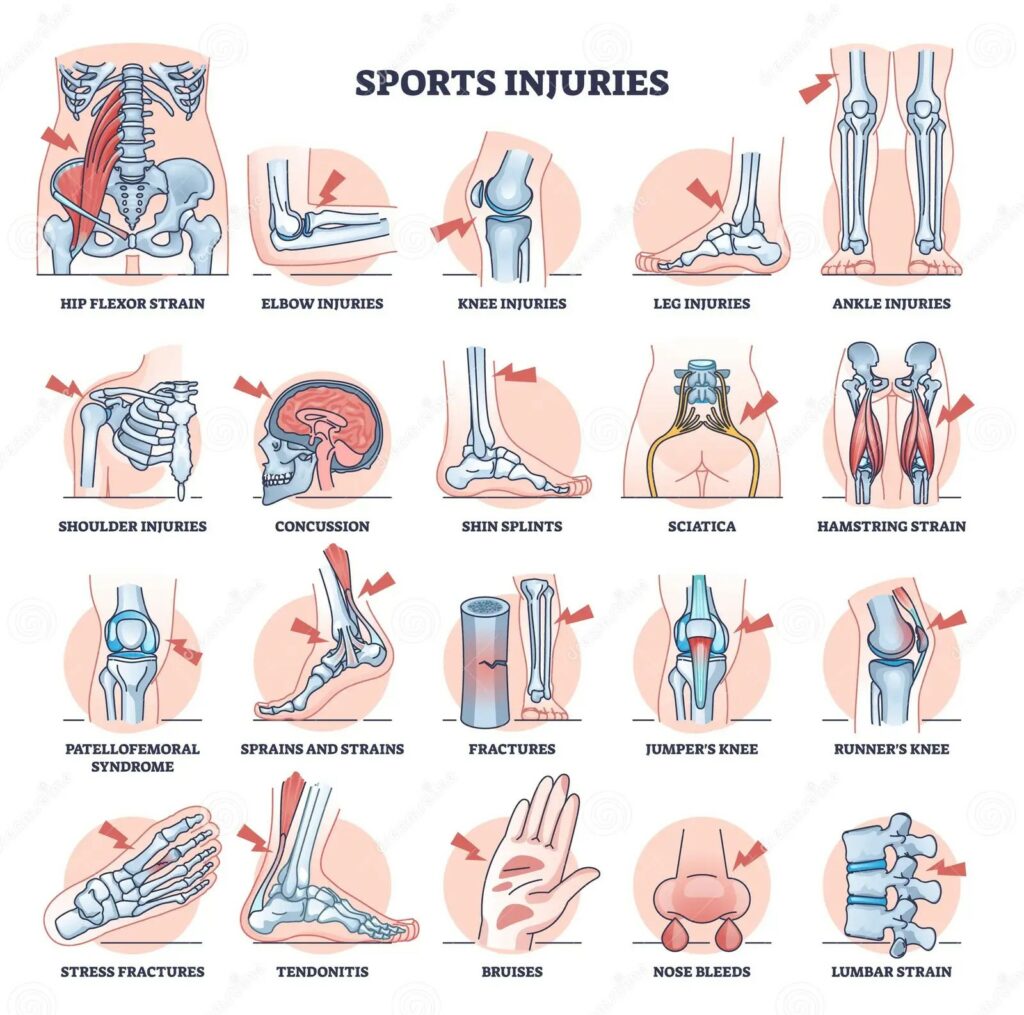
What are The Causes and Symptoms of Common Injuries in Sports?
Injuries in sports are usually the result of;
Overuse, improper technique, improper warm-up, imbalances, falls or sudden movements. Most of these types of injuries affect the muscles, joints, ligaments and bones. Although each sport has its own risks, some injuries are common regardless of the sport.
Here are the causes and symptoms of injuries that are frequently seen in sports:
-
Muscle Strain:
Causes:
-
Overexertion:
Using the muscle beyond its normal limits, excessive exercise or physical activities can cause the muscle to strain.
-
Not Warming Up:
Not warming up before starting the exercise can cause the muscles to strain more easily.
