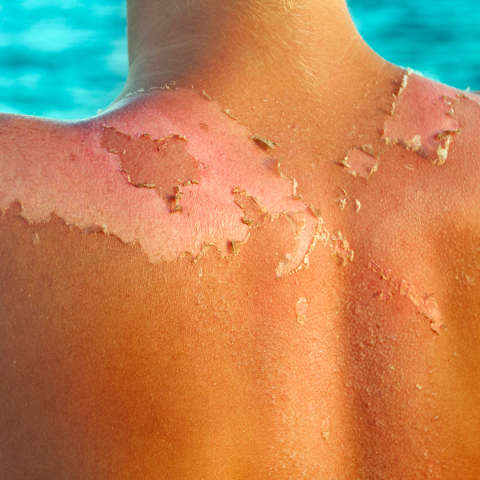
What is Sunburn?
Sunburn is a painful condition caused by exposure of the skin to intense amounts of sunlight. The sun’s rays, which normally help the body with tasks such as vitamin D synthesis and make people feel better, can cause various negative situations, especially in the summer months when there is excessive exposure to sunlight in the nude.
Exposure to intense amounts of sunlight can cause not only sunburn, but also discoloration, photoallergy or similar health problems. In fact, prolonged exposure of the body to sunlight unconsciously can lead to extremely serious health problems such as skin cancer. Therefore, it is very important to protect the skin against sunlight and not to be unconsciously exposed to sunlight for a long time.
What Causes Sunburn?
Too much exposure to ultraviolet light causes sunburn. This UV light can arise naturally from sunlight or from artificial sources such as sunlamps and tanning beds.
Melanin is a dark pigment that gives the outer layer of an individual’s skin its normal color. The body starts to protect itself by producing melanin faster when you are exposed to UV light. This extra melanin leads to darkening of the skin color and tanning. This tanning is the body’s primary method of blocking UV rays to prevent sunburn. However, this protection can be effective to a certain extent. Too much UV light causes skin burns.
It’s also possible to get sunburned on cool or cloudy days. Snow, sand, water, and other open or shiny surfaces can also reflect UV rays that cause skin burns and cause sunburn.
Being fair-skinned, blue-eyed, and having red or blond hair indicates naturally low levels of melanin in the body and increases the risk of sunburn. Living or vacationing in sunny, hot environments or at very high altitudes, in less shaded areas where the atmosphere offers less protection, and working outdoors again increases the risk of sunburn.
Moist and wet skin tends to burn more than dry skin, so spraying water on the skin, washing the skin, or swimming increases the risk of burns.
While spending time outdoors, drinking alcohol and using drugs that will make the individual sensitive to light increase the possibility of burns.
Regularly exposing the skin to artificial UV sources such as sun lamps or tanning beds without the use of protection leads to the possibility of sunburn on the skin.
What are The Symptoms of Sunburn?
The following are the most common symptoms of sunburn. However, each individual may experience symptoms differently.
Common symptoms include:
- Redness
- Swelling in the skin
- Pain
- Bubbles
- Fire
- Tremor
- Feelings of weakness, confusion or fainting
- Dryness, itching and peeling of the skin days after the burn
Severe sunburns can leave a person dehydrated and even go into shock as a result of fainting, low blood pressure, and profound weakness. In such a case, immediate medical attention is required.
Over time, redness and pain become visible and damage occurs. The pain usually reaches its worst 6 to 48 hours after the burn.
While the symptoms of sunburn may be temporary, the damage to the skin is permanent. The symptoms of sunburn can be similar to the symptoms of other skin problems. You should always consult your doctor for diagnosis.
What are The Degrees of Sunburn?
Sunburns can be examined in three different categories.
These categories are described below:
-
1st Degree Sunburn:
Redness on the skin surface, tightness and pain due to sensitivity are the symptoms of first degree sunburn.
-
2nd Degree Sunburn:
In case of second degree sunburn, symptoms such as redness of the skin, tightness, pain when touching the surface, as well as water-filled blisters on the skin can be seen.
-
3rd Degree Sunburn:
Severe pain and crusting may occur on the skin. However, the incidence of this type of sunburn is low.