-
Sudden Movements:
Fast or sudden movements can cause the muscles to suddenly become tense and stretch.
-
Insufficient Stretching:
Not stretching the muscles leads to stiffening of the muscles and an increase in the risk of strain.
-
Fatigue:
Muscle fatigue as a result of long-term physical activity can cause muscle strain.
-
Poor Posture and Movement Pattern:
Wrong posture or wrong movements can cause muscle strain.
-
Dehydration (Water Loss):
Not taking enough water can affect the ability of the muscles to contract, which can lead to strain.
-
Muscle Insufficiency:
If the muscles are not strong enough, strain can occur when working under more load.
Symptoms:
-
Pain:
Pain is felt in the area where the muscle is strained. This pain can be mild or severe.
-
Swelling:
Swelling may occur around the muscle as a result of strain.
-
Movement Restriction:
The movement of the muscle may be limited, and movements in the area where the muscle is used may become difficult.
-
Muscle Spasms:
Involuntary contractions of the muscle, i.e. muscle spasms, may occur.
-
Bruising:
Bruising may occur in the area (bleeding) after muscle strain.
-
Sensitivity:
The strained muscle area may be sensitive when touched.
-
Weakness:
The strength of the strained muscle may decrease and it may have difficulty performing its normal function.
-
Knee Injuries:
Causes:
-
Traumas and Accident Results:
Falls, collisions or direct blows can cause injuries to the knee. Such injuries usually occur during sports activities, car accidents or accidents at home.
-
Sports Activities:
Sports such as football, basketball, volleyball and tennis can cause strain and injuries to the knee as a result of sudden movements, turns and jumps.
Movements that cause the knee to turn or strain (for example, sudden stops, changes of direction) are common causes of injuries.
-
Aging and Wear:
With age, cartilage wear and diseases such as osteoarthritis can occur in the knee joints. This can weaken the knee and cause pain over time.
-
Knee Ligament and Meniscus Injuries:
The ligaments in the knee (for example, the anterior cruciate ligament or posterior cruciate ligament) can tear or stretch. In addition, the cartilage structures in the knee called menisci can also tear.
-
Postural Disorders and Incorrect Movements:
Posture disorders (e.g. flat feet) or incorrect exercise techniques can overload the knee and lead to injuries.
-
Overuse:
Activities such as continuous running, climbing stairs or standing for long periods of time can cause excessive load on the knee joint and lead to injuries.
Symptoms:
-
Pain:
Knee pain is the most common symptom of injury. This pain can increase with movement and decrease with rest. Pain can sometimes be severe, especially in cases of strain or ligament tear.
-
Swelling:
A sudden swelling in the knee is usually caused by fluid accumulation in it (e.g. bleeding or infection).
-
Movement Limitation:
Movement limitation in the knee can occur when injured ligaments, meniscus or bones are affected. Difficulty in turning or bending the knee may be experienced.
-
Sound (Breaking or Cracking):
During an injury, especially in the case of a ligament or meniscus tear, a breaking or cracking sound may be heard from the knee.
-
Heating and Redness:
After an injury, the skin surrounding the knee may become warm, red, and sometimes bruised. This is related to inflammation caused by the injury.
-
Instability in the Knee:
In ligament or meniscus injuries, a feeling of instability or sliding may be experienced in the knee. This indicates that the stability of the knee is impaired.
-
Stress Fractures:
Causes:
- Stress fractures can occur due to a combination of many different causes.
- People who do sports that involve running and jumping (such as basketball, football, long runs, high jumps). It is especially common in long-distance runners. The fracture is often observed in the tibia.
- Constantly going up and down stairs
- Obesity
- Constantly carrying heavy loads
- Sports that involve heavy lifting (such as weightlifting)
- Being a woman (it is known that women’s bone structure weakens more and faster than men, especially with aging)
- Bone diseases (such as osteoporosis)
- Inadequate nutrition (not taking enough minerals and vitamins such as calcium, phosphorus, vitamin D)
- A history of a previous fracture
Symptoms:
- Tenderness and swelling in the area where the fracture is located,
- Pain caused by the increased load on the bone due to movement,
- Redness, increased heat or bruising in the area,
- Pain that does not go away despite the completion of the activity,
- Stinging or pain that becomes apparent while resting,
- Difficulty in moving due to the fracture.
-
Patellar Tendinitis:
Causes:
-
Overuse and Repetitive Stress:
Participating in high-impact sports or activities without adequate rest can cause micro-tears in the patellar tendon, causing inflammation and pain.
-
Improper Training Techniques:
Poor biomechanics, such as improper jumping or landing techniques, can put unnecessary stress on the knee, increasing the risk of tendon injury.
-
Muscle Imbalance:
Weakness or tightness in the quadriceps and hamstring muscles can alter the mechanics of the knee joint, increasing the strain on the patellar tendon.
-
Inadequate Conditioning:
Inadequate warm-up or lack of flexibility and strength training can predispose individuals to tendon injuries.
Symptoms:
-
Pain in the Front of the Knee:
The most obvious symptom of patellar tendonitis is pain and discomfort in the front of the knee. The pain is usually felt just below the kneecap and in the area where the patellar tendon passes.
This pain is usually more pronounced when moving (for example, jumping, running, or climbing stairs).
-
Pain and Stiffness:
Pain and stiffness may be felt in the knee, especially in the morning, after sleep. The knee may need to be warmed up before starting the activity.
-
Increasing Pain After Activity:
Pain in patellar tendonitis usually becomes more pronounced after exercise and physical activity. Pain may increase especially during movements such as jumping, running, climbing stairs or bending the knee.
-
Swelling:
Mild swelling may occur under the kneecap or around the patellar tendon. This may be a sign of inflammation.
-
Weakening and Loss of Endurance:
The muscles around the knee may also weaken due to the weakening of the patellar tendon. This can affect the athlete’s performance and reduce endurance in the knee.
-
Painful Movements:
Pain may be felt especially when bending or extending the knee (for example, squatting or standing movements). Pain may also increase when weight is placed on the knee (for example, standing for a long time).
- Aggravation of Pain:
As patellar tendonitis progresses, the pain may become more constant and may be felt even at rest.
- Tenderness:
There may be tenderness or pain when the area where the patellar tendon passes is touched. This usually occurs under the kneecap.
-
Rotator Cuff Syndrome:
Causes:
The causes of rotator cuff syndrome include;
- Chronic movements
- Sudden movements
- Sports
- Due to impact in people who are interested in their activities
- Overloading of shoulder muscles
Symptoms:
- Pain in the arm and shoulder area
- Pain starting in the shoulder area extending to the wrist area
- Increased weakness and sensitivity in the shoulder area
- Restriction of shoulder movements
- Inability to lift hands to the back of the body or arms to the head area
- Difficulty performing shoulder movements
- Sound coming from this area during shoulder movements
- Inability to lie on the shoulder area where the pain occurs
- Difficulty sleeping due to pain in the shoulder area
-
Hand and Finger Injuries:
Causes:
Traumas:
-
Fall:
Sprain or fracture of fingers as a result of the hand hitting the ground.
-
Impact:
Hitting a heavy object or jamming the hand.
-
Cuts:
Injuries that occur when working with a sharp tool.
-
Crushes:
Hand being caught by a door, heavy object or machine.
-
Repetitive Movements:
Strains caused by prolonged typing, keyboarding or working with hand tools (e.g. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome).
-
Sports Injuries:
Sprains, dislocations or fractures of fingers in ball games.
Strengthening of hand muscles while lifting weights.
-
Occupational Risks:
Injuries caused by equipment used in physical work such as construction and carpentry.
Skin damage due to contact with chemicals.
Other Causes:
-
Rheumatic Diseases:
May cause weakness or tenderness in finger joints.
-
Infections:
May occur with the entry of microbes after an injury.
-
Burns:
Exposure to heat, chemicals or electric current.
Symptoms:
-
Pain and Tenderness:
Sharp or constant pain in the area of the injury.
Sensitivity to touch on the finger or hand.
-
Swelling and Bruising:
A change in color due to edema or blood accumulation at the site of the injury.