What are The Risk Factors for Sunburn?
- For sunburn
- Being fair-skinned, having blue eyes, or having red or blond hair,
- Living in a hot area with intense sun or in a high altitude area,
- Working outdoors,
- Being in the sea, pool, beach, snowy areas reflecting the sunlight,
- Regularly exposing unprotected skin to sunlight or UV light from artificial sources such as a solarium.
How is Sunburn Diagnosed?
Sunburn can be diagnosed as a result of a physical examination. During this examination, the doctor may ask the individual about their symptoms, length of exposure to ultraviolet light, and past sunburns.
In individuals who develop a sunburn or skin reaction after exposure to very small amounts of sunlight, the doctor may recommend phototesting, a test in which small areas of skin are exposed to moderate amounts of UVA and UVB light, to reproduce the problem under observation. If an individual’s skin overreacts to UV light as a result of this test, the individual may be considered photosensitive or sensitive to sunlight.
Who Gets Sunburn Most Commonly?
Sunburn can vary from person to person. The change in symptoms is determined by the person’s skin sensitivity and the amount of sun exposure.
People with sensitive skin or who have had skin problems before are also more sensitive to the sun. For this reason, the time to be affected by ultraviolet rays (harmful rays of the sun) is also much faster.
Sunburns are more common in fair-skinned people. On the other hand, sunburns can occur in dark skin depending on the duration of exposure to the sun.
Sunburns are quite common in babies as well as people with sensitive skin. Babies need more sun protection than adults because of their skin sensitivities. Otherwise, it may cause serious injury.
How to Treat Sunburn?
The effects of sunburn do not appear in the first moments of exposure to the sun. In order to fully understand the damage caused by the burn on the skin, it takes a period of 3 to 24 hours, depending on the severity of the burn. It usually takes a few days for the redness and pain sensation on the skin to disappear. In addition, there are various measures that can be taken to make the healing process more painless and shorter.
These are listed below:
- It will be the most guaranteed method for the person to apply to a health institution in order to determine the most appropriate treatment method. The doctor not only makes recommendations for treatment according to the condition of the person, but also can prescribe various pain relievers and ointments in order to alleviate the feeling of pain experienced by the person.
- Applying a cold compress with the help of a towel or cloth moistened with cold water to the areas affected by the rays and reddened helps the person to relax and prevents the burn from getting worse. This practice can be done for 10 to 15 minutes several times a day. Also, taking a shower with slightly cold water will have a similar effect.
- The area affected by the burn should be kept cool. In addition, the drying of the skin should be prevented with the help of various moisturizing creams. These moisturizing creams should be applied on average three times a day.
- Avoid cologne and similar products that contain alcohol or are likely to irritate the skin. In addition, consuming plenty of water also causes the skin to regenerate and is very important in this regard.
- It is not the right behavior to apply vaseline to the burned skin. Vaseline cuts off the skin’s contact with the air, thus making the healing process take longer.
- Water-filled blisters may form on the skin of people with second-degree sunburn. In most cases where blisters appear, an itching sensation of the skin also occurs. However, scraping, scratching or popping the blisters is definitely not correct and may spread the infection and cause more pain.
What Should Be Considered to Prevent Sunburn?
It is important to protect from the sun in areas and times where UV rays are intensely encountered.
For this reason, the following should be noted;
- Must be at the seaside before 10:00 and after 17:00 during the summer vacation, and spend other times with other activities that do not receive sunlight.
- After getting out of the sea, the whole body should be washed with fresh water, sunscreen should be applied, a t-shirt and hat should be worn, and sunglasses should be worn.
- When you go to the mountains for winter vacation, all face and eye protective measures such as sunglasses and masks must be taken.
- If field workers will work all day in rural areas, they must wear light-colored shirts and trousers that will protect their arms and legs from the sun, they must protect their face from the sun with a white veil, a wide-brimmed hat, and sunglasses.
- Those who lead a normal life by the sea and in mountainous regions should not be outside near noon as much as possible, they should apply sunscreen creams and lotions, and use hats and sunglasses.
- Solarium should not be entered for tanning purposes.