-
Movement Limitation:
Inability to move the fingers or hand fully.
Joint stiffness.
-
Deformity:
Fingers in an unnatural position (for example, dislocation or fracture).
-
Numbness and Tingling:
Numbness or electric shock-like sensations due to nerve damage.
-
Open Wounds and Bleeding:
Open wounds caused by cuts or punctures.
Blood loss.
-
Heat or Color Change:
Whitening, redness or bluish appearance of the skin (may be a sign of poor circulation).
-
Arm – Leg Injuries:
Causes:
Traumas:
-
Falls:
When the arms or legs are reflexively extended to support the ground during a fall, sprains, fractures or dislocations may occur.
-
Impacts:
Bones, muscles or joints may be damaged as a result of a collision with a heavy object.
-
Accidents:
High-impact traumas such as traffic accidents, sports injuries or work accidents can lead to serious injuries.
Sports in Injuries:
-
Muscle Strain:
Muscle tears due to overuse of muscles or incorrect movement during exercise.
-
Ligament Injuries:
Strains in the knee ligaments (such as ACL, MCL) or elbow and shoulder ligaments.
-
Bone Fractures:
High-energy impacts or twisting forces.
Repetitive Movements:
-
Tendonitis:
Inflammation of tendons caused by constant repetitive movements (for example, tennis elbow).
-
Stress Fractures:
Microfractures in bones, especially in runners or individuals who do intense physical activity.
-
Occupational Risks:
Musculoskeletal system strains caused by heavy workload in construction, factories or working in the same position for a long time.
Muscle fatigue or nerve compression due to incorrect ergonomics (for example, carpal tunnel syndrome).
Infections and Medical Conditions:
-
Infections:
It can spread to bone, joint and muscle tissue after injury.
-
Osteoporosis:
Easily fractured due to weakening of bones.
-
Rheumatic Diseases:
Weakness or tenderness in joints.
Symptoms:
-
Pain:
Sudden or constant pain in the area of the injury.
Increased pain during movement.
-
Swelling:
Edema caused by damage to the tissues in the area of the injury.
In some cases, swelling may be accompanied by a feeling of warmth.
-
Bruising:
Color changes caused by damage to the capillaries.
Usually seen due to impact.
-
Movement Restriction:
Inability to move fully due to damage to joints or muscles.
Especially noticeable in fractures or dislocations.
-
Deformity:
Abnormal shape or alignment in bone fractures or dislocations.
An unnatural posture in the joint.
-
Numbness or Tingling:
Feeling of numbness or electric shock as a result of nerve damage.
Usually seen after nerve compression or traumatic injuries.
-
Muscle Weakness:
Loss of strength in the relevant muscle group in muscle tears or tendon ruptures.
Inability to walk or bear weight, especially in leg injuries.
-
Open Wounds and Bleeding:
Cuts or puncture wounds in the skin as a result of trauma.
Risk of infection from open wounds.
-
Redness and Heat:
Increased feeling of warmth and redness in the injured area in case of infection or inflammation.
-
Back – Spine Injuries:
Causes:
Traumas:
-
Falls:
Strong pressure can occur on the spine as a result of falling from a high place or falling incorrectly.
-
Traffic Accidents:
Fractures or dislocations can occur in the spine bones as a result of exposure to sudden and high impacts.
-
Sports Injuries:
The spine can be strained, especially in contact sports (football, wrestling) or during weight lifting.
-
Lifting Heavy Loads:
Lifting heavy objects in the wrong posture can cause damage to the discs located between the vertebrae or hernia formation.
-
Repetitive Movements and Strains:
Continuous bending, twisting or repeated movements that put pressure on the spine can cause damage to the muscles, connective tissue and discs.
Chronic Conditions:
-
Osteoporosis:
As a result of decreased bone density, the spine bones become weaker and break more easily.
-
Degenerative Disc Disease:
Wear and tear on the spinal discs due to aging or excessive use.
-
Ankylosing Spondylitis:
Inflammation and stiffness in the spinal joints.
-
Spinal Tumors or Infections:
Tumors or infections that form around the spinal cord can cause pain in the back and damage to the spine.
-
Severe Impacts:
Hitting a hard surface or being hit in the back with a heavy object.
Symptoms:
-
Pain:
Constant or sudden sharp pain in the injured area.
The pain usually increases with movement; in severe cases, it may continue even at rest.
-
Movement Restriction:
Difficulty in bending, straightening or turning movements due to damage to the spine and back muscles.
-
Swelling or Bruising:
Edema or bruising may occur in the muscle tissue after trauma.
-
Numbness and Tingling:
In case of damage to the spinal cord or nerves, numbness or tingling may be seen, especially in the legs or arms.
-
Muscle Weakness:
Loss of strength in the legs or arms due to nerve compression or spinal cord damage.
-
Significant Deformity:
An abnormality in the natural curvature of the spine (for example, as a result of displacement of the vertebrae).
-
Pain Radiating to the Legs (Sciatica):
Severe pain radiating from the waist or back to the legs as a result of nerve compression in the spine.
-
Loss of Urinary or Bowel Control:
In cases where the spinal cord is severely damaged, urinary or bowel control may be lost (requires immediate medical attention).
-
Balance Problems:
Difficulty walking or standing due to damage to the spinal cord.
-
Signs of Infection:
Fever, redness and swelling in the area of the injury (suggests spinal infection).
-
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis):
Causes:
-
Overuse:
Excessive and repetitive use of the hand, arm or wrist muscles can lead to tennis elbow. This condition causes the muscles and tendons to be constantly stretched or strained.
-
Wrong Technique:
Especially in tennis or other racket sports, using wrong technique, such as incorrect strokes, can increase the pressure on the elbow.
-
Age Factor:
Individuals between the ages of 30-50 are at greater risk due to the weakening of their tendons with age.
-
Occupational Factors:
Physical work such as woodworking, construction, or work that strains the hands, arms, and wrists, such as computer use, can increase the risk of tennis elbow.
-
Inadequate Warm-Up:
Not warming up the muscles and joints sufficiently before playing sports can strain the muscles and cause injuries.
Symptoms:
-
Pain and Tenderness:
Pain is usually felt on the outside of the elbow (lateral epicondyle area). This pain can range from mild discomfort to severe aching.
-
Wrist Weakness:
Strain and loss of strength may be experienced, especially in movements that require strength in the wrist or fingers (such as gripping or holding something).
-
Increasing Pain:
The pain may worsen when applying pressure to the elbow or moving the arm.
-
Night Pain:
Some people may feel pain in the elbow, especially at night while sleeping.
-
Limited Movement:
Due to the pain, it may be difficult for people to fully use their arms or hands.
-
Sprains:
Causes:
-
Sudden Movements or Falls:
Sudden excessive load on the joint.
Slip, fall or loss of balance during sports.
-
Wrong Step or Ground Conditions:
Foot in the wrong position while walking or running on unstable surfaces.
Wearing high heels or inappropriate shoes.
-
Sports and Physical Activities:
Sudden jumps, turns and fast movements.
It is common in contact sports such as basketball, football and tennis.
-
Weak Muscles or Ligaments:
Weak muscles and ligaments increase the risk of sprains.
-
Inadequate Warm-up and Stretching:
Not warming up and not preparing the muscles before exercise.
-
Recurrent Injuries:
Weakening of ligaments due to previous sprains.
-
Accidents:
Traffic accidents, domestic accidents or work accidents.
Symptoms:
-
Pain:
Sudden and severe pain in the area of injury.
Increased pain when moving the joint.
-
Swelling:
Edema in the injured area (usually becomes apparent within a few hours).
-
Cyanosis:
Blood accumulation under the skin due to the rupture of damaged ligaments and surrounding small blood vessels.
-
Movement Limitation:
Inability to move the joint normally.
Increased pain when attempted.
-
Tenderness:
Sensitivity and pain when the injured area is touched or pressed.
-
Joint Instability:
A feeling of looseness or loss of stability in the joint due to damage to the ligaments.
-
Crackling Sound in the Joint:
A “crackling” sound may be heard due to the stretching or tearing of ligaments at the time of injury.